Comparison
between CPCC, FBEC & CRSD
Before doing the comparison study lets know what these terms
mean.
CPCC Cement-Polymer Composite Coated
Rebars
FBEC Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coated Rebars
CRSD Corrosion Resistant Steel Deformed
Rebars
1.0
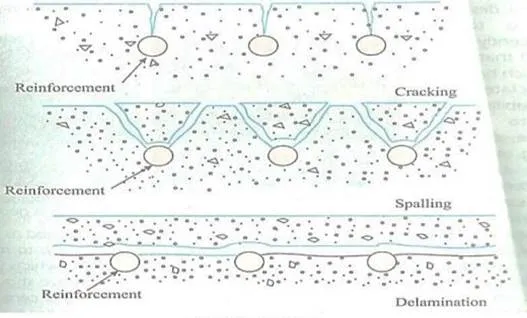
Corrosion Control of Reinforcement bars (Rebars)
40% of failure of structures is on account of corrosion of
embedded steel reinforcement in concrete. Therefore corrosion control of steel
reinforcement is a subject of paramount importance. First and foremost for
corrosion control is the good quality of concrete through good construction
practices.

2.0
Cement-Polymer Composite Coated Rebars (CPCC)
System at a glance
Products involved in CPCC normally are:
De-rusting Solution
Alkaline Powder
Phosphating Jelly
Inhibitor Solution
Sealing Solution
|
S No |
Parameter |
Requirement |
|
1. |
Pre-treatment (Surface reparation) |
Sand blasting to the near white metal |
|
2. |
Primer Coat |
To be given within 4 hours of sand blasting. |
|
3. |
Sealer Coat |
Within 30 minutes of primer coat, this
should be given. Thickness 150 microns plus minus 25 microns. |
|
4. |
Air curing |
Six hours before use in the work. |
|
5. |
Continuity of coating |
No defects such as cracking, bulging,
peeling, no rust mark. Inspect visually. |
|
6. |
Adhesion of coating test |
Coated bars are bent at 120 o around
a mandrel. NO peeling or cracking should be observed on outer radius. |
|
7. |
Stacking |
Stack bars on buffer material. |
|
8. |
Cutting , bending, welding |
Coat bars can be cut and bent. Cut ends and
weld positions should be treated with same formulation. |
This system has been developed mainly as a factory / shop
process.
The approach behind development of this system is that the
base metal of rebars, contains
? electrons which get readily
released in corrosive environment leading to oxidation of iron and thereby
formation of Ferrous Oxide (II) (rust) as principal deterrent.
In order to prevent this oxidation a surface coating capable
of interacting/nullifying the released electrons is provided.
Further pre-stressing and reinforcing steel, in concrete
during service life, are exposed to an alkaline environment and this
necessitates introductions of a top coat which should be compatible to primer
and alkaline environment.
3.0
Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coated Rebars (FBEC)
System at a glance
|
No. |
Parameter |
Requirement |
|
1. |
Pre-treatment (Surface reparation) |
1. Bars are first cleaned from surface
contamination such as
oil, grease etc. by chemical process before shot blasting. 2. The reinforcement bars are cleaned by shot blasting or grit blasting to white
or near white stage. 3. The blast cleaned bars are then heated through induction heaters
at preset temperature level around 230°C. |
|
2. |
Coating |
Hot bars are then fed to the coating booth,
where the epoxy powder
is sprayed electrostatically. |
|
3. |
Curing and Cooling |
Coated bars are then cured and forced cooled by
water spraying to enable handling and testing. |
|
4. |
Continuity of coating |
On line and off line holiday checks,
thickness checks are carried out. The adhesion of the coated bars is also
tested frequently by bending of the bar. |
|
5. |
Testing of Performance of rebar |
Various other tests are performed in
laboratory like chemical resistance, short spray, resistance in continuance
boiling water, abrasion resistance and impact resistance etc. These are
conducted on every batch of production. |
|
6. |
Handling & Stacking |
Fusion Bonded Epoxy Coated Bars require
padded contacts during transportation, stacking, handling and till the
concreting is done. |
|
7. |
Cutting, bending & welding |
The cut ends, welded spots and handling
damages are required to be repaired with special liquid epoxy compatible with
the coating material as per specification of the coating agency. |
Fusion bonded epoxy is basically 100% solid finely ground
fused powder particles, which when heated; melt to form a continuous adherent
film.
There is no passivating primer film provided in case of
FBEC rebars.
This coating introduces a medium of weakness in the path of an
intimate bond between rebar and alkaline concrete.
Extensive investigation carried out on 40 bridges in Florida
Key in USA has revealed that disbandment can occur easily in the FBEC rebars which lacked passivation layer of Ferrous oxide
(II) and is a precursor to corrosion.
Higher co-efficient of Thermal Expansion of fusion bonded
epoxies impose large thermal stresses in epoxy coating leading to its early
failure.
Epoxy coats the rebar in the following
manner:
Melts
Flows
Gels
Cures
Cools
Adheres as coating

4.0
Corrosion Resistant Steel Deformed Rebars (CRSD)
Mechanism of resistance to corrosion begins with the formation
of initial layer of protective oxide or rust. (Hypo oxides). Unlike common rust
on normal rebars, the CRSD rust is passive,
tenacious and self-renewing.
The protective oxide is fine textured, tightly adherent and a
barrier to moisture, oxygen, carbon dioxide, Sulphur dioxide and chloride
effectively preventing further corrosion.
Scale on normal bars of steel is coarse textured flaky oxide
that does not prevent moisture or oxygen from reaching the underlying bars and
continuing the corrosion.
As corrosion resistance is in the chemistry of the grade, if
the passive oxide layer gets removed somehow, a new passive layer is formed
immediately.
|
CRSD Mechanical
Properties |
||
|
Properties |
IS:1786 Fe500D |
CRSD |
|
Yield Stress, YS (min, N/mm2) |
500 |
500 |
|
% Elongation |
16 |
16 |
|
Ultimate Tensile Strength, UTS (min, N/mm2) |
565 |
580 |
5.0
Comparison (CPCC FBEC CRSD)
|
Parameters |
CPCC |
FBEC |
CRSD |
|
Thickness of Coating |
175 mm 300 mm |
300 mm 675 mm |
No coating required |
|
Type of Protection to rebar |
Extrinsic |
Extrinsic |
Intrinsic |
|
Pre-treatment |
Pretreatment is
required before coating |
Pretreatment is
required before coating |
No pre-treatment required |
|
Treatment to surface |
Before coating the surface made little
rough when some damage is introduced. |
Before coating the surface made little
rough when some damage is introduced. |
The surface of the finished good is not
disturbed or damaged at all. |
|
Temperature treatment |
The whole process is done at room
temperature. |
230°C 400°C |
No treatment required |
|
Special Bending requirement |
Modified mandrel diameter is specified by
Indian Standard |
Modified mandrel diameter is specified by
Indian Standard |
Same as other TMTrebars of
Fe 500D grade |
|
Defects introduced |
Holiday Effect |
Holliday Effect |
Nil |