Electromechanical Energy Conversion
The fourth and final physical law that captures, together with the previous three, all the physical processes occurring inside an electric machine, is the “principle of energy conversion.” Within the domain of the electromechanical world of an electric rotating machine, this principle states that:
All the electrical and mechanical energy flowing into the machine, less all the electrical and mechanical energy flowing out the machine and stored in the machine, equals the energy dissipated from the machine as heat.
It is important to recognize that while mechanical and electrical energy can go in or out the machine, the heat generated within the machine always has a
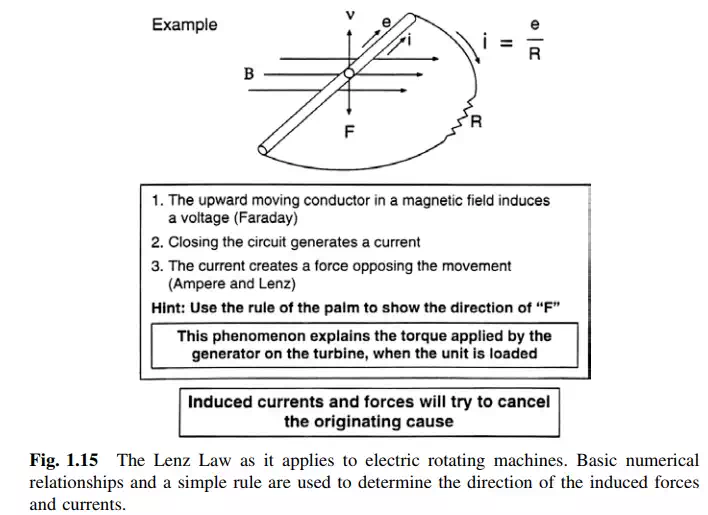
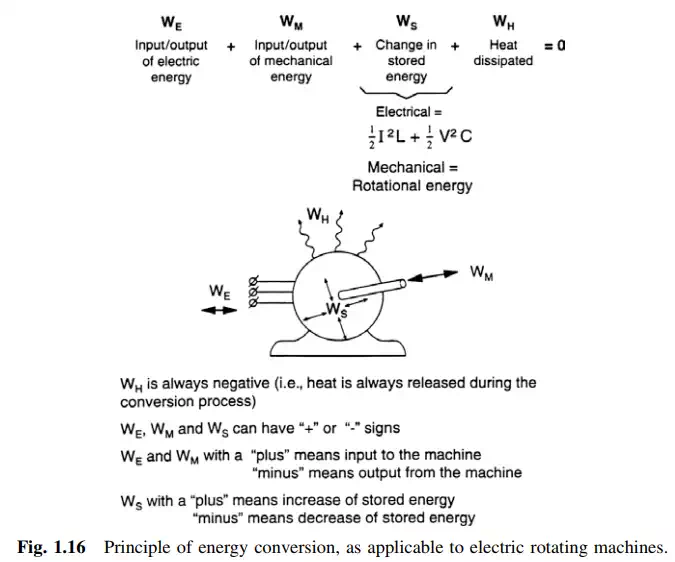
negative sign: namely heat generated in the machine is always released during the conversion process. A plus sign indicates energy going in; a minus indicates energy going out. In the case of the stored energy (electrical and mechanical), a plus sign indicates an increase of stored energy, while a negative sign indicates a reduction in stored energy.
The balance between the various forms of energy in the machine will determine its efficiency and cooling requirements, both critical performance and construction parameters in a large generator. Figure 1.16 depicts the principle of energy conversion as applicable to electric rotating machines.