WIND ENERGY
Definition
Moving air is called wind.
Energy recovered from the force of the wind is called wind energy.
The energy possessed by wind is because of its high speed.
The wind energy is harnessed by making use of wind mills.
Harvesting of wind energy
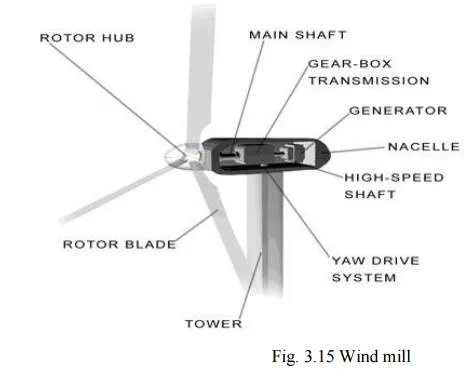
1. Wind Mills
The strike of blowing wind on the blades of the wind mill makes it rotating continuously.
The rotational motion of the blade drives a number of machines like water pump, flour mills and electric generators.

2. Wind farms
When a large number of wind mills are installed and joined together in a definite pattern it forms a wind farm.
The wind farms produce a large amount of electricity.
Conditions
The minimum speed required for satisfactory working of a wind generator is 15 km/hr.
Advantages
It does not cause any air pollution
It is very cheap.
OCEAN ENERGY
It can be generated by following ways.
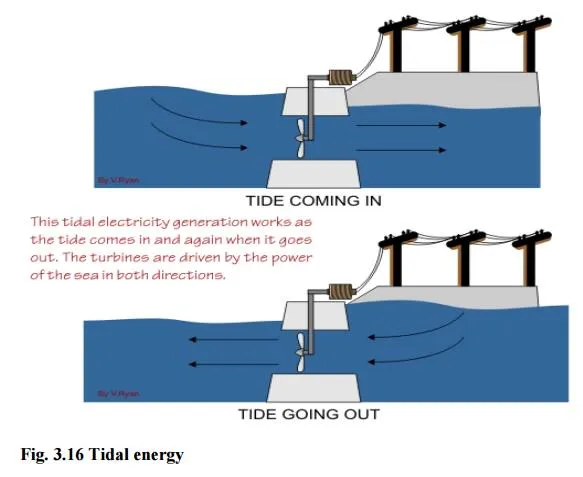
1. Tidal energy (or) Tidal power
Ocean tides, produced by gravitational forces of sun and moon, contain enormous amount of energy.
The “high tide” and “low tide” refer to the rise and fall of water in the oceans.
The tidal energy can be harnessed by constructing a tidal barrage.
During high tide, the sea-water is allowed to flow into the reservoir of the barrage and rotates the turbine, which intern produces electricity by rotating the generators.
During low tide, when the sea level is low, the sea water stored in the barrage reservoir is allowed to flow into the sea and again rotates the turbine.
2. Ocean thermal energy (OTE)
There is often large temperature difference between the surface level and deeper level of the tropical oceans.
This temperature difference can be utilized to generate electricity.
The energy available due to the difference in temperature of water is called ocean thermal energy.
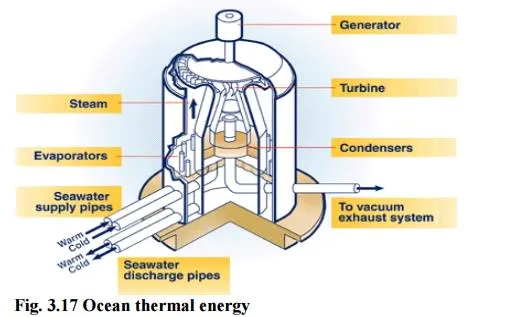
Fig. 3.17 Ocean thermal energy
Condition
The temperature difference should be of 200C or more is required between surface water and deeper water.
Process
The warm surface water of ocean is used to boil a low boiling liquid like ammonia.
The high vapour pressure of the liquid, formed by boiling is then to turn the turbine of the generator and generates electricity.
The cold water from the deeper ocean is pumped to cool and condense the vapour into liquid.
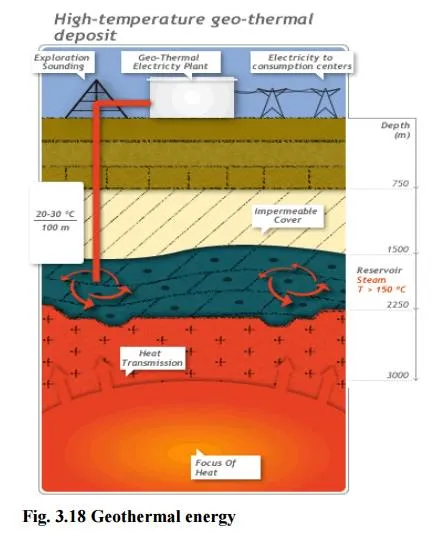
3. Geo-thermal Energy
· Temperature of the earth increases at a rate of 20-750C per km, when we move down the earth surface.
· High temperature and high pressure steam fields exists below the earth’s surface in many places.
· The energy harnessed from the high temperature present inside the earth is called geothermal energy.
3. Natural geysers
In some places, the hot water (or) steam comes out of the ground through cracks naturally in the form
2. Artificial geysers
In some places, we can artificially drill a hole up to the hot region and by sending a pipe in it, we can make the hot water or steam to rush out through the pipe with very high pressure.
Thus, the hot water (or) steam coming out from the natural (or) artificial geysers is allowed to rotate the turbine of a generator to produce electricity.