CRM - 21st Century
Customers
“We see our customers as invited guests to a party, and we are the
hosts. It’s our job every day to make every important aspect of the customer
experience a little bit better.”
…Jeff Bezos, CEO, Amazon.com
Customers in the last decade
only used to be concerned about quantity, quality, and price. In today’s
information-driven world, the customers have not remained merely as people
buying goods or services from a business. Along from being concerned about the
questions such as "how many", “how much”, and "what", they
are groomed smart enough to ask, "why?". Today’s
customers are hard to convince and are difficult to please too.
Who is an Empowered
Customer?
Today’s customers are
empowered. Empowered customers are those having the control to buy goods or
services from a business when and where they want it, by selecting from a vast
range of available choice. Empowered customers access the Internet and collect
information about products, dealers, and prices. They take advice from friends
or at times from strangers too, before making a buying decision.
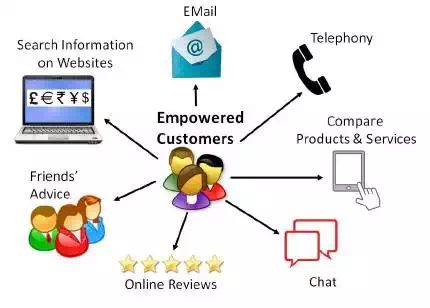
By using various digital
devices, they can find out the specifications of a product or service before
arriving at buying decision. They are smart and alert buyers who also keep high
expectations. When a business fulfills most
of the expectations, the empowered customers can be loyal to them.
Let us analyze the phases a customer goes through when a
business offers products/services to the customers.
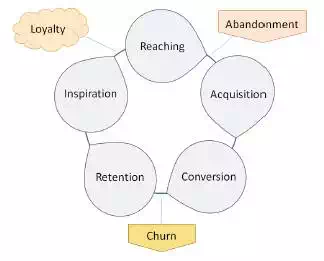
Customer Life Cycle
Customer Life Cycle is used to describe the phases through a customer goes. Here are the important stages of a customer life cycle −
● Reaching − It is the phase where a business
communicates with its target customer. It is mainly done through advertisements.
● Acquisition − Attracting and influencing the target
customer. The marketing team decides the scope of the target audience and
convinces the customers about the benefits of its products/services.
● Conversion − It is when customers decide to purchase a
product or service.
● Retention − In addition to flawless
products/services, the business offers some extra facilities to the customer
such as priority treatment, beautiful store ambience, free parking, etc., to
retain existing customers.
● Inspiration − To inspire a regular customer into a
loyal one by establishing a sound relationship. When a business puts efforts on
providing polite and quick service, personal attention from the staff,
knowledgeable sales staff, then the customers are automatically inspired to buy
a product/service from a particular vendor.
Let us now try to figure out
what differentiates a customer from a consumer.
Consumer vs. Customer
A consumer is
a user of a product or a service, whereas a customer is a
buyer of a product or service. A customer decides what to buy and executes the
deal of purchasing by paying and availing the product or service. A consumer
uses the product or service for oneself.
For example, the customer of a
pet food is not the consumer of that product. Similarly, if a mother in a
supermarket is buying Nestlé Milo for her baby, then she is a
customer and her baby is a consumer.
Types of Customers
There can be various types of customers a business have to deal with. Here are some prominent types of customers −
● Loyal Customers − They are completely satisfied customers.
Though they are less in numbers, they can promote more sales and profit. They
expect individual attention and demand polite and respectful response from the
supplier.
● Discount Customers − They visit the business outlets
frequently but transact only when business offers discounts on regular products
and brands. They are the ones who buy only low cost products. Their
buying behavior changes according to the
rate of discounts. They are important to a business, as they contribute a
significant portion of business profit.
● Impulsive Customers − They are with the business in urge and
buy on impulse. They don’t plan for buying anything specific in advance, but
they urge to buy anything that they find good and productive at the time when
they are in the store. These customers are challenging and very difficult to
convince. They are capable of bringing high profit when treated tactfully.
● Need-Oriented Customers − They have a specific product on mind and
they often plan before buying. They only buy when they need a product. They are
difficult to satisfy. They need reasons to switch to another product or brand.
● Wanderers − They are least profitable ones to a
business. At times, they are not sure what to buy. They are normally new in the
industry and mostly visit the suppliers only to confirm their needs on
products. They like to find out the features of the products in the market but
they are least interested in buying.
● High Volume Customers − They are the ones who consume a high
volume of products.
● High Future Lifetime Value
Customers − The ones who can contribute profits in
future.
● Benchmark Customers − They are the ones whom other customers
follow.
● Door Openers − They can open doors to a new market for
the supplier.
● Inspiring Customers − They force the suppliers to change for
betterment. They suggest product improvements or inform the suppliers about
opportunities of cost reduction.
Customer Orientation
There are three types of customer orientations −
● Cost-Oriented Customers − They concentrate on products with least
costs and are ready to compromise on efficacy, performance, and quality. They
are ready to blame the supplier on the occurrence of fault in product without
thinking that they are responsible for choosing less quality product. Some
customers tend to fix problems with a local, less-skilled dealer or by
themselves without taking a supplier’s direct help as it is cheaper. These
customers also at times buy second hand products and expect it to perform as
efficiently as a new one. The suppliers always find themselves arrested in
payment-related issues with these customers.
● Value-Oriented Customers − They always look for efficient and high-performing
products, as they know that they are making a profitable deal for a long run.
For them, paying a high initial cost is their long-term investment to enjoy its
hassle-free benefits in future. They are satisfied customers. They often tend
to maintain a healthy relationship with the suppliers.
● Technology-Oriented
Customers − They opt for the best technology
products rather than less cost, good quality, or performance. They are
technology-conscious as they find using products with latest technology would
sustain in the ever-changing technological environment. These customers have
detailed eye towards technical aspects of a product and tendency to interact
with other customers of their type. They are also satisfied customers and tend
to maintain healthy relationship with supplier.
Customer Management Strategies
There are seven core customer management strategies −
● Start a relationship − When a customer is identified as having a
high potential to bring profits, start a relationship.
● Protect the relationship − When the customer is significant for the
business and when there is a possibility of the competitor’s attraction, then
the managers need to protect the relationship.
● Relationship re-engineering − This is necessary when the managers find
that the customer is not profitable as desired at the current stage. In such a
case, serve the customer by low-cost automated channels.
● Enhance the relationship − The managers identify up-selling and
cross-selling opportunities and try to boost the customer on the scale of value.
● Harvest the relationship − When the managers do not want to spend
much on the existing customer development, they use the cash flow from these
customers to develop new customers.
● End the relationship − It is good to end the relationship when
the customer shows no sign of contributing to future business profit.
● Regain the customer − When the customer goes to the competitor
while choosing another option to fulfill his
requirement, then the managers need to implement win-back strategies to regain
the customer and understand the reason of departing the customer.
Customer Acquisition
Customer acquisition is the
art of persuading the customers to buy products or to avail services offered by
a business. Each time a business invents new strategies for acquiring new
customers, the strategy gets saturated over some time.
The strategy that worked in
the past may not remain effective in the future. Hence the businesses need to
keep tuned with the market situations, government policies and plan the new
strategies.
It requires diligent planning,
forming acquisition strategy, communicating with customers, advertising the
products aggressively on various media, conducting flash sales, etc., to
acquire new customers.