Membrane Proteins
Phospholipid bilayers are embedded with proteins, which may be either permanently or temporarily attached to the membrane
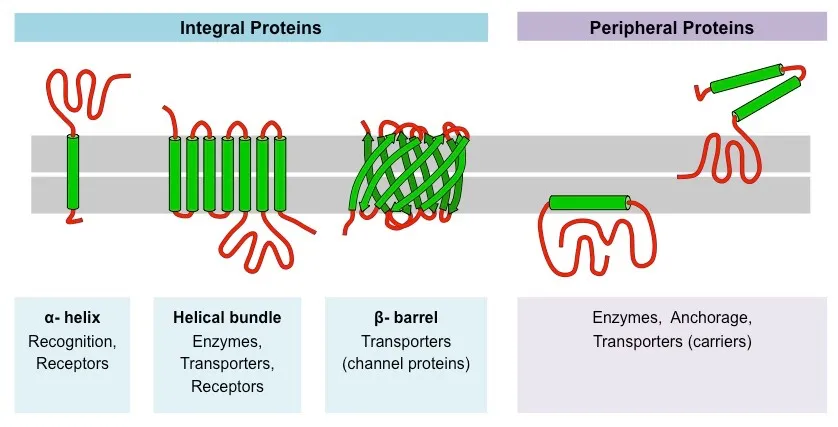
§ Integral proteins are permanently attached to the membrane and are typically transmembrane (they span across the bilayer)
§ Peripheral proteins are temporarily attached by non-covalent interactions and associate with one surface of the membrane

Structure of Membrane Proteins
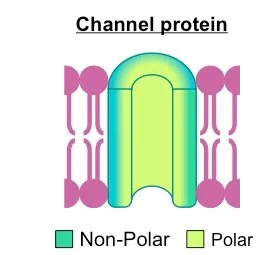
The amino acids of a membrane protein are localised according to polarity:
§ Non-polar (hydrophobic) amino acids associate directly with the lipid bilayer
§ Polar (hydrophilic) amino acids are located internally and face aqueous solutions
Transmembrane proteins typically adopt one of two tertiary structures:
§ Single helices / helical bundles
§ Beta barrels (common in channel proteins)
Membrane Protein Structures

Functions of Membrane Proteins
Membrane proteins can serve a variety of key functions:
§ Junctions – Serve to connect and join two cells together
§ Enzymes – Fixing to membranes localises metabolic pathways
§ Transport – Responsible for facilitated diffusion and active transport
§ Recognition – May function as markers for cellular identification
§ Anchorage – Attachment points for cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix
§ Transduction – Function as receptors for peptide hormones