CRM - Types
“A business absolutely devoted to Customer Service Excellence will
have only one worry about profits. They will be embarrassingly large.”
− Sir Henry Ford
In the past twenty years, the
focus of global markets has shifted from sellers to customers. Today, customers
are more powerful than sellers, if we consider the driving factors of market.
We have different types of CRM according to the changes in customer portfolios,
speed of business operations, requirement of handling large data, and the need
of sharing information, resources, and efforts jointly.
CRM systems are divided based on their prominent characteristics. There are four basic types of CRM systems −
● Strategic CRM
● Operational CRM
● Analytical CRM
● Collaborative CRM
The following table lists the types of CRM and their characteristic features −
|
Type |
Characteristic |
|
Strategic CRM |
Customer-centric, based
on acquiring and maintaining profitable customers. |
|
Operational CRM |
Based on
customer-oriented processes such as selling, marketing, and customer service. |
|
Analytical CRM |
Based on the intelligent
mining of the customer data and using it tactically for future strategies. |
|
Collaborative CRM |
Based on application of
technology across organization boundaries with a view to optimize the
organization and customers. |
Strategic CRM
Strategic CRM is a type of CRM
in which the business puts the customers first. It collects, segregates, and
applies information about customers and market trends to come up with better
value proposition for the customer.
The business considers the
customers’ voice important for its survival. In contrast to Product-Centric CRM
(where the business assumes customer requirements and focuses on developing the
product that may sometimes lead to over-engineering), here the business
constantly keeps learning about the customer requirements and adapting to them.
These businesses know the
buying behavior of the customer that happy
customers buy more frequently than rest of the customers. If any business is
not considering this type of CRM, then it risks losing the market share to
those businesses, which excel at strategic CRM.
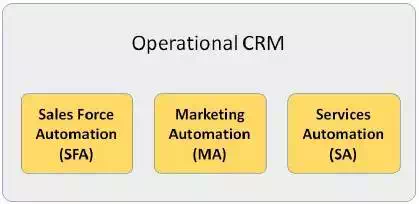
Operational CRM
Operational CRM is oriented
towards customer-centric business processes such as marketing, selling, and
services. It includes the following automations: Sales Force Automation, Marketing
Automation, and Service Automation.
Salesforce is the best suitable CRM for large
established businesses and Zoho is
the best CRM for growing or small-scale businesses.
Sales Force Automation
SFA is the application of technology to manage selling activities. It standardizes a sales cycle and common terminology for sales issues among all the sales employees of a business. It includes the following modules −
● Product Configuration − It enables salespersons or customers
themselves to automatically design the product and decide the price for a
customized product. It is based on if-then-else structure.
● Quotation and Proposal Management − The salesperson can generate a quotation
of the product prices and proposal for the customer by entering details such as
customer name, delivery requirements, product code, number of pieces, etc.
● Accounts Management − It manages inward entries, credit and
debit amounts for various transactions, and stores transaction details as
records.
● Lead Management − It lets the users qualify leads and
assigns them to appropriate salespersons.
● Contact Management − It is enabled with the features such as
customers’ contact details, salespersons’ calendar, and automatic dialing numbers. These all are stored in the form of
computerized records. Using this application, a user can communicate
effectively with the customers.
● Opportunity Management − It lets the users identify and follow
leads from lead status to closure and beyond closure.
Marketing Automation
Marketing automation involves
market segmentation, campaigns management, event-based marketing, and
promotions. The campaign modules of Marketing Automation enable the marketing
force to access customer-related data for designing, executing and evaluating
targeted offers, and communications.
Event-based (trigger)
marketing is all
about messaging and presenting offers at a particular time. For example, a
customer calls the customer care number and asks about the rate of interest for
credit card payment. This event is read by CRM as the customer is comparing
interest rates and can be diverted to another business for a better deal. In
such cases, a customized offer is triggered to retain the customer.
Service Automation
Service automation involves
service level management, resolving issues or cases, and addressing inbound
communication. It involves diagnosing and solving the issues about product.
With the help of Interactive
Voice Response (IVR) system, a customer can interact with business computers by
entering appropriate menu options. Automatic call routing to the most capable
employee can be done.
Consumer products are serviced
at retail outlets at the first contact. In case of equipment placed on field,
the service expert may require product servicing manual, spare parts manual, or
any other related support on laptop. That can be availed in service automation.
Analytical CRM
Analytical CRM is based on
capturing, interpreting, segregating, storing, modifying, processing, and
reporting customer-related data. It also contains internal business-wide data
such as Sales Data (products, volume, purchasinghistory), Finance
Data (purchase history, credit score) and Marketing Data (response
to campaign figures, customer loyalty schemes data). Base CRM is
an example of analytical CRM. It provides detailed analytics and customized
reports.
Business intelligence
organizations that provide customers’ demographics and lifestyle data over a
large area pay a lot of attention to internal data to get more detail
information such as, “Who are most valuable customers?”, “Which consumers
responded positively to the last campaign and converted?”, etc.
Analytical CRM can set
different selling approaches to different customer segments. In addition,
different content and styling can be offered to different customer segments.
For the customers, analytical CRM gives customized and timely solutions to the
problems. For the business, it gives more prospects for sales, and customer
acquisition and retention.
Collaborative CRM
Collaborative CRM is an
alignment of resources and strategies between separate businesses for
identifying, acquiring, developing, retaining, and maintaining valuable
customers. It is employed in B2B scenario, where multiple businesses can
conduct product development, market research, and marketing jointly.
Collaborative CRM enables
smooth communication and transactions among businesses. Though traditional ways
such as air mail, telephone, and fax are used in communication, collaborative
CRM employs new communication systems such as chat rooms, web forums, Voice
over Internet Protocol (VoIP), and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI).
There are collaborative CRMs
with in-built Partner Relationship Management (PRM) software
application which helps in managing partner promotions. SugarCRM is a popular collaborative CRM. It
enables expert collaboration and provides state-of-the-art social capabilities.
CRM Software Buying Considerations
A business needs to consider the following points while selecting a CRM software −
● Business strategy and
processes − It helps to automate a customer
management strategy. Hence before selecting a CRM software, a business should
be clear with its strategies and desired processes.
● Business requirements − CRM systems range from domain specialty
solutions that focus on solving a specific area such as sales force automation,
marketing automation, services automation, partner management, etc., to
complete enterprise management solutions.
● Size of business − Small businesses require tools that are
easy to learn and can handle a wide range of the most common tasks. Large
businesses opt for applications that handle more complex tasks and thousands of
users.
● Customer base − The size of the customer base a
business is required to handle.
● Budget − A business needs to set a budget prior
vendor selection. The budget allocated for CRM varies according to the degree
of customization required.
● Context − The context in which a business is
functioning, e.g., B2B or B2C, determines which CRM the business should go for.
● Sales channels − The sales channels a business is
employing: Direct sale, channel sale such as distributors, or Direct to
customers via retail. They matter while selecting the most suitable CRM
software.
● System integration − All the interfaces the business needs and
the CRM vendor can support without requiring too much custom services effort.
● Strength of partners − The partners must be able to provide a
business with additional support, or help to implement the CRM successfully.