Influence of water on the deprotonation and the ionic mechanisms of a Heck alkynylation and its resultant E-factors
Abstract
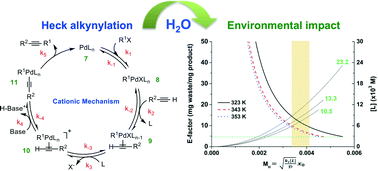
The influence of water on deprotonation and ionic mechanisms of a Heck alkynylation and its resultant E-factors were investigated. Estimation of the Hatta modulus, MH < 0.02, in cationic deprotonation, anionic deprotonation, and the ionic mechanism each separately confirmed an infinitely slow rate of reaction with respect to the diffusive flux within the thin film of the immiscible aqueous–organic interface. As a consequence, intrinsic kinetic expressions for far-equilibrium conditions were derived from first principles for each mechanism. Analyses of Gibbs free energies revealed that water potentially switched the rate-determining steps of cationic and anionic deprotonation to any of oxidative addition of organohalide to form Pd-complex (ΔG++ = 97.6 kJ mol−1), coordination of the alkyne with the oxidative addition adduct (ΔG++ = 97.6 kJ mol−1), or ligand substitution to form the cationic Pd-complex (ΔG++ = 94.9 kJ mol−1). Hydrogen-bonding in the transfer mechanism might account for the switch. Water, in general, was found to influence which step governs each catalytic cycle and the magnitude of its Gibbs free energy. Transformation of the synthesis from batch to continuous-flow was also studied by analyses of E-factors within the thin film. The amount of waste generated, as indicted by estimations of E-factors, was less in continuous-flow operation than in batch when the fastest step of deprotonation (ligand substitution) was infinitely fast with respect to the diffusive flux. The concentration of hydrophilic phosphine ligand was observed to influence mass transport limitations and the E-factor. Increasing ligand concentrations beyond (10.5), (13.3), and (23.2) × 10−3 mol L−1 for reaction temperatures of 353, 343, and 323 K increased the E-factor above its minimum value of 4.7, and it also induced mass-transfer-limitations. The switch from intrinsic to mass-transport-limited kinetics by finite changes in the ligand concentration explains ambiguity when performing aqueous-phase catalyzed Heck alkynylations and possibly multiphase Pd-catalyzed C–C cross-couplings in general. The potential exists to inadvertently mask the reactivity of useful ligands during discovery and to force mass transport limitations during manufacture. Understanding why the E-factor can be minimized is vital to the sustainable discovery and manufacture of fine chemicals, materials, natural products, and pharmaceuticals.
Thermolysis of 1,3-dioxin-4-ones: fast generation of kinetic data using in-line analysis under flow
Abstract
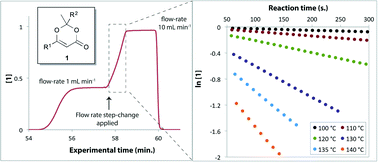
Rapid acquisition of kinetic data is demonstrated with a commercial meso-scale flow reactor, using a step-change in flow rate or ‘push-out’ from the flow line. For thermolysis of 1,3-dioxin-4-ones (1), we obtain excellent reproducibility in the activation energies measured from spectroscopic data collected by in-line UV or transmission FT-IR monitoring of the output during the transitional period between two flow rates (±3 kJ mol−1, 0.7 kcal mol−1). Analysis of multi-component UV and IR data is conducted using an orthogonal projection approach (multivariate curve resolution by alternating least squares) for complex spectra, or by calibration-less integration of non-overlapping peak absorbance. All analysis methods were validated using off-line 1H NMR analysis, and kinetic parameters obtained using the method of a flow rate step-change were validated against conventional steady-state measurements in which time-series data were acquired across multiple experiments. Thermal transfer and dispersion effects are addressed. The experimental methods described herein are valuable for accelerated reaction study and in process development.