Make Yourself a Simple Homemade
Electronic Buzzer
The design of a simple buzzer
described in this article uses just a single transistor and few other passive
components to produce a sound thatís really sharp. Read more about how to make
a homemade buzzer.
In general terms a buzzer may be
understood as a device that can produce an audible tone in the influence of an
externally applied voltage. This audible output may be either in the form of a
buzzing or a beeping sound. The sound is created by inducing rapid movements in
the diaphragm of the buzzer.
In electronic buzzers these
vibrations are made by an oscillator circuit which drives a piezo to produce
the sound. In electromechanical buzzers these oscillations are self-made
through a rapid switching of an electromagnet. The best example of an
electromechanical buzzer is the call bell used in offices; the horn used in
automobiles is another example of an electromechanical buzzer.
Before learning how to make a
buzzer, letís first see how these electro-mechanical buzzers function.
How Electromechanical Buzzers Function?
An electromagnet forms the main
part of all types of electromechanical buzzers. These may be either AC operated
or DC operated.
In AC buzzers, the AC Mains
voltage is applied to an electromagnet coil. The alternating voltage induced in
the coil generates a varying magnetic field in accordance to the applied
voltage, which in turn vibrates an iron plate to produce the required audible
buzzing sound.
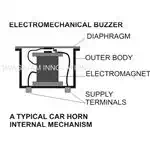
In DC buzzers or horns as used in
cars and other vehicles, when a DC battery voltage is applied to its
electromagnet, it instantly pulls an iron diaphragm. But the DC supply to the
coil is so arranged that when the diaphragm is pulled the supply is cut-OFF (see figure). Due to this the electromagnet is
switched OFF, the diaphragm is released to its original position when again the
DC supply is restored to repeat the cycle. This cycle repeats at a very high
speed to generate the typical loud honk from it.
How Electronic Buzzers Function?


Electronic buzzers mostly
incorporate a piezoelectric transducer as the diaphragm. They operate at very
low currents and yet are able to produce high pitched, sharp beeping sounds.
The heart of the circuit of most electronic buzzers is an electronic
oscillator. The alternating voltage produced by the oscillator is dumped into
an inductor which effectively converts these signals into high voltage pulses
to drive the piezo and produce an audible note.
How to Make a Simple Buzzer?
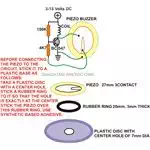

The circuit design of the
electronic buzzer shown is amazingly simple in design and yet is able to
produce a sound output thatís quite sharp to the ears. The construction
procedure does not require much of explanation, as the whole circuit can be
built within minutes with the help of the given schematic and the parts list.
The circuit description given
below will surely help you to understand better regarding how to make a buzzer:
As can be seen in the circuit
diagram, the circuit uses just one transistor, two resistors, a buzzer coil and
a piezo- electric transducer. Here no external oscillator is required to drive the
piezo, rather the circuit is a self oscillatory one.
To maintain oscillations in an electronic circuit a feedback voltage is always
required and here it is received through the centre tap of the piezo (thanks to
these simple low cost 3-terminal transducers). The buzzer coil here performs
the function of amplifying the low voltage oscillations into high voltage
oscillations required by the piezo to create a strong audible tone. The
resistor R1 is used just for providing the required biasing to the transistor,
whereas R2 has been included so that the oscillations do not stall due to
overloading of the circuit.
Well, now you just donít have to
wonder how to make a homemade buzzer, as you simply know how to do it.