Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility
Utility refers to the amount of satisfaction a person gets from
consumption of a certain item.and marginal utility refers to the addition made
to total utility, we get after consuming one more unit.
An individual's wants are unlimited in number yet each individual's want is
satiable. Because of this, the more we have a commodity, the less we want to
have more of it.
This law state that as the amount consumed of a commodity increases, the
utility derived by the consumer from the additional units, i.e marginal utility
goes on decreasing.
The law of diminishing marginal utility explains the downward sloping demand
curve
Definition
According to Marshall, “The additional benefit a person derives from a given
increase of his stock of a thing diminishes with every increase in the stock
that he already has”
Assumptions:
All the units of a commodity must be same in all respects
The unit of the good must be standard
There should be no change in taste during the process of consumption
There must be continuity in consumption
There should be no change in the price of the substitute goods
Explanation:
As more and more quantity of a commodity is consumed, the intensity if desire
decreases and also the utility derived from the additional unit.
Suppose a person eats Bread. and 1st unit of bread gives him maximum
satisfaction. When he will eat 2nd bread his total satisfaction would increase.
But the utility added by 2nd bread(MU) will be less then the 1st bread and this
MU will continue to decrease as he will keep on eating additional piece of
bread and once his stomach is full, MU will become negative, decreasing the
total utility.
His Total utility and marginal utility can be put in the form of a
following schedule.
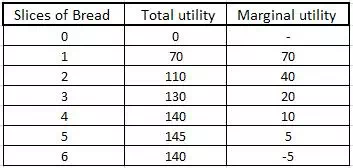
Plotting the above data on a graph gives
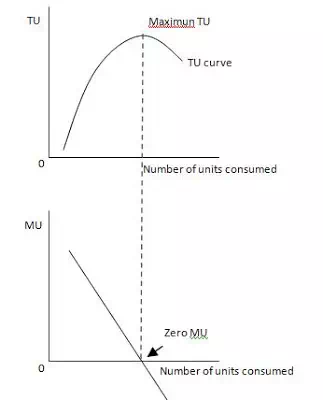
· Here, from the MU curve we can see that MU is declinig as consumer consumes more of the commodity.
· When TU is maximum, MU is Zero.
· After that, TU starts declining and MU becomes negative.
Exceptions:
· Money
· Hobbies and Rare Things
· Liquor and Music
· Things of Display
Importance:
· Basis of Law of Demand
· Basis of Consumption Expenditure
· The basis of Progressive Taxation
Law of Equip-Marginal Utility
This law states that the consumer maximizing his total utility
will allocate his income among various commodities in such a way that his
marginal utility of the last rupee spent on each commodity is equal
Or
The consumer will spend his money income on different goods in such a way that
marginal utility of each good is proportional to its price
Explanation
yet to write
Limitations of Law of Equi-Marginal Utility
· It is difficult for the consumer to know the marginal utilities from different commodities because utility cannot be measured.
· Consumer are ignorant and therefore are not in a position to arrive at an equilibrium.
It does not apply to indivisible and inexpensive commodity