Equilibrium Price
Equilibrium Price refers to the the market price at which the supply of an item
equals thedemand of it. equilibrium is an important concept in economics.
Equilibrium price is also referred as the equilibrium output.
Market equilibrium.
Market equilibrium occurs where the amount consumers wish to purchase at a
particular price is the same as the amount producers are willing to offer for
sale at that price. It is the point at which there is no incentive for
producers or consumers to change their behaviour.
Equilibrium price and output are found at the point of intersection of demand
and the supply curve.
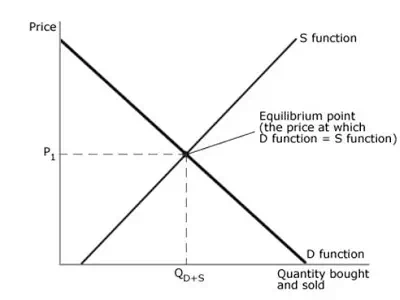
Equilibrium Point is the Point where Quantity
Demanded = Quantity supplied.
( Both quantity Demanded and quantity supplied are displayed on x-axis.)
Here, P1 is the equilibrium
price. At P1,
Quantity demanded = Quantity supplied.
Q D+S is the equilibrium level of quantity demanded and
supplied
Example to Find out equilibrium Price
Given Demand and Supply functions are
Qd = 3P + 2 (1)
Qs = 10 - P (2)
In equilibrium, Qs = Qd.
And so, we can equate (1) and (2)
Qd = Qs
or 3P + 2 = 10 - P
or 3p + p = 10 - 2
or 4p =8 or p = 2
So, for the given equations, Equilibrium Price = 2
And to calculate the quantity Demanded, we will
put the value of p in equation (1)
Qd = 3P + 2
= 3(2) + 2 = 8
And Qs = 8
And the equilibrium level of output is Qd = Qs = 8
Changes in Market Equilibrium
Market equilibrium refers to a situation in which quantity demanded is equal to
the quantity supplied, the point at which demand and supply curve meets.
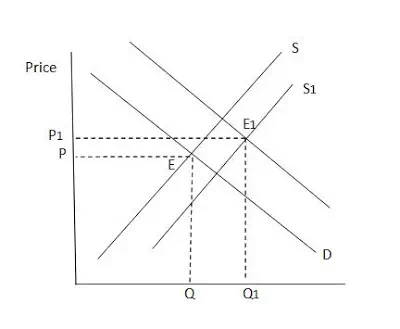
Increase in Supply results in a right ward shift in supply curve,
leading to a new equilibrium point( the intersection point of demand and new
supply curve.)
· With the increase in supply, supply curve shifts rightward.
· The new equilibrium point is E1
· It would result in fall in prices and increase in quanity demanded.
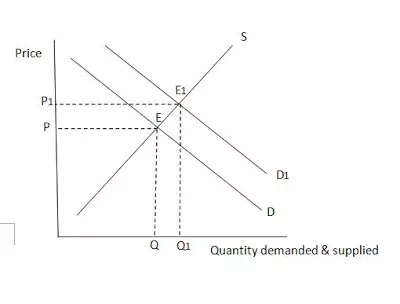
Increase in demand results in a right ward shift in demand curve, leading to a new equilibrium point( the intersection point of demand and new supply curve.)
· With the increase in demand, demand curve shifts rightward.
· The new equilibrium point is E1
· It would result in rise in prices and increase in quanity demanded.
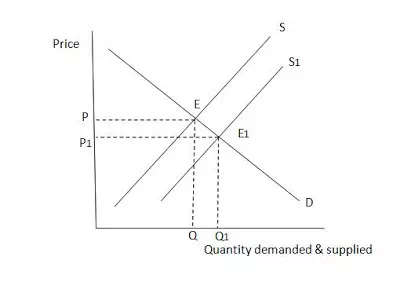
Simultanous Increase in demand and supply results in a right ward shift in demand curve and supply curve, leading to a new equilibrium point( the intersection point of demand and new supply curve). The changes in both demand and supply is a real market situation, The supply and demand curve changes as a result of change in market conditions.
· With the simultaneous increase in demand and supply, demand and supply curves shift rightward.
· The new equilibrium point is E1
· Here, It would result in rise in price P1 and increase in quanity demanded Q1.