CAD vs CAE vs CAM: What is the Difference?
What is CAD? What is CAE? What is CAM? What are these softwares and how are they different from one another? The first thing to know about all three of these systems is the first two letters in each abbreviation. “CA” stands to Computer-Aided, which means that all three systems are created to help the user to achieve his goal faster by using the power of computers for processing. The last letter for CAD, is Design, for CAE, is Engineering, and for CAM, is Manufacturing. These are engineering and manufacturing software programs. Each one is has its own purpose. The article will dive into a high-level look at all three systems and how they are used and their overall purpose.
Computer-Aided Design Overview
A CAD program is a computer technology that
designs a product and documents the design phase of the engineering process.
CAD may facilitate the manufacturing process by transferring detailed diagrams
of product’s materials, processes, tolerances, and dimensions. It can be used
to produce either 2D or 3D diagrams, which can then be rotated to be viewed
from any angle, even from the inside looking out.
Computer-Aided Design is the use of computer systems to assist in the creation,
modification, and optimization of design. This is often considered an
engineering software program.

Modern CAD Programs can improve the following:
1. Increase the Productivity of the Engineer
2. Improve the Quality of Design
3. Improve Communications through Documentation
4. Create a Database for Manufacturing
CAD output is often in the form of electronic files for print, machining, or other manufacturing operations.
Modern CAD programs for mechanical design uses either vector-based graphics for objects, or may produce raster graphics showing the overall appearance of design objects.
However, engineering software programs require
more than just shapes. As in the manual drafting or technical and engineering
drawings, the output of CAD programs must convey information, such as
materials, processes, dimensions, and tolerances, according to
application-specific conventions.
CAD is important industrial art extensively used in many applications,
including automotive, shipbuilding, and aerospace industries, architecture,
prosthetics, and much more. CAD is also widely used to produce computer
animation for special effects in movies, advertising, and technical manuals,
often called DCC (digital content creation). CAD has been a major driving force
for research in computational geometry, computer graphics, and discrete
geometry.
Modern CAD Programs Uses
Computer-Aided Design is one of the many tools used by engineers and designers and is used in many ways depending on the profession of the user and the type of software in question. CAD is one part of the whole Digital Product Development (DPD) activity within the Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) processes, and as such CAD programs are used together with other tools, which are either integrated modules or stand-alone products such as:
1. Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE)
2. Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM)
3. Photo Realistic Rendering
4. Document Management and Revision Control using Product Data Management (PDM)
CAD has been proven to be useful to engineers as well, using four properties which are:
1. History
2. Features
3. Parameterization
4. High Level Constraints
The construction history can be used to look back into the model's personal features and work on the single are rather than the whole model. Parameters and constraints can be used to determine the size, shape, and other properties of the different modelling elements.
Who Uses Computer-Aided Design
Here is a short list of some people who would most likely use CAD in the job.
· Architectures
· Civil Engineers
· Electrical Engineers
· Facilities Manager
· Interior Designers
· Mechanical Engineers
· Structural Engineers
· Surveyors
· Manufacturing Engineers
· Acoustics Engineers
· Fire Protection Engineers
· Food Services Designers
This list goes on and on. Computer-Aided Design is used in many industries from aerospace, automotive, textiles, electronics, and much more. Computer-Aided Design allows companies to explore modelled ideas before physical prototyping is implemented. Mainly engineering software programs are utilized by engineers.
Computer-Aided Engineering Overview
Is the broad usage of computer software to aid
in engineering analysis tasks. Engineering software programs includes finite
element analysis (FEA), computational fluid dynamics (CFD), multibody dynamics
(MDB), and optimization.
Engineering software programs that have been developed to support these
activities are considered CAE tools. CAE tools are being used, for example, to
analyze the robustness and performance of components and assemblies. The term
encompasses simulation, validation, and optimization of products and
manufacturing tools. In the future, CAE systems will be major providers of
information to help support design teams in decision making.
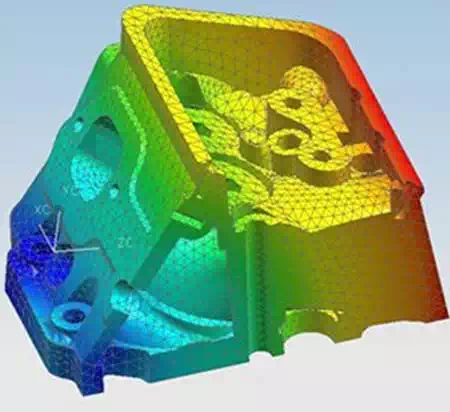
Computer-Aided Engineering
Nodal Network
In regard to information networks, CAE systems are individually considered a single node on a total information network and each node may interact with another node on the network. These nodes play a part in the finite element method which utilizes the existing model geometry to construct a nodal network through the entire model which then is used to determine how the model will perform, based on parameter input that the actual part would experience, in the real-world. The following parameters are typically used in mechanical engineering for CAE simulations:
1. Temperature
2. Pressure
3. Component Interactions
4. Applied Forces
Most of the parameters used for simulation are based on the environment and interactions that the model would experience during operation. These are inputted into the CAE software as a way to see if the part could theoretically handle the design constraints.
CAE systems can provide support to businesses. This is achieved by the use of reference architectures and their ability to place information views on the business process. Reference architecture is the basis from information model, especially product and manufacturing models.
CAE areas covered included:
1. Stress Analysis on Component Assembly using FEA
2. Thermal and Fluid Flow Analysis using CFD
3. Multibody Dynamics (MBD) and Kinematics
4. Analysis Tools for Process Simulation for Manufacturing Processes
5. Optimization of process documentation
6. Optimization of product developing
7. Smart nonconformity verification
8. Safety Analysis of Assemblies
In general, there are three phases in any computer-aided engineering tasks:
1. Pre-processing: defining the model and environmental factors to be applied.
2. Analysis Solver
3. Post-processing of results
Engineering software programs include such as Abaqus, Ansys, MSC Adams Car, and much more. Modern CAD programs export models to engineering software programs for virtual prototype analysis.
Computer-Aided Manufacturing
Computer-aided manufacturing is the use of computer software to control machine tools and related machinery in the manufacturing process. It is not technically considered a system for engineering software programs, but rather for machinist on the fabrication side. But, engineers often get exposure to it. CAM may also refer to the use of a computer to assist in all operations of a manufacturing plant, including planning, management, transportation and storage. Its primary purpose is to create a faster production process and components and tooling with more precise dimensions and material consistency. CAM is a subsequent computer-aided process after computer-aided design (CAD) and sometimes after computer-aided engineering (CAE), as model generated in CAD and verified in CAE can be input into CAM software, which controls the machine tool.
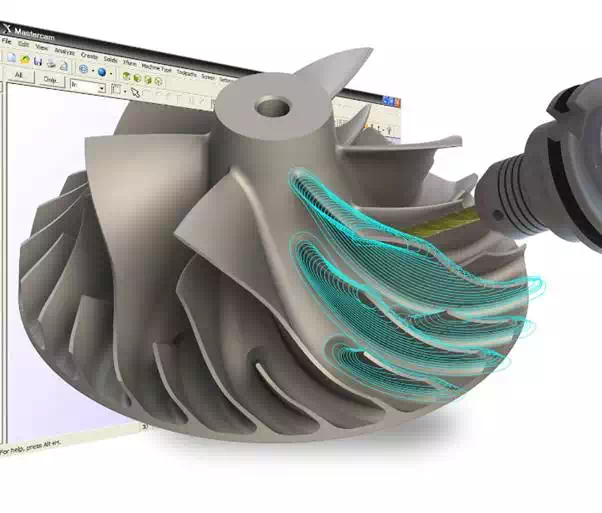
Computer-Aided Manufacturing
Mill Routing
CAM used for Computer Numerical Controlled machines
Computer-Aided Manufacturing is the software code behind the machines that manufacture the products. Computer Numerical Controlled machines are the devices that utilize the CAM code for manufacturing of products. CNC machines include:
· Mills
· Lathes
· Engravers
· Surface Grinders
· Welders
· Electrical Discharge Manufacturing
Everything that an operator would be required to do with conventional machine tools is programmable with CNC machines. CAM provides step-by-step instructions that the machine tools will follow to complete the manufacturing of the product. Before CAM, machinist had to manually type in the code before implementing the program. This manual input could be laborious based on the complexity of the final product. CAM made this simpler by incorporation intelligent software to develop the code based on the GUI (Graphical User Interface) platform. This made manufacturing code easy to produce with little more than simply clicking a button on the process desired and generating the code for the CNC machine.
How CAD, CAE, and CAM work together
A modern CAD program is necessary for using either manufacturing, CAM, or engineering software programs, CAE. As both systems require a model in order to perform either analysis or manufacturing. CAE requires the geometric model to determine the integrated nodal network to use for the analysis. CAM requires the part geometry to determine machine tool routes and cuts. Both require CAD, but CAD can be used as a stand alone system for engineering virtual models. CAD is the backbone for either CAM or CAE and is required for them to function properly. Each software are powerful tools for engineers and machinist that make daily job functions easier and more efficient, using them correctly would provide optimum benefit for the individuals and the companies that utilize them.