BIOMASS ENERGY
Biomass is the organic matter, produced by plants or animals, used as sources of energy. Most of the biomass is burned directly for heating, cooling and industrial purposes.
Eg: Wood, crop residues, seeds, cattle dung, sewage, agricultural wastes.
Biogas
Mixture of methane, carbondioxide, hydrogen sulphide, ete. It contains about 65% of methane gas as a major constituent
Biogas is obtained by the anaerobic fermentation of animal dung or plant wastes in the presence of water.
Bio fuels
Biofuels are the fuels, obtained by the fermentation of biomass.
Eg: Ethanol, Methanol
(a)Ethanol
Ethanol can be easily produced from the sugarcane. Its calorific value is less when compared to petrol, and produces much less heat than petrol.
(b)Methanol
Methanol can be easily obtained from ethanol or sugar-containing plants.
Its calorific value is also too low when compared to gasoline and diesel.
(c)Gasohol
Gasohol is a mixture of ethanol+gasoline.
In India trial is being carried out to use Gasohol in cars and buses.
Gasohol is common fuel in Brazil and Zimbabwe for running cars and buses.
Methanol is very useful since it burns at a lower temperature than gasoline or diesel. Due to its high calorific value, hydrogen can serve as an excellent fuel.
Moreover it is non-polluting and can be easily produced.
Presently H2 is used in the form of liquid hydrogen as a fuel in spaceships.
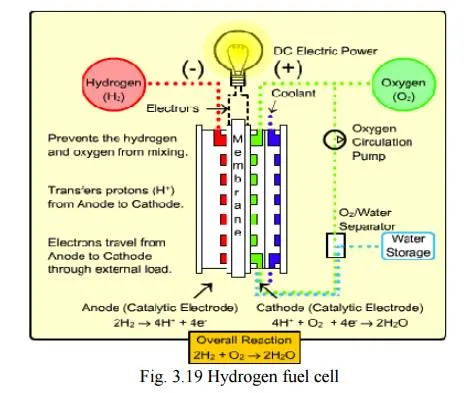
Hydrogen Fuel
Hydrogen can be produced by thermal dissociation or photolysis or electrolysis of water. It possesses high calorific value.
It is non polluting, because the combustion product is water. 2H2+O2---->2H2O+150KJ

Disadvantages of hydrogen fuel
· Hydrogen is highly inflammable and explosive in nature
· Safe handling is required
· It is difficult to store and transport.