Liquid water
The water molecule is composed of two hydrogen atoms, each linked by a single chemical bond to an oxygen atom. Most hydrogen atoms have a nucleus consisting solely of a proton. Two isotopic forms, deuterium and tritium, in which the atomic nuclei also contain one and two neutrons, respectively, are found to a small degree in water. Deuterium oxide (D2O), called heavy water, is important in chemical research and is also used as a neutron moderator in some nuclear reactors.

A water molecule is made up of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom. A single oxygen atom contains six electrons in its outer shell, which can hold a total of eight electrons. When two hydrogen atoms are bound to an oxygen atom, the outer electron shell of oxygen is filled.
Although its formula (H2O) seems simple, water exhibits very complex chemical and physical properties. For example, its melting point, 0 °C (32 °F), and boiling point, 100 °C (212 °F), are much higher than would be expected by comparison with analogous compounds, such as hydrogen sulfide and ammonia. In its solid form, ice, water is less dense than when it is liquid, another unusual property. The root of these anomalies lies in the electronic structure of the water molecule.
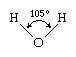
The water molecule is not linear but bent in a special way. The two hydrogen atoms are bound to the oxygen atom at an angle of 104.5°.

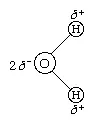
The O―H distance (bond length) is 95.7 picometres (9.57 × 10−11 metres, or 3.77 × 10−9 inches). Because an oxygen atom has a greater electronegativity than a hydrogen atom, the O―H bonds in the water molecule are polar, with the oxygen bearing a partial negative charge (δ−) and the hydrogens having a partial positive charge (δ+).
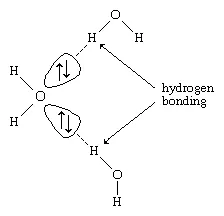
Hydrogen atoms in water molecules are attracted to regions of high electron density and can form weak linkages, called hydrogen bonds, with those regions. This means that the hydrogen atoms in one water molecule are attracted to the nonbonding electron pairs of the oxygen atom on an adjacent water molecule. The structure of liquid water is believed to consist of aggregates of water molecules that form and re-form continually. This short-range order, as it is called, accounts for other unusual properties of water, such as its high viscosity and surface tension.
water dropletsWater is a polar molecule and is attracted to other polar molecules. Thus, droplets, or beads, of water form on a nonpolar surface because water molecules adhere together instead of adhering to the surface.
An oxygen atom has six electrons in its outer (valence) shell, which can hold a total of eight electrons. When an oxygen atom forms a single chemical bond, it shares one of its own electrons with the nucleus of another atom and receives in return a share of an electron from that atom. When bonded to two hydrogen atoms, the outer electron shell of the oxygen atom is filled.
The electron arrangement in the water molecule can be represented as follows.
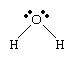
Each pair of dots represents a pair of unshared electrons (i.e., the electrons reside on only the oxygen atom). This situation can also be depicted by placing the water molecule in a cube.
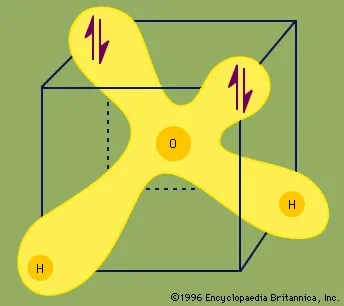
Each ↑↓ symbol represents a pair of unshared electrons. This electronic structure leads to hydrogen bonding.