Manufacturing
in RCC Construction – Prefabricated rebars

Three decades back, a construction site was a place where all
building materials were brought in fabricated or mended as per need and then
used. For example cement, sand, stonechips and
water was assembled at construction site; mixed as per design and used. Brick
kilns were the only manufacturing/ prefabrication done in advance for
construction. Storing of inventory at construction sites wasvery much prevalent.
The concept of factories and automobile industry like ‘lean
engineering’, ‘just in time delivery’ and prefabrication have changed the very
picture of construction site. But till early 2000 prefabrication in
construction rebars was only in concept.
Around 2010 prefabrication of TMT rebars started
in India and now it has become indispensable for both large as well as small
scale project.
In low rise houses like G+1 to G+4 the usual cut and bend
in rebars are stirrups for beams, links for
columns, C-shaped & L-shaped bars for isolated footings and crank bars for
columns. There are primary steel manufacturers in India which provide
prefabrication service for rebars. These
manufacturers also make the commonly used shapes and sizes already available at
retail shops which are only a call away.








Advantages of using prefabricated rebar’s
V/S manually cut and bent material at site
|
Sl. No. |
Prefabricated steel rebar’s |
Site made rings and pieces |
|
1. |
Available in most common sizes. One can
even mix and match the sizes. |
Need based manufacturing, needs lead time
to cut and bend. |
|
2. |
Machine made with accurate shape and size
confirming to IS: 1786 & IS: 456. |
Manually bent at site, expertise depends on
the expertise available at site |
|
3. |
No need of power connection at site for
cutting rebars. |
Mostly electrical equipment are used for
cutting, which is at times dangerous too. |
|
4. |
No on-site bending required |
On-site bending is required |
|
5. |
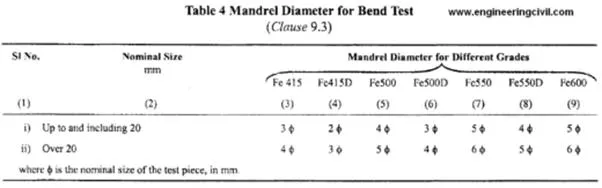
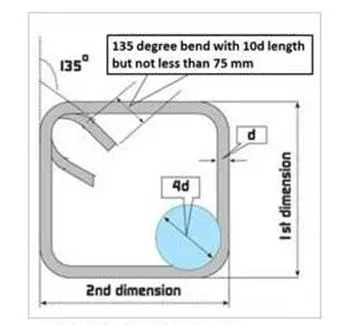
No micro cracks on the bends as proper
mandrels are used |
During manual bending, bar benders ignore
the norms for correct mandrel diameter to be used for bending as per IS:1786. |
|
6. |
Zero wastage of cut lengths |
10% wastage of rebar in quantity |
|
7. |
Available in ready to use bundles at local
steel dealers |
Not applicable |
|
8. |
Need only 2 days to finish concreting
foundation alone |
Need 7 days to finish concreting foundation
alone |
|
9. |
No dependence on labor at
site for cut and bend |
Dependence on availability of skilled labor to cut and bend. |
|
10. |
No pilferage at site |
Pilferage and hence loss of money at site |