Operations Support System
The operations support system provides information about the day-to-day activities of the organization. They support the operations of the organization, by keeping track of the resources and the transactions. For example, in a banking operation, the operations support system are used to keep track of current balance of the customer; in a manufacturing unit, it helps to keep track of the inventory of the items; and, in a sales unit, it keeps track of the number of units of each item sold. Thus, transaction processing is the main function of the operations support system.
Transaction Processing System (TPS)
· Transaction is a basic level of activity that is performed during the business operations. It is the business-related exchange of payments to employees, sales to customers, and payments to suppliers. Examples of transactions are—withdrawal of money from bank, booking ticket for an airline, selling of goods to the customer etc.
· TPS is an organized collection of people, procedures, software, databases, and devices used for recording the business transactions. TPSs are essential parts of any business organization.
· TPSs are used for routine, repetitive, and ordinary business transactions, and transactions that are critical to the daily function of the business. TPS records the business transactions and generates the documents related to the transaction. For example, daily routine transactions for sales orders from customers, bank deposits and bank withdrawals.
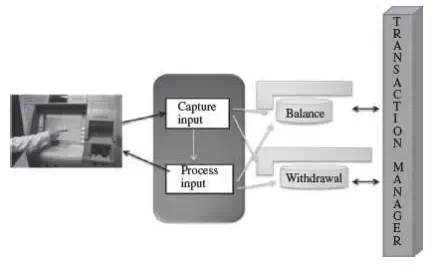
Transaction processing
· TPS automates handling of the data for the business activities and transactions.
· The goal of TPS is to increase transaction processing speed, enhance productivity, and simplify the processes.
· TPS gathers all the input necessary for other types of systems. It provides the basic input to the company’s database. A transaction generates data, which is recorded by the transaction processing system. This data forms the input for the generation of the other information systems, like MIS, DSS and EIS. For example, based on the daily transactions, a monthly sales report for middle management and marketing information for senior managers is generated.
· In an organization, there are different functional areas like manufacturing, human resource, accounts, finance, administration, sales, and marketing. The TPS information systems are developed for and used by people in the different functional areas. Examples of TPS are Payroll TPS, Sales TPS, and Marketing TPS.
Office Automation System (OAS)
OAS supports automation of the tasks in an office. It supports general office work for handling and managing documents. It facilitates communication, both within the office, and, between the office and its environment. It provides support for the traditional office operations like managing the documents, sending messages for interaction, arranging and conducting meetings, scheduling of the projects etc.

Some parts of office automation system
· OAS allows use of text processing systems like word processors and desktop publishing system, to enable the creation of professional documents with graphics and special layout features.
· Spreadsheets, presentation packages like PowerPoint, personal database systems, and, note- taking systems like appointment book, notepad and calendar, are parts of an OAS.
· OAS includes the communication systems required for transmitting the messages, documents, images, video or voice. For this, it uses the network and the Internet. It incorporates the e-mail facility, voice mail, teleconferencing capabilities, accessing web sites etc. Figure shows an automated office.
