What is nested PCR?
In the nested PCR, the specificity of the PCR reaction is enhanced by reducing the non-specific binding with the help of the two sets of primer.
The specificity is the main aim of any of the PCR reaction. Every PCR modifications are mean to increase the specificity as well as the sensitivity of the reaction.
Because of this, modification in the native PCR technique is always required to achieve best results.
In the last article “what is Hot start PCR” we had discussed about the reasons of non-specific bindings. First, read that, what is hot start PCR?
Nested PCR is a simple and easy modification of conventional PCR which actually increases the specificity of any reaction.
The nested PCR is the best choice in the microbial identification and 16s RNA analysis. We will discuss it in the latter part of this article.
Two sets of primers are used to achieve high sensitivity in the nested PCR. Here both primers have different and unique properties.
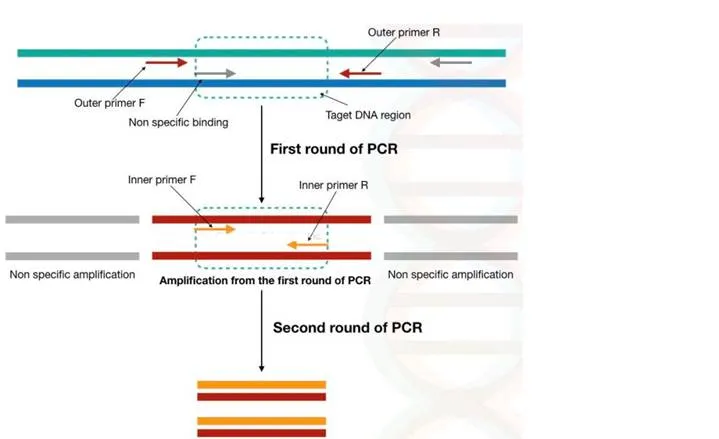
The first set of primer binds outside of our target DNA and amplifies larger fragment, this set of primer is referred to as an outer primer.
Another set of primer binds specifically at the target site and in the second round of amplification, it amplifies only the target DNA, this set of primer is referred to as an inner primer.
Here, in the nested PCR, our template DNA is the primary binding site for the outer set of primers while the amplicon of the first set of the PCR is the site for binding for the inner set of primers.
See the image below,

The set up of inner as well as an outer set of primers in nested PCR.
Interestingly, the technique does not require any additional reagent, chemical or instrumentation besides conventional PCR reactions.
Only one extra single set of primer is sufficient.
Here, the common problem with the single set of primer or conventional PCR is the early activation of Taq DNA polymerase, primer-dimer and the non-specific bindings of primer to the template DNA.
The outer set of primer:
The outer primers are primers that are upstream to the inner set of primers. The outer primers are bind to the outside to the flanking region of out target DNA.
In the first round of PCR, It is possible that this primer can bind to the site other than the target site and amplifies it. Multiple DNA bands might be observed and lead to false-positive results.
However, the magic begins with the use of the inner set of primer.
The inner set of primer:
Even if the non-specific DNA sequences can be amplified in the first round of PCR, that non-specific DNA will not be amplified in the second set of amplification.
The second set of primer is specific to the inner sequence (amplicon of the first round of PCR).
It is very unlikely that the inner set of primers binds to other than its specific site because the amplicon from the first round of PCR is the template for the second round of amplification.

In the year 1993, Kamolvarin and coworkers described the method for use of two sets of primers for increasing sensitivity and specificity of the PCR.
The nested PCR reaction is complete into two steps, a first round of amplification with the outer forward and reverse primers. The protocol is as described,
Component | Concentration | Quantity |
Master mix | 1X | 12µL |
PCR reaction buffer | 1X | 5µL |
Outer Forward primer | 10pM | 1µL |
Outer Reverse primer | 10pM | 1µL |
Template DNA | 30ng | 3µL |
Water |
| 3µL |
Total | ——————————- | 25µL |
After the reaction preparation, put the PCR as shown into the table below,
PCR Steps | Initial Denaturation | Denaturation | Annealing | Extension | Final extension |
Temperature | 90 ̊C-95 ̊C | 90 ̊C-95 ̊C | 55 ̊C-60 ̊C | 72 ̊C | 72 ̊C |
Time | 3min | 1min | 50sec | 1min | 7 min |
| ——————– | ——————- | 25 cycles | ————— | ——————— |
After the completion of the first round of amplification, take the tubes and prepare the reaction for the second round of amplification.
Now add 1µL inner forward primer and 1µL inner reverse primer to the PCR reaction tubes of the first round of amplification.
Or
We can use another method in which, 3µL of PCR product is taken from the first amplification and use it as a template, prepare the reaction as followed.
Component | Concentration | Quantity |
Master mix | 1X | 12µL |
PCR reaction buffer | 1X | 5µL |
Inner Forward primer | 10pM | 1µL |
Inner Reverse primer | 10pM | 1µL |
The amplicon from the first PCR (as a template DNA) | —————————————- | 3µL |
Water |
| 3µL |
Total | —————————————- | 25µL |
Place it back into the PCR machine.
PCR Steps | Initial Denaturation | Denaturation | Annealing | Extension | Final extension |
Temperature | 90 ̊C-95 ̊C | 90 ̊C-95 ̊C | 55 ̊C-60 ̊C | 72 ̊C | 72 ̊C |
Time | 3min | 1min | 50sec | 1min | 7 min |
| ——————– | ——————- | 35 cycles | ————— | ——————— |
Instead of 25 cycles, set the PCR at 35 cycles. Higher amplification is achieved by increasing the cycles in the second round of PCR. we can amplify more amount of gene of our interest.
· It is beneficial in studies such as phylogenetic analysis and genetic polymorphism.
· The main advantage of the present method is that it gives 100% accuracy, specificity and sensitivity.
· For the impossible templates where the GC content might be high or chance of non-specific banding is higher, nested PCR offers the best results.
· It is also useful in the amplification of genes with the low abundance.
· Further, nested PCR is the best choice for carcinoma and viral infection studies.
Yet, due to several limitations, the nested PCR is not the first choice for many reactions.
· The method is time-consuming.
· Required more reagents such as an extra set of primer and one extra round of agarose gel electrophoresis. Which means the method is quite costly.
· The chance of contamination is also higher.