A World With out Cords: An Overview of Wireless Charging
Qi
(pronounced as "chee") charging is an
optimized inductive charging, also known as “wireless charging” allowing you to
charge your devices wirelessly. Only compatible devices’ batteries are charged
by using induction transfer without requiring separate chargers, cables or adapters...
Simply place your compatible device on top of the wireless pad and watch your
device charge.
What is Qi Charging?
It is an optimized inductive
charging, also known as “wireless charging.” This allows you to charge your
devices wirelessly. Only compatible devices’ batteries are charged by using
induction transfer and there are no separate chargers, cables or adapters
needed while travelling. Simply place your compatible device on top of the
wireless pad and let your phone be charged!
In this technical article, we
will give a detailed explanation of how this wireless charger works.
Global Standard of Wireless Charging:
Qi is the universal interface
standard for wireless charging. It is the Chinese word for “air energy flow” or
“spiritual energy flow” and pronounced as “chee”.
This standard was developed by Wireless Power Consortium, to transfer inductive
electrical power over the distance of up to 4 cm i.e. 1.6 inches.
It was established in
December 2008 by WPC (Wireless Power Consumption). The Qi low-power
specification was published by WPC in 2009. In 2011, the WPC began to extend
the Qi specification to medium power.
System
Overview
A Qi system comprises of:
● Base station
● Mobile devices
● Power conversion
● Communication
Let’s take a look at how
these devices operate in order to charge a battery.
Base Station:
It contains one or more power
transmitters that comprise of a transmitting coil, which generates an
oscillating magnetic field. The base stations are typically of flat surfaces
i.e. Interface Surface, on which multiple devices can be placed.
Mobile Devices:
These are the devices that
consume inductive power. They can be either smartphones or tablets and hold a
receiver coil that contains a power receiver. This receiver provides power to
the battery. Communication and control units are also there in power receivers.
Power Conversion:
The transmitter in the base
station has a power conversion unit that converts electrical power to wireless
power signal. Whereas, the receiver in the mobile devices comprises of a power
pick-up unit that converts wireless power signal back to electrical power.
Communication:
The communication and control
unit are present in power receivers and this communication is always followed
by a technique called modulation.
● The receiver in mobile device modulates
the load by switching modulation resistor (Rm) or modulation capacitor (Cm).
● The transmitter in the base station
demodulates reflected load by sensing primary coil current (IP) or primary coil voltage (VP).
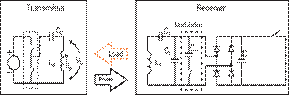
Figure 1. Qi
Charging Wireless Power Communication System
How it Works?
As we know, an
electromagnetic field is used to transfer energy between two objects. You will
probably remember magnetic induction technology from your physics class. The
same method is used by inductive charging.
As we have discussed above,
there are two coils: one in the transmitter and the other in the receiver. A
magnetic field is generated with an alternating current in the transmitter
coil, and this magnetic field induces voltage in the receiver coil. In a real
scenario, the receiver in the mobile device takes power from the
electromagnetic field and converts it into electrical current to charge the
battery.
Mobile device manufacturers
that are working with this standard includes: Asus, HTC, Huawei, LG
Electronics, Motorola Mobility, Nokia, Samsung, BlackBerry, and Sony. All the
devices with Qi logo are compatible to wireless chargers.
Methods to align the coils:
For power transfer, there are
two methods to align the transmitting and receiving coil:
Guided positioning:
Since the transmitter coil is
in the base station and the receiver coil is in the mobile device, the mobile
device must be placed on a certain position on the surface of the base station.
Free positioning:
In this method, the mobile
device is not required to be placed on a certain position on the base station’s
surface. There is no need of a direct alignment with the coil. In this way,
numerous transmitting coils can be used at the location of the receiving coils,
to generate a magnetic field and inductively charge the batteries.
Wireless Charging Modes:
All Qi receivers can be
charged in two modes:
1. Inductive Mode
2. Resonant Mode
The operation mode is defined
by the transmitter. Let’s discuss how these modes are processed.
Inductive Mode:
For inductive charging,
tightly-coupled systems are considered. For best results, the transmitter needs
to operate at a frequency that is slightly different from the resonant
frequency i.e. of the Qi receiver. In this mode, distance between transmitter and
receiver is limited to few millimeters. These
tightly-coupled systems helps to achieve high power efficiency.
When the coils are of the
same size and the distance between them is less than their diameters, they are
said to be tightly coupled (see the figure above). Here, coil distance z is
less than coil diameter D.
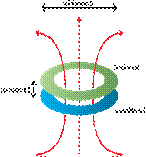
Figure 2. In
Inductive Mode
Resonant Mode:
When the system has
loosely-coupled coils, charging is done in resonant mode. When the distance
between the transmitter and the receiver coils is larger than their coil
diameters, the magnetic coupling between the coils will decrease.
Referring to the figure, the
coil distance z is larger than the coil diameters and so it weakens the
magnetic field between them. Consequently, systems that have low coupling have
to manage at the resonant frequency of receiver and have lower power transfer
efficiency.
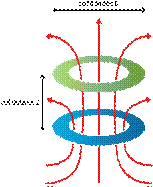
Figure 3. In
Resonant Mode
What is the best choice from
inductive and resonant mode?
Tightly-coupled systems are
best suitable due to their high-power transfer and their low heat production.
This is an advantage for heat-sensitive devices such as smartphones. The
downside is that tightly coupled coils are sensitive to misalignment.
Loosely-coupled systems have
low-power transfer efficiency. Such types of systems are best suitable for the
applications that have tight electromagnetic induction or electromotive force.
The best choice depends on
your needs.
Qi Charging Power:
Qi wireless charging with low
power is able to deliver up to 5 Watts of power at the receiver output whereas
Qi charging with medium power can deliver up to 120 Watts. Also, the
communication between transmitter and receiver should be enabled during charging
process; the charging process will not start without any interoperable
communication.
In comparison to the traditional charging, wireless charging
is considered slower but the good news is that it causes no harm to humans
since wireless chargers emit non-ionizing radiations.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Wireless charging has various
pros and cons:
Advantages:
● Wireless technology has the biggest
advantage of having compatibility with all cell phones and chargers from
different manufacturers.
● Non-radiative energy is transferred and
so it is not harmful to humans.
● No need to constantly plug and unplug
the device for charging purposes.
● It has protected connections with no
corrosion.
Disadvantages:
● Loosely-coupled systems have lower
efficiency that waste heat.
● Charging is slow as compared to
traditional charging.
● Complex and increased cost of
manufacturing.