CRM - Service Automation
ďTo give
real service, you must add something which cannot be bought or measured with
money, and that is sincerity and integrity."
− Douglas Adams
Service automation is the
process that works as a supporting system for the service staff and managers to
achieve their work related objectives. Infrastructure, Data, Devices, and
Software are the key components of service automation.
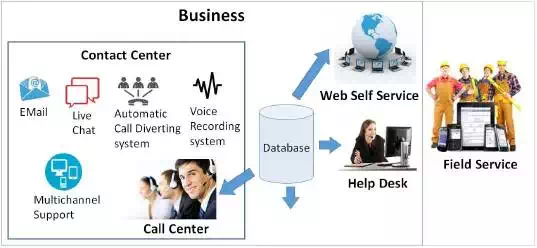
There are five major domains of service automation −
● Contact centers − They are the main basis of customer relationship. They
address customer queries via Email, telephone, instant messaging, SMS, or fax.
They have databases, Automatic Call Diversion (ACD) system, and voice recording
system. The staff responds to Emails and chats with customers regarding problem
and solution.
● Call centers − They are a part of contact centers which
majorly handle inbound and outbound calls. They perform typically more generic
duties, deal with people and calls which are outside the business, and at times
can make outgoing calls. The staff needs to have excellent patience, and
reading and listening skills.
● Help desks − They are internal to the business. They
are oriented towards supporting the business staff. Helpdesks generally
provides diagnostic and troubleshooting help.
● Field service − The service engineers or technicians
visit customerís workplace or home to install, repair, or maintain the
products. They visit factories, workshops, warehouses, and offices to provide
service. They also help the customer to specify the product, test, and
demonstrate it after installation.
● They need to access and update the data
from their computing devices. Technology businesses such as Aesta, Corrigo,
Oracle, Ventyx, etc. provide powerful software
applications to cater the need of service force.
● Web-based Self Service − Some businesses offer solutions to the
customersí problems on the web itself. The customers can buy products online,
track installation and service issues, and conduct online diagnostics.
Benefits of Service
Automation
The benefits of implementing service automation are −
● Enhanced service processes − Service requests are attended quickly and
routed to appropriate service staff.
● Enhanced productivity − Since optimal number of customers are
scheduled, the service time take is used at its best thus increasing
productivity.
● Increased customer
experience − Since service staff has full access to
the service history, they ensure that right service is delivered to the
customer at appropriate service status. This improves customer satisfaction.
Service Automation Software Applications
There are large number of service automation software applications available in the market. Some important ones are as follows −
● Activity management − It enables the service staff to track
workload, assign priorities to the service according to urgency, set
appointment alerts, set alarms on attended but unresolved services, etc.
● Agent management − It enables businesses to manage globally
dispersed, employed or outsourced, operating in different time zones service
agents.
● Case management − It ensures each customer enquiry or issue
is routed to appropriate agent or technician according to the agentís
competencies and skills. When the customer raises double ticket by email or
otherwise for an issue, the software automatically communicates with the
customer at various stages of resolving the issue. It enables the technicians
to diagnose and close the case quickly.
● Customer self-service − It enables for the customers to track the
packages they sent or expecting to receive from courier service. The customers
can transact online, track their shipments, and pay for the service, all by
themselves.
● Email Response Management
System (ERMS) − It provides automated and
customized Email responding to large volume of customers. It also provides
multilingual spellchecker, and Email analytics and templates.
● Scheduling − It enables to schedule the service
technicianís work on the basis of hours, days, or months. It deals with the
record of technician details, skills, availability of working, charges taken,
etc. It also records customer details, accessing hours, location, distance,
issue, and service level agreement.
● Inbound Communication
Management (ICM) − It
is uses by contact centers for equal
distribution, queuing, and routing of incoming communication via phones,
Emails, SMSs, Chat, IMs, etc.
● Outbound Communication
Management (OCM) − It
enables service staff to acknowledge service requests, invoicing for out of
warranty services, advising on pre-servicing tasks to the customer, track the
service tasks, and post-service communication with the customer.
● Job management − It helps field technicians or service
engineers to manage their work related issues such as taking preventing
measures against failure, system servicing, recording meter readings,
installation, upgradation, and inspection.
● Spare parts management − It serves the field technicians with the
data about the number of parts available. The technicians can also check the
availability of parts with fellow technicians or at regional warehouse. It also
enables to purchase, transfer and manage faulty parts so that when they attend
to resolve a service issue, they are completely equipped.