Types Of OS
OS are classified into different types depending on their capability of processing—(1) Single user, (2) Multiuser, (3) Multitasking, (4) Multiprocessing, (5) Real time, and (6) Embedded.
· Single User and Single Task OS is for use by a single user for a standalone single computer for performing a single task. Operating system for Personal Computers (PC) are single user OS. For example, if the user is editing a document, then a document cannot be printed on the printer simultaneously. Single user OS are simple operating system designed to manage one task at a time. MS-DOS is an example of single user OS.

A single user performing a single task
· Single User and Multitasking OS allows execution of more than one task or process concurrently. For this, the processor time is divided amongst different tasks. This division of time is also called time sharing. The processor switches rapidly between processes. For example, the user can listen to music on the computer while writing an article using a word processor software. The user can switch between the applications and also transfer data between them. Windows 95 and all later versions of Windows are examples of multitasking OS.

A single user performing multitasking (issuing print command and making drawings)
· Multiuser OS is used in computer networks that allow same data and applications to be accessed by multiple users at the same time. The users can also communicate with each other. Linux, UNIX, and Windows 7 are examples of multiuser OS.
· Multiprocessing OS have two or more processors for a single running process. Processing takes place in parallel and is also called parallel processing. Each processor works on different parts of the same task, or, on two or more different tasks. Since execution takes place in parallel, they are used for high speed execution, and to increase the power of computer. Linux, UNIX and Windows 7 are examples of multiprocessing OS.

Multiple users working on connected computers
· Real Time OS are designed to respond to an event within a predetermined time. These operating systems are used to control processes. Processing is done within a time constraint. OS monitors the events that affect the execution of process and respond accordingly. They are used to respond to queries in areas like medical imaging system, industrial control systems etc. LynxOS is an example of real time OS.
· Embedded OS is embedded in a device in the ROM. They are specific to a device and are less resource intensive. They are used in appliances like microwaves, washing machines, traffic control systems etc.
Functions Of Os
Operating system is a large and complex software consisting of several components. Each component of the operating system has its own set of defined inputs and outputs. Different components of OS perform specific tasks to provide the overall functionality of the operating system. Main functions of the operating system are as follows:
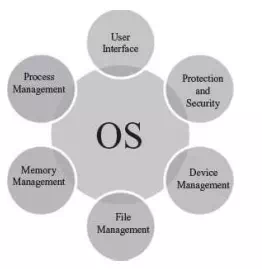
Functions of OS
· Process Management The process management activities handled by the OS are—(1) control access to shared resources like file, memory, I/O and CPU, (2) control execution of applications, (3) create, execute and delete a process (system process or user process), (4) cancel or resume a process (5) schedule a process, and (6) synchronization, communication and deadlock handling for processes.
· Memory Management—The activities of memory management handled by OS are—(1) allocate memory, (2) free memory, (3) re-allocate memory to a program when a used block is freed, and (4) keep track of memory usage.
· File Management—The file management tasks include—(1) create and delete both files and directories, (2) provide access to files, (3) allocate space for files, (4) keep back-up of files, and (5) secure files.
· Device Management—The device management tasks handled by OS are—(1) open, close and write device drivers, and (2) communicate, control and monitor the device driver.
· Protection and Security—OS protects the resources of system. User authentication, file attributes like read, write, encryption, and back-up of data are used by OS to provide basic protection.
· User Interface or Command Interpreter—Operating system provides an interface between the computer user and the computer hardware. The user interface is a set of commands or a graphical user interface via which the user interacts with the applications and the hardware.