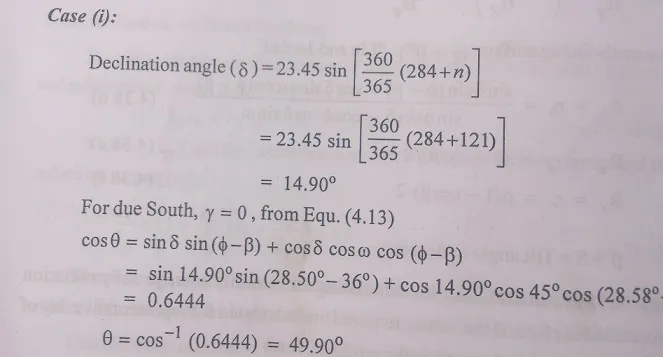
SOLAR RADIATION DATA
Most radiation data is measured for horizontal surfaces. A fair, smooth variation with the maximum occurring around noon is obtained on a clear day. In contrast an irregular variation with many peaks and valley may be obtained on a cloudy day.
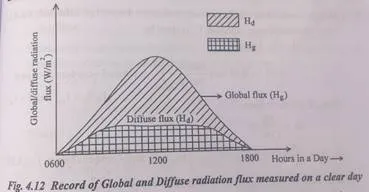
Since solar radiation fluxes do not normally change rapidly with time, Ig and Id represents hourly values also. These quantities are expressed in KWh/m2h or Kj/m2-h. Hg and Hd represents global flux respectively are shown in Fig.4.12.
Solar radiation flux is sometimes reported in longeys per hour or per day(1 longley = 1 cal/m2 = 1.163x10-2kWh/m2). The unit ‘langley’ has been adopted in honour of Samual Langley who made the first measurement of the spectral distribution of the Sun.

The maximum values measured over the whole country are about 300langleys per day in Gujarat on July, while minimum values, between 75 and 100 langely per day, are measured over many parts of country during November and December as winter sets in.
Estimating Solar Radiation Empirically
In order to calculate the amount of solar radiation falling on a collector at a given time and location the direct or beam radiation and diffuse radiation should be either measured or estimated using empirical equation.
1. Monthly average daily global radiation on horizontal surface
The monthly average daily global radiation on a horizontal surface Hga is given by the ollowing equation.

Integration of extra- terrestrial radiation over a day will give the daily value of extra- teriestrial solar radiation. H0 is given by,
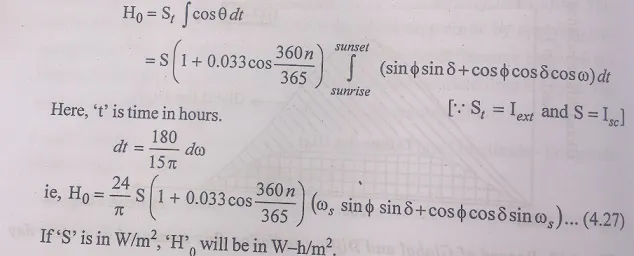
Equ.(4.26), from which the normally average solar radiation for a given location, if the data on sunshine hours are available and the constants for the location of nearly location, with similar climate are known.
2. Monthly average daily diffuse radiation on horizontal surface
Estimate of the monthly average daily diffuse radiation on horizontal surface, (Had), can be obtained using the following relationships.
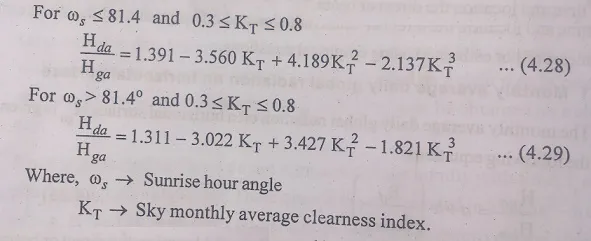
Thus, if clearness index of a location and its monthly average daily global radiation on horizontal surface is known, the monthly average daily diffuse radiation on the horizontal surface for a given location can be estimated. And also we can express equation interms of cleaness Index and sunshine ratio,

3. Monthly Average Hourly Global and Diffuse Ratiation on Horizontal Surface
Estimate of the global hourly radiation Ig from global daily radiation data on a horizontal surface can be obtained using the following relationship,

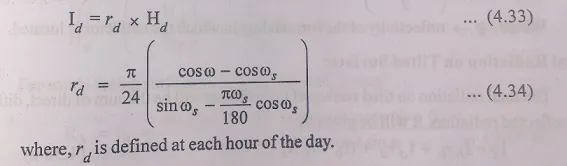
4. Solar Radiation on Tilted Surface
Many of the solar radiation measuring instruments also measure the radiation on horizontal surface. The radiation falling on tilted surface will be the sum of direct radiation and reflected radiation or albedo.