Consequences of occurrence of Faults
Faults are of two type
· Short circuit fault- current
· Open circuit fault- voltage In terms of seriousness of consequences of a fault, short circuits are of far greater concern than open circuits, although some open circuits present some potential hazards to personnel
Classification of short circuited Faults
• Three phase faults (with or without earth connection)
• Two phase faults (with or without earth connection)
• Single phase to earth faults
Classification of Open Circuit Faults
• Single Phase open Circuit
• Two phase open circuit
• Three phase open circuit
Consequences
• Damage to the equipment due to abnormally large and unbalanced currents and low voltages produced by the short circuits
• Explosions may occur in the equipments which have insulating oil, particularly during short circuits. This may result in fire and hazardous conditions to personnel and equipments
• Individual generators with reduced voltage in a power station or a group of generators operating at low voltage may lead to loss of synchronism, subsequently resulting in islanding.
• Risk of synchronous motors in large industrial premises falling out of step and tripping out.
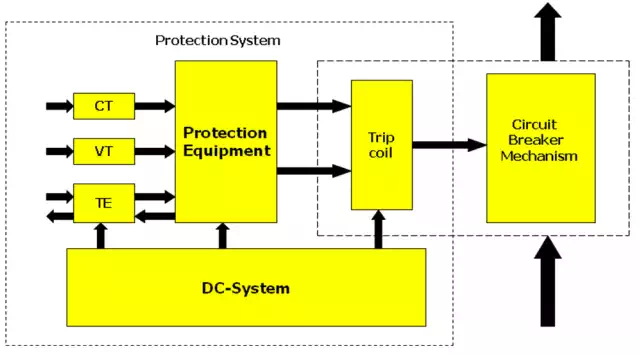
The general layout of a protection system may be viewed as given in the following figure