Selecting Output Signals with a Multiplexer
A multiplexer is a signal switcher that selects an output signal from among multiple input signals. Its operation resembles that of a vending machine: press one of many available buttons, and the selected product appears at the machine's single outlet.
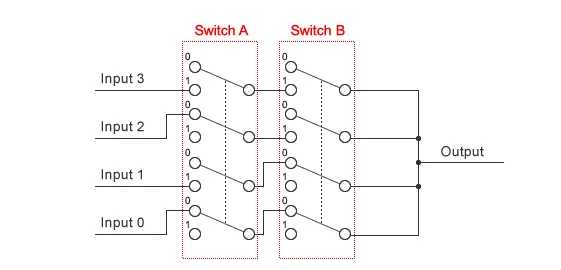
We can represent the action of a multiplexer as a series of switches, as shown in Fig.5. Switch A and Switch B each consist of a bank of four internal switches. If Switch A and Switch B are both set to 0, input 0 will connect to the output, as you can see from the figure. In other words, the signal carried by input 0 will propagate through the output, while other inputs will be blocked. Similarly, {A = 1 and B = 0} selects input 1 for output; {A = 0 and B = 1} selects input 2, and {A = 1 and B = 1} selects input 3. As you can see, then, the two switches A and B implement a multiplexer that can be used to select and propagate any one of four inputs.

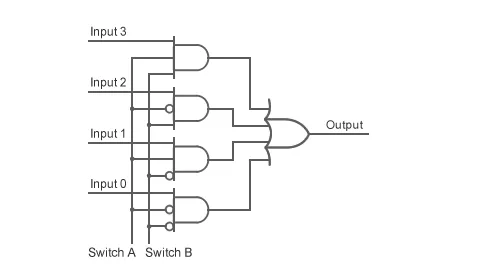
how this multiplexer can be represented in terms of combinational logic. As you can see, the multiplexer can be built entirely from AND and OR gates. Judgments made by the AND section are narrowed down to one by the OR gate