CRM - Customer Related Databases
“How you gather, manage, and use information to serve your clients
will determine whether you win or lose in the business.”
− Bill Gates
The customer related database
gives a business an insight on the customer behavior.
It is the foundation on which the CRM software strategies work. For any
business using the CRM, the customer-related database is highly important to
impart the customer-based strategies and tactics.
The database supports all the forms of CRM − Strategic, Operational, Analytical, and Collaborative.
What is Customer-Related
Database?
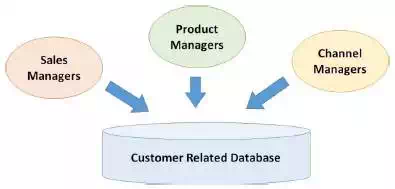
It is the collection of customer-related information focusing on historic sales, current opportunities, and future opportunities. These databases are maintained by a number of different functions such as sales managers, channel managers, product managers, etc. It can store information such as −
● Customer’s personal information
containing fields for name, address, contact details, contact preferences, age,
marital status, birthdate, anniversary, professional and social status, etc.
● Sales managers can record past
transactions, product preferences, opportunities, campaigns, enquiries,
billing, etc.
● Channel managers can record
business-owned retail outlets, online retail information.
● Product managers may record product preference,
price band, product categories explored, etc.
Based on the respective
purposes, there are two types of databases − Operational and Analytical.
The operational data resides in Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) database
and analytical data resides in Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) database.
Developing and Maintaining Customer-Related
Database
The database is a repository
of collection of files (or tables). The files contain a number of records (or
rows of the table), which in turn contain various fields (or columns of the
table). Each file contains information about a topic such as customer, sales,
products, etc.
The steps given below are followed to create and maintain a customer-related database −
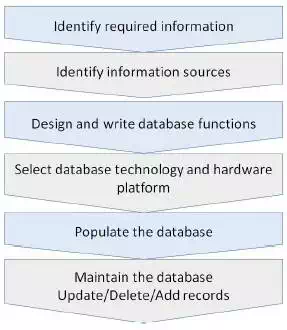
The database always needs to
be very accurate and up-to-date.
Types of Customer Data
There are mainly two types of
CRM data − Primary and Secondary. The
primary data is the one which is collected for the first time. The secondary
data is the one which has been collected earlier.
The primary data is collected
by conventional means such as conducting surveys, holding a skill competition,
inviting the customers to subscribe for the newsletter or to register their
purchase, etc.
Database and Hardware for CRM
The CRM software use
Relational Database architecture. It is composed of tables with rows and
columns. The tables are connected to other tables by a unique identification
number stored in the ID field, named primary key.
Database Management Systems for CRM
There are many database
management systems available in the market today. Some popular ones are
Microsoft’s SQL server, Oracle, DB2 from IBM, etc. These systems help to update
and administer the database.
Hardware Considerations for CRM Database
The hardware platform on which the database will reside is selected based on the following factors −
● The database size.
● The existing technology used in the
business.
● The location of CRM users. Especially in
case of global use of CRM, the multilingual users from different time zones can
access the CRM for operational and analytical purposes.
Data Attributes
The CRM data must have the following attributes −
● It must be sharable because
many people need to access it from various geographical locations.
● It must be relevant means
pertaining to the given purpose.
● It should be most accurate.
Inaccurate data wastes the marketing efforts of the business, predicts wrong
opportunities and serves the customers with insufficient and inaccurate
service. Data should be reviewed timely to ensure removal of inaccuracy taken
place while acquiring and entering the data.
● It should be up-to-date means
it should store and show the latest information.
● It should be transportable from
one location to other. It should be available where the users need it. The
technology of compiling and handling data electronically is essential for
today’s fast-paced businesses.
● It should be secured.
Businesses need to keep their data safe from loss and theft and unethical
snooping as many businesses can subscribe to the same CRM software through the
same portal.
Data Warehousing (DW)
Data warehouses are huge
repositories of customer related data accepted from various databases. These
repositories can be as much as a few terabytes (240bytes).
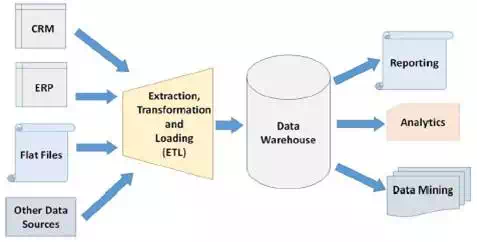
Numerous global businesses operating from various countries and continents generate huge volume of data. This data needs to be converted into useful information for further operations and analysis. Data warehouse does this task by −
● Accepting the data from ETL system that
extracts valuable data, transforms it into a required format, and loads it into
the database.
● Organizing data according to subjects of
business and various time periods.
● Standardizing data coming from various
sources in a single format. For example, bringing salutations, codes (m/f or
male/female), units of measurement, etc. in the same format.
● Conducting periodic update of data, say
daily or weekly, depending upon business requirements. It is not done in real
time.
● Providing updated data for the purpose of
analytics, data mining, and reporting.
Data Marts
It is the smaller version of a
data warehouse which caters to a particular business or a function. Data mart
projects are inexpensive than data warehouse projects as the volume of the data
is smaller and the functions for which it is used are specific. The costs,
time, and efforts required to handle such data are less.
Data Access and Interrogation
CRM applications allow users
to interact with the database. For example, a salesperson adds customer data at
the time of billing or after the customer service call is attended. Also, the
users need to interrogate the data for analytical purpose.
Thus, data access and interrogation is essential and is carried out by the following three ways −
Data Mining
Data mining is the process of
sifting through the huge volume of data to get most relevant information in the
shortest possible time. CRM takes the help of Artificial Intelligence to find
out the solutions for the most important questions of the business.
In the context of CRM, data mining is the application of predictive analytics to support marketing, sales, and services. In CRM, data mining finds associations among data, classifies the customers according to business value, and helps to find answers of the following questions −
● Which customers the business should
target?
● What is the cost of customer acquisition?
● Which customers are buying (or not
buying) the products?
● Who are high/medium/low margin customers?
● What profile customers are defaulting
payment repeatedly?
● How can a business segment its market?
● Can the business offer a common price for
all customer segments?
For example, an analyst of
Walmart noticed that the sale of beer and diapers is high on Fridays. Having
this fact brought to the notice of Walmart, the business kept the two products
close to each other on the shelves. This resulted in the sale rise of both the
products.
Thus, data mining helps in
generating sales volumes by providing most relevant data for marketers’
analysis.
Database Queries
The queries are the tools to
access and modify the database. Structured Query Language (SQL)
is used for management of Rational Databases. The queries come in the form of
statements such as SELECT, ADD, DELETE, UPDATE, DROP, etc.
For example, look at the following query statements −
CREATE
DATABASE Db_Name
DELETE * FROM EMPLOYES
SELECT Emp_Name, Emp_Salary
FROM Employees
WHERE Emp_Salary >= 25000
Reports
CRM Applications generate
reports on periodic basis for analyzing the
traits of sale, performance, and many other allied activities. Reports are
generally accessed by management people of the business for performance
assessment.
OLAP technology is capable of
showing data at a level as lowest as a salesperson’s and as highest as a region,
which can be helpful to assess the performance and question the
underperformance.
Position of CRM with Respect to Database
After having known various types of CRM in earlier chapter, let us see which CRM stands where with respect to the customer database −
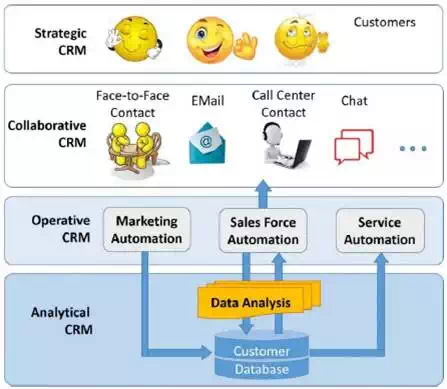
Analytical CRM works most
closely with the customer database and strategic CRM works farthest from the
database.