Half and Full Subtractor
Subtractor circuits take two binary numbers as input and subtract one binary number input from the other binary number input.
SUBTRACTOR
Subtractor circuits take two binary numbers as input and subtract one binary number input from the other binary number input. Similar to adders, it gives out two outputs, difference and borrow (carry-in the case of Adder). There are two types of subtractors.
· Half Subtractor
· Full Subtractor
Half Subtractor
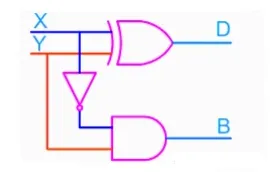
The half-subtractor is a combinational circuit which is used to perform subtraction of two bits. It has two inputs, X (minuend) and Y (subtrahend) and two outputs D (difference) and B (borrow). The logic symbol and truth table are shown below.
Symbol

Truth Table
From the above table we can draw the Kmap as shown below for "difference" and "borrow". The boolean expression for the difference and Borrow can be written.
From the equation we can draw the half-subtractor as shown in the figure below.
Full Subtractor
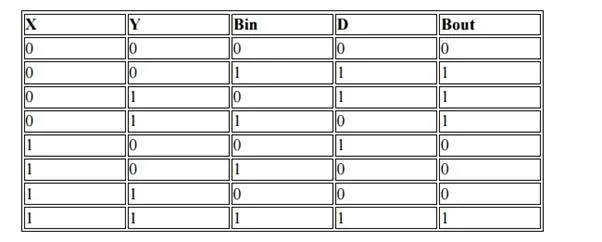
A full subtractor is a combinational circuit that performs subtraction involving three bits, namely minuend, subtrahend, and borrow-in. The logic symbol and truth table are shown below.
Symbol
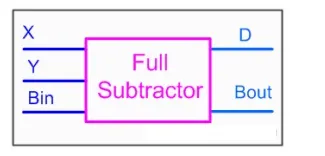
Truth Table

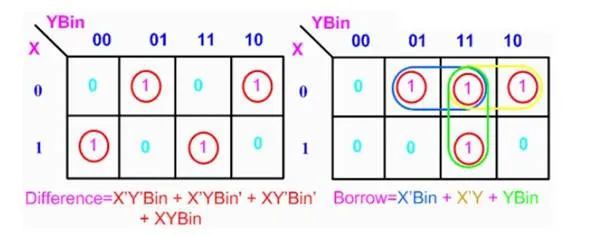
From above table we can draw the Kmap as shown below for "difference" and "borrow".

The boolean expression for difference and borrow can be written as
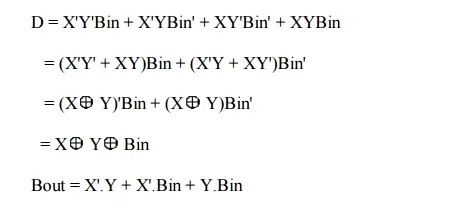
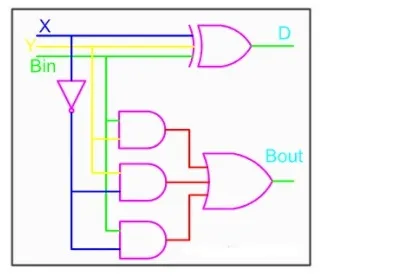
From the equation we can draw the full-subtractor as shown in figure below.
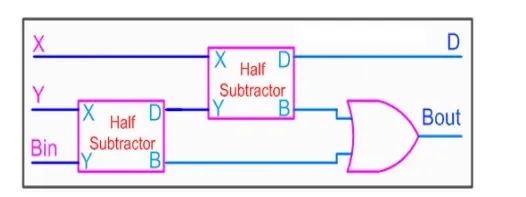
Full-subtractor circuit is more or less same as a full-adder with slight modification.
