Heat transfer
Heat transfer, any or all of several kinds of phenomena, considered as mechanisms, that convey energy and entropy from one location to another. The specific mechanisms are usually referred to as convection, thermal radiation, and conduction . Conduction involves transfer of energy and entropy between adjacent molecules, usually a slow process. Convection involves movement of a heated fluid, such as air, usually a fairly rapid process. Radiation refers to the transmission of energy as electromagnetic radiation from its emission at a heated surface to its absorption on another surface, a process requiring no medium to convey the energy.

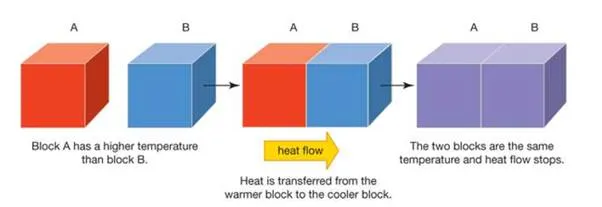
heat transferHeat is transferred via conduction from a warm block to a cool block.
Transfer of heat, whether in heating a building or a kettle of water or in a natural condition such as a thunderstorm, usually involves all these processes.
Energy
Energy, in physics, the capacity for doing work. It may exist in potential, kinetic, thermal, electrical, chemical, nuclear, or other various forms. There are, moreover, heat and work—i.e., energy in the process of transfer from one body to another. After it has been transferred, energy is always designated according to its nature. Hence, heat transferred may become thermal energy, while work done may manifest itself in the form of mechanical energy. All forms of energy are associated with motion. For example, any given body has kinetic energy if it is in motion. A tensioned device such as a bow or spring, though at rest, has the potential for creating motion; it contains potential energy because of its configuration. Similarly, nuclear energy is potential energy because it results from the configuration of subatomic particles in the nucleus of an atom.
Energy can be neither created nor destroyed but only changed from one form to another. This principle is known as the conservation of energy or the first law of thermodynamics. For example, when a box slides down a hill, the potential energy that the box has from being located high up on the slope is converted to kinetic energy, energy of motion. As the box slows to a stop through friction, the kinetic energy from the box’s motion is converted to thermal energy that heats the box and the slope.
Energy can be converted from one form to another in various other ways. Usable mechanical or electrical energy is, for instance, produced by many kinds of devices, including fuel-burning heat engines, generators, batteries, fuel cells, and magnetohydrodynamic systems.
In the International System of Units (SI), energy is measured in joules. One joule is equal to the work done by a one-newton force acting over a one-metre distance.
Energy is treated in a number of articles. For the development of the concept of energy and the principle of energy conservation, see principles of physical science; mechanics; thermodynamics; and conservation of energy. For the major sources of energy and the mechanisms by which the transition of energy from one form to another occurs