Over Voltage And Low Voltage Protection Circuits: Easy Home Projects
The article describes few useful
protection circuit designs that can be easily built and installed in your
domestic power line. These will provide an excellent overvoltage protection to
all the connected appliances as well as save them from dangerous low voltages.
Introduction
In this article we will try
to understand a few circuit ideas that can provide low voltage and over voltage
protection to connected electrical assets. Though these circuits won’t be able
to stabilize the input voltage, even so may prove very effective in providing
total safety to your precious electrical home appliances against dangerous
input voltages.
The first design of a low voltage
indicator circuit may be used to indicate the presence of dangerous low voltage
conditions.
A low voltage may appear to be
something that is lower in magnitude and power, but that is what makes it more
lethal. For example a refrigerator working at 230 volts AC mains will never
“like" voltages below 190, since in such cases its compressor due to the
lack of sufficient voltage, will try to compensate by drawing heavy currents
and may get damaged if the situation persists. The same is true for other types of AC operated motors.
Also in vehicles, for
example a car, if the battery voltage falls below 9 volts, it may be quite
harmful for the life of the battery itself and moreover the vehicle will just
not start at that voltage.
The second circuit is similar but
opposite in response. It is basically a high voltage detector circuit and when
attached to an electrical system will warn you of detrimental high voltages.
These voltages are perhaps more risky, as under such conditions the equipment
may not get enough time to withstand the jolt and may be instantly burnt or
damaged.
We will also learn how these two
circuits can be joined into one and used to sense both the levels of “bad"
voltages and CUT the supply under such circumstances to safeguard your precious
electrical gadgets.
It’s Easy to Build These Simple Circuits
The circuits described below are
pretty simple in design and may be easily built over a small piece of a general
purpose PCB. Once you understand how the below shown circuits function, things
will get much simpler:
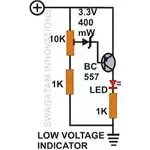
Low voltage indicator circuit
Referring to the figure we can see
that the circuit utilizes mainly a single PNP transistor and a zener diode to sense a low voltage. As per the setting
of VR1, the moment the input voltage falls below the predetermined reference,
the transistor conducts and switches ON the LED to show a low voltage
condition. The circuit may be used in vehicles operating on 12 volt batteries,
to display the “health" of the battery. Here VR1 should be adjusted such
that the LED begins to glow at around 10.5 battery voltage, indicating that it
needs a proper charging. Preferably a flashing type of LED may be used rather
than a continuous one to attract immediate attention of the driver. It can be
accommodated on the vehicle dashboard itself.
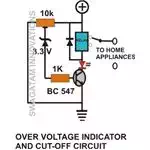
High voltage indicator circuit: Another simple configuration shown in the
figure is of a high voltage detector circuit. Here instead of a PNP, a NPN
transistor is used to detect high voltages. If the input voltage rises above
the set level of VR1, the transistor will conduct to put ON an alarm or an LED.
This circuit alone won’t be practically useful in any application, as during
high voltages there is always a chance of the equipment in the line of fire
getting damaged instantly, just an indication won't help. So it becomes
important to arm the circuit with an additional cut-OFF facility,
so that it can switch OFF the supply voltage in such dangerous scenarios and
provide an impeccable overvoltage protection to the connected unit.
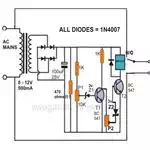
High voltage-low voltage cut-OFF circuit: As shown in the circuit diagram, a couple of transistor stages
are integrated together along with an output relay, which is able to perform
the function of super safe voltage guard equipment. As explained above the
transistors sense the presence of the dangerous voltage levels respectively and
activate the relay to protect the connected appliance from drastic situations.
The cut OFF supply will be immediately restored back once the voltage returns
to a safe level. The circuit may be used as a home protection system and
installed inside the existing main switch board with the relay contacts
connected in series with the mains supply line. Thus this circuit will not only
cut OFF during low voltages but also will provide a total over voltage
protection to the entire house or premises.
The Ultimate High/Low Voltage Protector Circuit
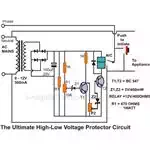
This circuit is a modified version
of the previous one and is able to switch of the load and itself in case the
input voltage reaches dangerous levels. It can thus provide an ultimate
protection to any gadget connected at its output.
The circuit may be understood in
the following manner (Click Image to Enlarge):
After the required settings of
the presets are done as explained above,
pressing the push button will initiate the circuit by connecting the AC supply
to the transformer.
On receiving the supply voltage
the circuit will operate by energizing T2 and the relay.
The relay contacts will get
latched so that the entire circuit now receives the supply voltage through its
N/O contacts and the push button may be simply released.
As long as the supply voltage is
within the normal range, the circuit remains latched and the output appliance
is safely powered. Now, if the voltage increases to an undesirable extent, T1
will conduct, bringing the base voltage of T2 to ground and thus deactivating
T2 and the relay.
Once the relay contacts are
dislodged, the supply to the appliance as well as the whole system is broken.
The circuit will remain unlatched until two conditions are met viz. the push
button is pressed and the voltage is restored to its normal position.
The same will happen during the
unsafe low voltages.
QUIZ: Can anybody tell us why R1 has been
included in the circuit?