Electrical
Motor
The motor or
an electrical motor is a device that has brought about one of
the biggest advancements in the fields of engineering and technology ever since
the invention of electricity. A motor is nothing but an
electro-mechanical device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy. Its because of motors, life is what it
is today in the 21st century. Without motor we had still been living in Sir Thomas Edisonís Era where the only
purpose of electricity would have been to glow bulbs. There are different types
of motor have been developed for different specific purposes.
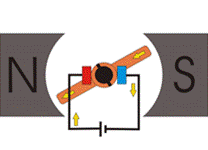
In simple words we can say a device that produces rotational force is a motor.
The very basic principal of functioning of an electrical motor lies
on the fact that force is experienced in the direction perpendicular to magnetic field and the current,
when field and current are made to
interact with each other.
Ever since
the invention of motors, a lot of advancements has taken place in this field of
engineering and it has become a subject of extreme importance for modern
engineers. This particular webpage takes into consideration, the above
mentioned fact and provides a detailed description on all major electrical
motors and motoring parts being used in the present era.
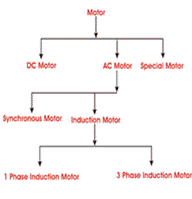
Classification or Types of Motor
The primary classification of motor or types of motor can
be tabulated as shown below,
History of Motor
In the year 1821 British scientist Michael Faraday explained the conversion of
electrical energy into mechanical energy by placing a current carrying
conductor in a magnetic field which resulted in the rotation of the conductor
due to torque produced by the mutual action of electrical current and
field. Based on his principal the most primitive of machines a DC (Direct
Current) machine was designed by
another British scientist William Sturgeon in the year 1832. But his model was
overly expensive and wasnít used for any practical purpose. Later in the year
1886 the first electrical motor was invented by scientist Frank Julian Sprague.
That was capable of rotating at a constant speed under a varied range of load,
and thus derived motoring action.
INDEX
● DC Motor
● Synchronous Motor
● 3 Phase Induction Motor
● 1 Phase Induction Motor
● Special Types of Motor
Among the four basic classification of motors mentioned above
the DC motor as the name
suggests, is the only one that is driven by direct current. Itís the most
primitive version of the electric motor where rotating
torque is produced due to flow of current through the
conductor inside a magnetic
field.
Rest all are AC electrical motors, and are driven by alternating current, for
e.g. the synchronous motor, which always runs at synchronous speed. Here the
rotor is an electro - magnet which is
magnetically locked with stator rotating magnetic field and rotates with it.
The speed of these machines are varied by varying the frequency (f) and number
of poles (P), as Ns = 120 f/P.
In another
type of AC motor where rotating magnetic field cuts the rotor conductors, hence
circulating current induced in these short circuited rotor conductors. Due to
interaction of the magnetic field and these circulating currents the rotor
starts rotates and continues its rotation. This is induction motor which is also
known as asynchronous
motor runs
at a speed lesser than synchronous speed, and the rotating torque, and
speed is governed by varying the slip which gives the difference
between synchronous speed Ns, and rotor speed speed Nr,
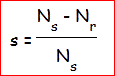
It runs governing the principal of EMF induction due to varying flux density,
hence the name induction machine comes. Single phase induction motor like a 3 phase,
runs by the principal of emf induction due
to flux, but the only difference is, it runs on single phase supply and its
starting methods are governed by two well established theories, namely the
Double Revolving field theory and the Cross field theory.
Apart from
the four basic types of motor mentioned above, there are several types Of
special electrical motors like Linear Induction motor(LIM),Stepper motor, Servo motor etc with special features that has been developed
according to the needs of the industry or for a particular particular gadget like the use of hysteresis
motor in hand watches because of its compactness.