CRM - Implementing CRM Projects
“Ideas are easy. Implementation is hard.”
− Guy Kawasaki
Implementing a CRM project in
an organization takes more than purchasing and installing the CRM form a
vendor. It needs setting up the features of CRM system according to the
business requirement, training the staff, and overall shifting from conventional
work culture to a new method of handling work and customer relationships.
There are various phases a
business needs to go through while implementing CRM projects. Here in this
chapter, we will discuss in brief how to implement a CRM project.
Developing CRM Strategy
This is the first stage. CRM
strategy is a top management level plan of aligning employees, CRM process, and
technology to achieve business goals.
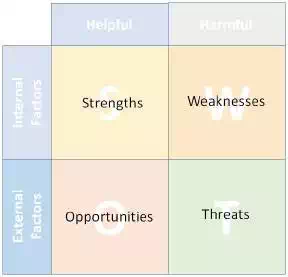
Situation Analysis
The business conducts
situation analysis by considering internal and external factors. This is
nothing but SWOT (Strength, Weakness, Opportunities, and Threats) analysis to
find out how the business is doing with the objective of examining readiness
for CRM implementation.
The managers analyze and appraise existing customer strategy, served market segments, market position of business, marketing channels, etc. They try to find out the answers for the questions such as −
● Which customer segments does the business
serve?
● What are the marketing and customer
related objectives of the business?
● What is the business position and market
share?
● What is the cost to customer management?
● How effective the present strategies of
customer acquisition and retention?
● Which products/services under what
category does the business offer?
● To what extent the customers are aware of
the products/services?
● Who are business competitors, and what
are profit margins?
● Which channels we use for product
distribution? What is the depth of channel penetration?
● Which channels are effective? Which are
becoming obsolete?
● How do channel partners find dealing with
our business?
● Will the business buy, rent, or create
its own CRM? What is each option’s feasibility?
Thus, situation analysis
serves as a foundation to know what the managers want to achieve by
implementing CRM.
Building CRM Project Foundation
Before implementing CRM projects, there are various changes required to bring in the business environment such as −
● The working culture changes present in
the business organization.
● As the CRM can mean different to the
people from different domains, it is necessary for the business to start
educating the staff on CRM systems.
● The top management of business also sets
up the vision on how CRM will change the business to benefits regarding serving
the customer better and earning high revenue.
● Clear priorities are set for objectives
and activities such as enhancement of customers’ experience, cost reduction,
increasing revenue, etc.
● Goals (qualitative results) and
objectives (quantitative results) are set.
● Governance structure of experts is formed
which is essential to identify and allocate resources and responsibilities
appropriately.
● The internal IT staff of the organization
is put to perform several CRM related roles such as networking, database management,
front-end development, system integration, etc.
● The management identifies change and
project management needs in the organization, and risk factors.
Identifying Business Processes
The processes are the ways by which the business gets the things done. The processes can be of the following types −
● Vertical − Located completely within a department.
For example, customer acquisition is only marketing related process, whereas
annual revenue and tax calculation are accounts processes.
● Horizontal − They span across various departments in
the business. For example, product manufacturing is cross functional across
R&D, finance, material management, sales, etc.
● Primary − They have major impact on the business
costs or revenue. For example, picking and delivering packages is primary
process for a courier company.
● Secondary − They have minor impact on the cost or
revenue of the business.
● Front-Office − They encounter the customers. For
example, complaint handling.
● Back-office − They are where customers are directly
involved. They are not known to the customers. For example, database
management, procurement, etc.
The business needs to
anticipate which existing processes may get affected and to what extent.
Specifying Requirements
During this step, the business
identifies the stakeholders (staff, sales team, marketing team, channel
partners, IT specialists, etc.), processes, data requirements, and technology.
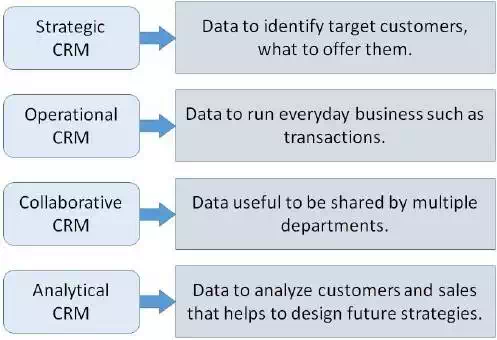
Data Requirements
The business needs to create the inventory for the available data for the CRM purposes. There are different data requirements for different CRM types as shown −
● Which database system the business will
require for CRM?
● What is the number of customers the
business have?
● How much the number of customers can
increase in future?
● Which fields of data are mandatory and
which are additional for the business?
The business develops a
customer related database to store the customer information, such as contact
data, contact history, transaction history, communication preferences,
opportunities with customer, and so on.
Technology Requirements
It includes selection the
required CRM technology from a wide choice.
● How to access the CRM software: from
business server (On-Premise) or from vendor’s server (Hosted or Online) via
internet?
● Which CRM applications can fulfill the business vision and objectives among a
myriad number of applications under CRM.
● What hardware is required for sales,
services, and marketing staff?
● What is the required hardware platform on
which the database will reside and function?
|
On Premise CRM |
Hosted or Online CRM |
|
It is installed at user
premises. A CRM purchasing business bears the cost of infrastructure,
customization, and implementation. |
It requires payment of
fees on annual basis. For example, USD 50 per user, per month. |
|
Costs are variable. |
Costs are fixed and known. |
|
It imposes significant
burden on staff and budgets of a business. |
There is less burden on
business staff with this CRM. |
|
The vendor provides CRM
upgrades at user premises. Upgrade costs are additional to the initial costs. |
Vendor performs CRM
upgrades away from the area of using it. Hence no interference in the
business work. |
Creating Proposals
The business forms a
well-structured Request for Proposal (RFP) in which it lists down the idea and
vision of CRM, the type of CRM required, process, technology, costs, time
frames, contracts, and staff issues.
The proposal is descriptive
enough to give idea to the vendor about the business structure and
requirements. The business then invites at least three and at the most six
technology vendors by sending the proposal.
Selecting Partner
When a business receives
response from various vendors, it need to select a right vendor. The business
management assesses the proposal responses on the scale of importance of issues
included in the RFP. It the shortlists the technology vendors and invites them
for demonstrating their CRM products.
Implementing the CRM Project
The business takes the following steps to −
● Chalk out the internal project plan.
● Refine the project plan with
incorporating the technology vendor.
● Identify customization needs as no
off-the-shelf CRM software can completely satisfy the CRM needs of a business.
It is done with lead developer, database developer, front-end developer, and
vendor.
● Create a prototype of the customized
software.
● Test the prototype on dummy database and
users. Test it first on the newly acquired customers rather than directly on
the customer database.
● Identify further customization and
training requirements.
● Create in-house awareness on the final
system installation.
Performance Evaluation
As a final and continual stage
for large span of time, the business evaluates how well does the CRM perform.
When a business implements new technology, the users take a large span of time
to get acquainted and comfortable with the technology.
There are two variables the business considers −
● Project outcomes − Whether or not the project went on as per
the plan without overrunning budgets, costs, and time. Is it working smoothly
and successfully?
● Business outcomes − Has the business objectives set
initially have achieved?
If the business objective was
to improve the rate of customer retention, the rate was 70% before CRM coming
to aid, and it went up to 78% after CRM implementation then the business has
achieved its objective.