
Quality Management Systems in health care organizations
International Organization for Standardization – ISO

In 1946 65 delegates from 25 countries met in London at the Institute of Civil Engineers to discuss International Standardization. In order “to facilitate the international coordination and unification of industrial standards” the decision was made to establish a new international organization. In February 1947 the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) was founded with 67 technical committees.
Today the ISO is a network of national standards institutes from more than 160 countries, each one representing various national standards organizations. The ISO is a non-governmental organization and is based in Genevia, Switzerland.
The International Organization for Standardization develops with technical experts from all over the world and in consensus with their members International Standards and publishes them. Through providing specifications for products, services and good practice businesses and industries should become more efficient and effective. By now over 19 000 International Standards have been published covering almost every aspects of technology and manufacturing (www.iso.org).
The aim of the ISO International Standards is to make “that products and services are safe, reliable and of good quality. For business, they are strategic tools that reduce costs by minimizing waste and errors and increasing productivity. They help companies to access new markets, level the playing field for developing countries and facilitate free and fair global trade.” (www.iso.org)

The ISO 9000 family is a set of International Standards which focuses on fundamental areas of a quality management system. The International Standards should help that a product or a service meets the customers’ expectations. There are many different standards in the ISO 9000 family:
» ISO 9001:2008 – defines requirements of a quality management system
» ISO 9000:2005 - describes basic concepts and language
» ISO 9004:2009 - focuses on how to improve a quality management system
» ISO 19011:2011 - sets out guidance on internal and external audits of quality management systems.
One of the most recognized International Standard is the ISO 9001:2008. This standard defines the criteria for a quality management system and is the base for a certification. The standard can be applied in any organization, regardless of its size or area of activity. Over one million organizations in over 170 countries have implemented this standard (www.iso.org).
In 2012 a new European Standard DIN EN 15224:2012 for requirements on quality management systems in health care services was published. This standard is based on EN ISO 9001:2008 but includes additional specifications for health care organizations (www.named.din.de)
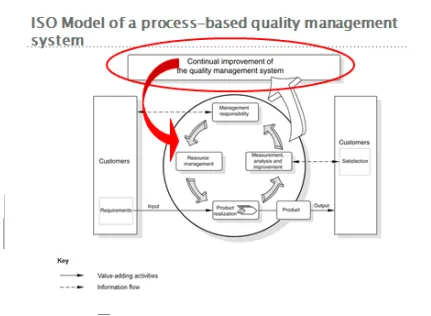
The quality management model of the ISO 9000:2008 supports a process based management approach so a quality management system can be developed, implemented and continuously improved. By meeting customers’ requirements customers’ satisfaction should increase.
All activities of an organization which transform inputs into outputs are considered as processes. Often the output of one process can be the input of the next process. The model also shows that one hand customers play a very important role when it comes to defining requirements of the inputs and on the other when it comes to defining the outputs (www.iso.org)
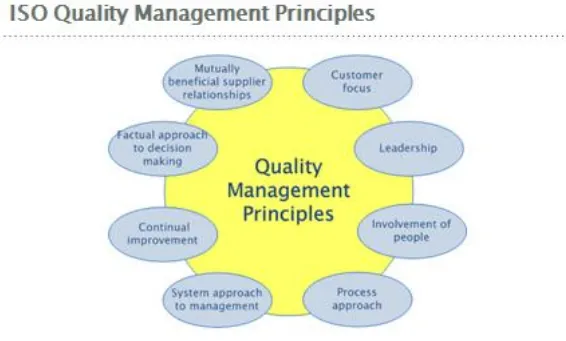
The ISO Standard is based on eight quality management principles. These principles are following (www.iso.org):
“Principle 1 – Customer focus: Organizations depend on their customers and therefore should understand current and future customer needs, should meet customer requirements and strive to exceed customer expectations.
Principle 2 – Leadership: Leaders establish unity of purpose and the direction of an organization. They should create and maintain the internal environment in which people can become fully involved in achieving the organization’s objectives.
Principle 3 – Involvement of people: People at all levels are the essence of an organization and their full involvement enables their abilities to be used for the organization’s benefit.
Principle 4 – Process approach: A desired result is achieved more efficiently when activities and related resources are managed as a process.
Principle 5 – System approach to management: Identifying, understanding and managing interrelated processes as a system contributes to the organization’s effectiveness and efficiency in achieving its objectives.
Principle 6 – Continual improvement: Continual improvement of the organization’s overall performance should be a permanent objective of the organization.
Principle 7 – Factual approach to decision making: Effective decisions are based on the analysis of data and information.
Principle 8 – Mutually beneficial supplier relationships: An organization and its suppliers are interdependent and a mutually beneficial relationship enhances the ability of both to create value.
Although a certification is not a requirement organizations often want to get certified to ISO’s management system standards .The International Organization for Standardization does not certify a organisation or issue a ISO certificate. There are registered insitutions, external accreditation bodies, which are qualified to carry out the certification. The issued certificate, which is valid for three years, proves that an organization is in conformity to the standard. The certification procedure consists of following steps:

Sometimes the two terms “certification” and “accreditation” are being used wrongly in an synonymous way, which can cause confusions. Following definition explains the difference of the terms:
