Discussion
With an understanding of the macroeconomics and microeconomics, it is possible to get an insight into what kind of factors that can affect the building industry and the parties within. Further, the outlined phases in a construction project makes is possible to understand how cost estimation is carried out in the procurement phase. Cost estimations hold many uncertainties and has many factors which must be considered. Critical factors has been emphasised such as the time affect on money and project appraisal with focus on income an probability. To finalise the economic understand accounting has been accounted for. Taking all these areas into account, an overall picture of the economical aspect has been highlighted. To improve the building industry and the different project initiated by investors, a system has been proposed for implementation.
Value Engineering
Another system that can be used for evaluation is value engineering, which was developed accidentally during World War II. Due to a shortage of materials different companies were forced to use substitutes. However, through the use of substitutes the cost was reduced and the quality improved. Lawrence Miles was by this selected to identify these substitutions intentionally instead of accidentally. He then developed the value engineering. Value engineering is a systematic approach with the objective of optimising cost and performance for a facility or system. Value engineering focuses on dealing with errors of sub-optimisation, which are partial systems optimised for performance at the expense of the performance of the overall system. This occurs in for instance the sub-groups; architects, structural engineers, mechanical engineers, etc. Value engineering tries to substitute with less expensive alternatives without decreasing the performance, which therefore take all the sub-groups into consideration, when the optimal solutions must be found. The analysis consist of a top-down process, which means value engineering assess the overall system first, and work down trough the subsystems. By this it is also possible to identify sub-systems not required. Value engineering is therefore an evaluation of systems to reduce cost and increase functionality for an increase of value of the product. Cost is usually educed at the expense of quality, which is a simple cost-cutting strategy. However, with the use of value engineering quality is not effected.
Value engineering consists of five phases:
• Information: Generate database and select areas for detailed assessment
• Speculative: Outline alternatives meeting requirements
• Analytical: Evaluate alternatives and optimise
• Proposal: Identify best alternative to decision making
• Final report: Define and quantify results
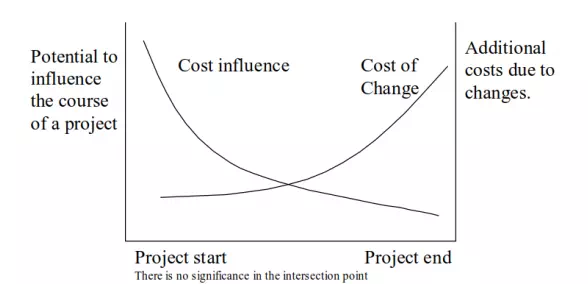
Following these steps it is possible to utilise value management. Different techniques can be used to support value engineering. One technique is function analysis. Through this the primary and secondary functions of the project are identified, which can give an insight into potential unnecessary secondary functions that does not create value. To support the functional analysis the verb-noun approach can be used. The function identified must only be described by two words consisting of a verb and a noun. For instance would a table be referred as "support weight". By this a bigger focus on the purpose of the function is clarified. Other techniques exist, however these are some that can facilitate value engineering and in the end affect the project positively