Data, Information And Knowledge
Let’s understand the distinction between data, information, and knowledge.
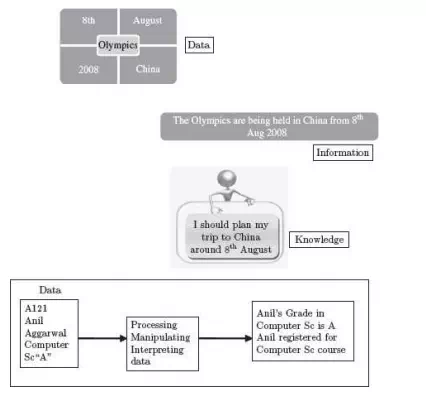
Data, information, and knowledge
· Data are raw facts. Data is isolated values which by themselves do not have much significance. Data may be numbers, letters or characters, image represented as graphic images and pictures, audio or video. It represents something in the real world. Data forms the raw material for the production of information. Data is not organized and does not convey a meaning. For example, the data elements like ‘8th’, ‘Aug’ 2008’, ‘China’, and ‘Olympics’ just represent values.
· Information is processed, manipulated, and interpreted data. It is the collection of data organized in such a way that they have value beyond the data itself. Information is created by defining and organizing relationships among data. For example, ‘The Olympics are being held in China from 8th Aug 2008’. The processed data gives us information which can be used for different purposes.
· Knowledge is an inference or conclusion drawn from the information. For example, a person from India who wishes to go to China can use the information ‘The Olympics are being held in China from 8th Aug 2008’. to enhance his knowledge so that this person can plan his trip to China accordingly.
Characteristics Of Information
Information that is meaningful for the people and the organization must have certain characteristics. The characteristics of the information are listed as follows—
· Accurate: Information must not contain any errors. It must be accurate.
· Accessible: Authorized users should be able to access the information whenever required.
· Complete: Information must contain all important and related data.
· Economical: Information should be economical to produce both in terms of time and cost.
· Format: Information should be available in the desired format.
· Flexible: Information should be flexible enough to be used for different purposes.
· Reliable: Information is dependable and is generated using correct data.
· Relevant:. Information must be relevant so that it can be used by the organization.
· Secure: Unauthorized users should not be able to access the information. Access is allowed only to authorized individuals.
· Simple: Information must be easily understandable and usable. Complex information is difficult to use and may not serve its purpose.
· Timely: Information must be available when it is needed. Late or outdated information is of no use.
· Verifiable: There should be a means to cross check the available information.
The information having the above characteristics is valuable and is used by the organization for achieving its goals. The organization may use the information for different purposes like decision making, managing the organization etc.