Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL)
Logic Gates like NAND, NOR are used in daily applications for performing logic operations. The Gates are manufactured using semiconductor devices like BJT, Diodes or FETs. Different Gate’s are constructed using Integrated circuits. Digital logic circuits are manufactured depending on the specific circuit technology or logic families.
1. RTL(Resistor Transistor Logic)
2. DTL(Diode Transistor Logic)
3. TTL(Transistor Transistor Logic)
4. ECL(Emitter Coupled Logic)
5. CMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor Logic)
Out of these RTL and DTL are rarely used.
1. Fan Out: Number of loads the output of a GATE can drive without effecting its usual performance. By load we mean the amount of current required by the input of another Gate connected to the output of the given gate.
2. Power Dissipation: It represents the amount of power needed by the device. It is measured in mW. It is usually the product of supply voltage and the amount of average current drawn when the output is high or low.
3. Propagation Delay: It represents the transition time which elapses when the input level changes. The delay which occurs for the output to make its transition is the propagation delay.
4. Noise Margin: It represents the amount of noise voltage allowed at the input, which doesn’t effects the standard output.
It is a logic family consisting completely of transistors. It employs transistor with multiple emitters. Commercially it starts with the 74 series like the 7404, 74S86 etc. It was build in 1961 by James L Bui and commercially used in logic design in 1963
TTLs are classified based on the output.

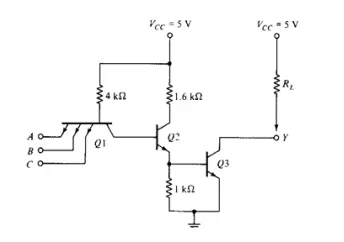
Transistor Q1 actually behaves as cluster of diodes placed back to back. With any of the input at logic low, corresponding emitter base junction is forward biased and the voltage drop across the base of Q1 is around 0.9V, not enough for the transistors Q2 and Q3 to conduct. Thus output is either floating or Vcc, i.e. High level.
Similarly when all inputs are high, all base emitter junctions of Q1 are reverse biased and transistor Q2 and Q3 get enough base current and are in saturation mode. Clearly output is at logic low. (For a transistor to go to saturation, collector current should be greater than β times the base current).
It is used in 3 major applications:
1. In driving lamps or relays
2. In performing wired logic
3. In construction of a common bus system
Totem Pole means addition of an active pull up circuit in the output of the Gate which results in reduction of propagation delay.
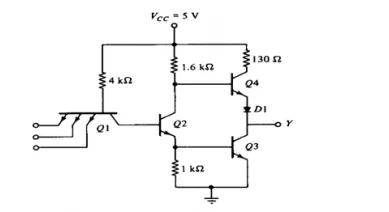
Logic operation is same as the open collector output. Use of transistors Q4 and diode is to provide quick charging and discharging of parasitic capacitance across Q3. Resistor is used to keep the output current to a safe value.
It provides 3 state output.
1. Low level state when lower transistor is ON and upper transistor is OFF.
2. High level state when lower transistor is OFF and upper transistor is ON.
3. Third state when both transistors are OFF. It allows a direct wire connection of many outputs.
1. Logic low level is at 0 or 0.2V.
2. Logic high level is at 5V.
3. Typical fan out of 10. It means it can support at most 10 gates at its output.
4. A basic TTL device draws a power of almost 10mW, which reduces with use of schottky devices.
5. Average propagation delay is about 9ns.
6. The noise margin is about 0.4V.
TTL ICs mostly start with the 7 series. It has basically 6 subfamilies given as:
1. Low Power device with propagation delay of 35 ns and power dissipation of 1mW.
2. Low power Schottky device with delay of 9ns
3. Advanced Schottky device with delay of 1.5ns.
4. Advanced low power Schottky device with delay of 4 ns and power dissipation of 1mW.
In any TTL device nomenclature, first two names indicate the name of the subfamily the device belongs to. The first two digits indicate the temperature range of operation. The next two alphabets indicate the subfamily the device belongs to. The last two digits indicate the logic function performed by the chip.
Examples are: 74LS02- 2 neither input NOR gate.
74LS10- Triple 3 input NAND gate.
1. Used in controller application for providing 0 to 5Vs
2. Used as switching device in driving lamps and relays
3. Used in processors of mini computers like DEC VAX
4. Used in printers and video display terminals
Logic Gates are used in daily life in applications like in clothes dryer, computer printer, door bell etc.
The 3 basic Logic gates implemented using TTL logic are given below:-
· NOR Gate
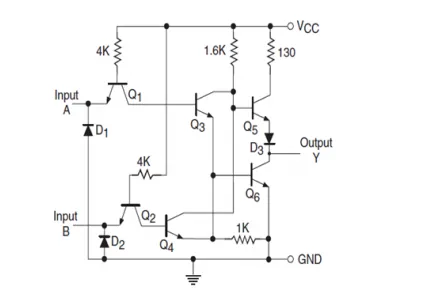
Suppose input A is at logic high, corresponding transistor’s emitter base junction is reverse biased and base collector junction is forward biased. Transistor Q3 gets base current from supply voltage Vcc and goes to saturation. As a result of low collector voltage from Q3, transistor Q5 goes to cut off and on the other hand if another input is low, Q4 is cut off and correspondingly Q5 is cut off and output is connected directly to ground through transistor Q3. In a similar way, when both inputs are logic low, the output will be at logic high.
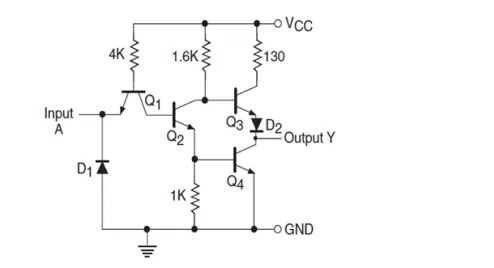
When input is low, corresponding base emitter junction is forward biased, and base collector junction is reverse biased. As a result transistor Q2 is cut off and also transistor Q4 is cut off. Transistor Q3 goes to saturation and diode D2 starts conducting and output is connected to Vcc and goes to logic high. Similarly, when input is at logic high, output is at logic low.