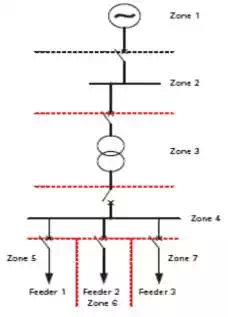
Zones and types of Protection system
Zones of Protection system
• An electric power system is divided into several zones of protection. Each zone of protection, contains one or more components of a power system in addition to two circuit breakers.
• When a fault occurs within the boundary of a particular zone, then the protection system responsible for the protection of the zone acts to isolate (by tripping the Circuit Breakers) every equipment within that zone from the rest of the system.
• The circuit Breakers are inserted between the component of the zone and the rest of the power system. Thus, the location of the circuit breaker helps to define the boundaries of the zones of protection.
• Different neighbouring zones of protection are made to overlap each other, which ensure that no part of the power system remains without protection. However, occurrence of the fault with in the overlapped region will initiate a tripping sequence of different circuit breakers so that the minimum necessary to disconnect the faulty element.
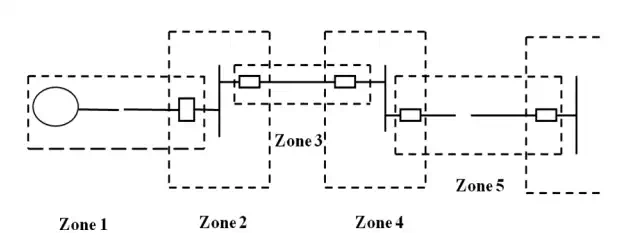
Primary Protection
– The primary protection scheme ensures fast and selective clearing of any fault within the boundaries of the circuit element, that the zone is required to protect. Primary Protection as a rule is provided for each section of an electrical installation. However, the primary protection may fail. The primary cause of failure of the Primary Protection system are enumerated below.
1. Current or voltage supply to the relay.
2. D.C. tripping voltage supply
3. Protective relays
4. Tripping circuit
5. Circuit Breaker
Back-up Protection
Back-up protection is the name given to a protection which backs the primary protection whenever the later fails in operation. The back-up protection by definition is slower than the primary protection system. The design of the back-up protection needs to be coordinated with the design of the primary protection and essentially it is the second line of defence after the primary protection system.