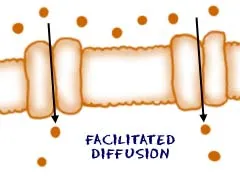
Passive Transport

Letting Concentration Do the Work
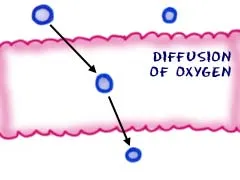
Sometimes cells are in an area where there is a large concentration difference. For example, oxygen molecule concentrations could be very high outside of the cell and very low inside. Those oxygen molecules are so small that they are able to cross the lipid bilayer and enter the cell. There is no energy needed for this process. In this case, it's good for the cell because cells need oxygen to survive. It can also happen with other molecules that can kill a cell.

Osmosis
Another big example of passive transport is osmosis. This is a water specific process. Usually, cells are in an environment where there is one concentration of ions outside and one inside. Because concentrations like to be the same, the cell can pump ions in an out to stay alive. Osmosis is the movement of water across the membrane.
For a cell to survive, ion concentrations need to be the same on both sides of the cell membrane. If the cell does not pump out all of its extra ions to even out the concentrations, the water is going to move in. This can be very bad. The cell can swell up and explode. The classic example of this type of swelling happens when red blood cells are placed in water. The water rushes in to the cells, they expand and eventually rupture (POP!).