Basics of Power Transformers & Distribution Transformers.
Many industry standards limit the difference between the distribution and power transformer with the KVA rating, such as distribution transformer is rated as between 5 to 200 or 500 or 1500KVA.
As per IEEE this is discouraged, as there is up to 5000KVA distribution transformer is now available. So the difference is what their purpose in type of use.
Distribution and power transformer- difference as per IEEE
As per IEEE (C57.12.80);
Definition of Distribution transformer
Distribution transformer is a transformer for transferring electrical energy from a primary distribution circuit to a secondary distribution circuit or a consumer circuit.
Definition of Power transformer
Power transformer transfers electrical energy in any parts of electrical circuit between generator and primary distribution circuit.
So as per IEEE Difference between Power & Distribution transformers should not be as per KVA rating, should be as per their type of use which reflects to their special requirements.
Special requirements for distribution transformer
· Low iron loss as distribution transformer is energized for 24 hour even if it is not in load.
· Maximum efficiency at low load, as they are not usually operated at full load.
· Leakage reactance should be kept minimum to avail minimum voltage regulation and hence to achieve higher efficiency. As usually there is no provision of tap changers.
Special requirements for power transformer
· Higher insulation and cooling class.
· Tap changer to cope up with voltage regulation.
· To be able to cope up with higher mechanical and electro-dynamic stress.
Autotransformer – how it works.
Autotransformer or auto step down transformer is an electrical transformer that has only one winding. This one winding acts as both primary and secondary. By the name “Autotransformer” it does not mean any sorts of automatic mechanism. Here “auto” means “auto” (Greek for “self”) – acting on itself.
Though Autotransformer use one winding but it use time-varying magnetic fields to transfer power. They require alternating currents to operate properly and will not function on direct current.
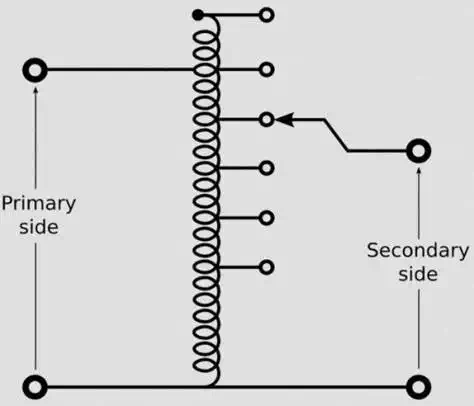
Operation of Autotransformer
Autotransformer diagram
In Autotransformer the primary voltage is
applied in two end terminals and in secondary there are several tap point from
which variable voltage can be achieved.
Advantage of Autotransformer
With fewer windings and a smaller core Autotransformer is lighter, cheaper and smaller than conventional dual winding transformer. Autotransformer is efficient up to a voltage ratio of about 3:1; beyond that range, a two-winding transformer is usually more economical.