Types of ICs (Integrated Circuits)
Based on the method or techniques used in manufacturing them, types of ICs can be divided into three classes:
1. Thin and thick film ICs
2. Monolithic ICs
3. Hybrid or multichip ICs
Below is the simple explanation of different types of ICs as mentioned above.
Thin and Thick ICs:
In thin or thick film ICs, passive components such as resistors, capacitors are integrated but the diodes and transistors are connected as separate components to form a single and a complete circuit. Thin and thick ICs that are produced commercially are merely the combination of integrated and discrete (separate) components.
Thick and thin ICs have similar characteristics, similar appearance except the method of film deposition. Method of deposition of films distinguished Thin ICs from Thick ICs.

Thin film ICs are made by depositing films of a conducting material on a glass surface or on a ceramic base. By varying the thickness of the films deposited on the materials having different resistivity, Passive electronic components like resistors and capacitors can be manufactured.
In Thick film ICs, silk printing technique is used to create the desired pattern of the circuit on a ceramic substrate. Thick-film ICs are sometimes referred to as printed thin-film. The screens are actually made of fine stainless steel wire mesh and the links (connections) are pastes having conductive, resistive or dielectric properties. The circuits are fired in a furnace at a high temperature so as to fuse the films to the substrate after printing.
Monolithic ICs
In monolithic ICs, the discrete components, the active and the passive and also the interconnections between then are formed on a silicon chip. The word monolithic is actually derived from two Greek words “mono” meaning one or single and Lithos meaning stone. Thus monolithic circuit is a circuit that is built into a single crystal.
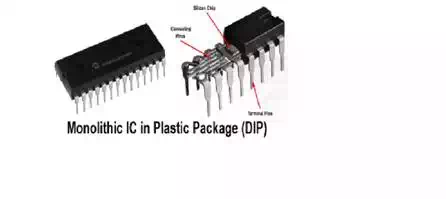
Monolithic ICs are the most common types ICs in use today. Its cost of production is cheap and is reliable. Commercially manufactured ICs are used as amplifiers, voltage regulators, in AM receivers, and in computer circuits. However, despite all these advantages and vast fields of application of monolithic ICs, it has limitations. The insulation between the components of monolithic ICs is poor. It also have low power rating, fabrication of insulators is not that possible and so many other factors.
DIP (Dual in-line package) IC
In term of Electronics or microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), or dual in-line pin package (DIPP) is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins.
Hybrid or Multi chip ICs
As the name implies, “Multi”, more than one individual chips are interconnected. The active components that are contained in this kind of ICs are diffused transistors or diodes. The passive components are the diffused resistors or capacitors on a single chip.
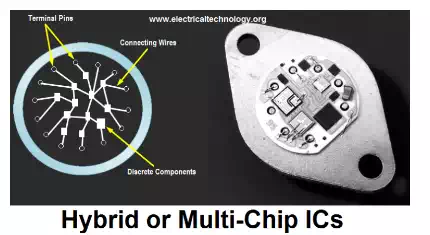
These components are connected by metallised patterns. Hybrid ICs are widely used for high power-amplifier applications from 5W to more than 50W. Its performance is better than that of monolithic ICs.
Digital Integrated Curcuits
These types of ICs work on the basic digital system i.e. two defined level which is 0’s and 1’s (in other words, Low and High or ON and OFF respectively). Microprocessor and Micro controller is the example of Digital ICs which contains of million of flip flops and logic gates.
Analog Integrated Circuits
Analog ICs work by processing continuous signals i.e. analog signal. OP-AMP (Operational Amplifier), NE 555 Timers and Sensors are the example of Analog ICs. These types of ICs are used for amplification, filtering, modulation, demodulation etc.
Mixed Signal ICs
Mixed Signal Integrated Circuit is a kind of ICs where both Digital and Analog ICs are combine on a single chip.
Advantages and Applications of ICs
ICs have advantages over those that are made by interconnecting discrete components some of which are its small size. It is a thousand times smaller than the discrete circuits. It is an all in one (components and the interconnections are on a single silicon chip). It has little weight. Its cost of production is also low. It is reliable because there is no soldered joints. ICs consumes little energy and can easily be replaced when the need arises. It can be operated at a very high temperature. different types of ICs are widely applied in our electrical devices such as high power amplifiers, voltage regulators, TV receivers and computers etc.
Limitation for different types of ICs
Despite the advantages that ICs provide us with, it have limitations some of which are:
· Limited power rating
· It operates at low voltage
· High grade of PNP is not possible
· It produces noise during operation
· Its components such as resistors and capacitors are voltage dependent
· It is delicate i.e it cannot withstand rough handling etc.