Transition state
The transition state of a chemical reaction is a particular configuration along the reaction coordinate. It is defined as the state corresponding to the highest potential energy along this reaction coordinate.[1] It is often marked with the double dagger ‡ symbol.
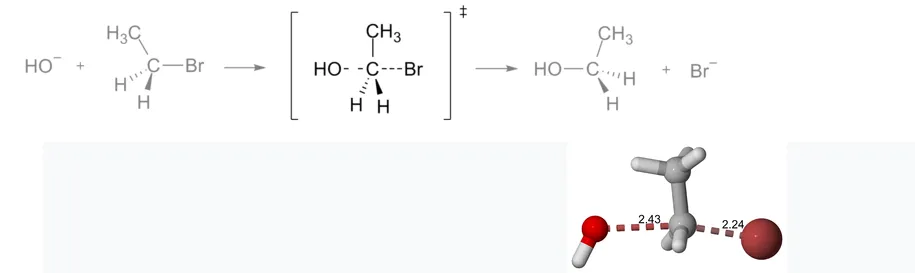
As an example, the transition state shown below occurs during the SN2 reaction of bromoethane with a hydroxyl anion:

The DFT-determined geometry for the transition state of the above reaction. Distances are listed in angstroms. Note the elongated C-Br and C-O bonds, and the trigonal bipyramidal structure.
The activated complex of a reaction can refer to either the transition state or to other states along the reaction coordinate between reactants and products, especially those close to the transition state.
According to the transition state theory, once the reactants have passed through the transition state configuration, they always continue to form products
Observing transition states
Because of the rules of quantum mechanics, the transition state cannot be captured or directly observed; the population at that point is zero[citation needed][further explanation needed]. This is sometimes expressed by stating that the transition state has a fleeting existence. However, cleverly manipulated spectroscopic techniques can get us as close as the timescale of the technique allows. Femtochemical IR spectroscopy was developed for that reason, and it is possible to probe molecular structure extremely close to the transition point. Often, along the reaction coordinate, reactive intermediates are present not much lower in energy from a transition state making it difficult to distinguish between the two.
Determining the geometry of a transition state
Transition state structures can be determined by searching for first-order saddle points on the potential energy surface (PES) of the chemical species of interest.[4] A first-order saddle point is a critical point of index one, that is, a position on the PES corresponding to a minimum in all directions except one. This is further described in the article geometry optimization.
The Hammond–Leffler postulate
The Hammond–Leffler postulate states that the structure of the transition state more closely resembles either the products or the starting material, depending on which is higher in enthalpy. A transition state that resembles the reactants more than the products is said to be early, while a transition state that resembles the products more than the reactants is said to be late. Thus, the Hammond–Leffler Postulate predicts a late transition state for an endothermic reaction and an early transition state for an exothermic reaction.
A dimensionless reaction coordinate that quantifies the lateness of a transition state can be used to test the validity of the Hammond–Leffler postulate for a particular reaction.[5]
The structure–correlation principle
The structure–correlation principle states that structural changes that occur along the reaction coordinate can reveal themselves in the ground state as deviations of bond distances and angles from normal values along the reaction coordinate.[6] According to this theory if one particular bond length on reaching the transition state increases then this bond is already longer in its ground state compared to a compound not sharing this transition state. One demonstration of this principle is found in the two bicyclic compounds depicted below.[7] The one on the left is a bicyclo[2.2.2]octene, which, at 200 °C, extrudes ethylene in a retro-Diels–Alder reaction.
Compared to the compound on the right (which, lacking an alkene group, is unable to give this reaction) the bridgehead carbon-carbon bond length is expected to be shorter if the theory holds, because on approaching the transition state this bond gains double bond character. For these two compounds the prediction holds up based on X-ray crystallography.
One way that enzymatic catalysis proceeds is by stabilizing the transition state through electrostatics. By lowering the energy of the transition state, it allows a greater population of the starting material to attain the energy needed to overcome the transition energy and proceed to product.