Theory of Production
In economics, production theory explains the principles in which the business has to take decisions on how much of each commodity it sells and how much it produces and also how much of raw material ie., fixed capital and labor it employs and how much it will use. It defines the relationships between the prices of the commodities and productive factors on one hand and the quantities of these commodities and productive factors that are produced on the other hand.
Concept
Production is a process of combining various inputs to produce an output for consumption. It is the act of creating output in the form of a commodity or a service which contributes to the utility of individuals.
In other words, it is a process in which the inputs are converted into outputs.
Function
The Production function signifies a technical relationship between the physical inputs and physical outputs of the firm, for a given state of the technology.
Q = f (a, b, c, . . . . . . z)
Where a,b,c ....z are various inputs such as land, labor ,capital etc. Q is the level of the output for a firm.
If labor (L) and capital (K) are only the input factors, the production function reduces to −
Q = f(L, K)
Production Function describes the technological relationship between inputs and outputs. It is a tool that analysis the qualitative input Ė output relationship and also represents the technology of a firm or the economy as a whole.
Production Analysis
Production analysis basically is concerned with the analysis in which the resources such as land, labor, and capital are employed to produce a firmís final product. To produce these goods the basic inputs are classified into two divisions −
Variable Inputs
Inputs those change or are variable in the short run or long run are variable inputs.
Fixed Inputs
Inputs that remain constant in the short term are fixed inputs.
Cost Function
Cost function is defined as the relationship between the cost of the product and the output. Following is the formula for the same −
C = F [Q]
Cost function is divided into namely two types −
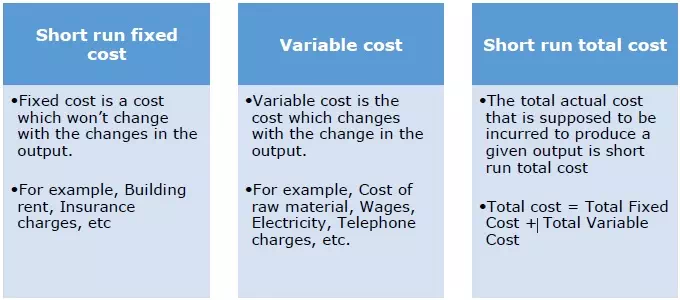
Short Run Cost
Short run cost is an analysis in which few factors are constant which wonít change during the period of analysis. The output can be changed ie., increased or decreased in the short run by changing the variable factors.
Following are the basic three types of short run cost −
Long Run Cost
Long-run cost is variable and a firm adjusts all its inputs to make sure that its cost of production is as low as possible.
Long run cost = Long run variable cost
In the long run, firms donít have the liberty to reach equilibrium between supply and demand by altering the levels of production. They can only expand or reduce the production capacity as per the profits. In the long run, a firm can choose any amount of fixed costs it wants to make short run decisions.