
Structure of DNA
Primary structure and its double helix: Sequence in which four nitrogen bases are attached to the sugar phosphate backbone of a nucleotide chain is called primary structure.

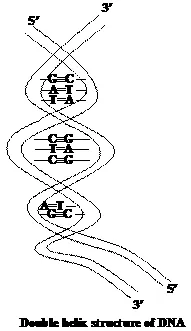
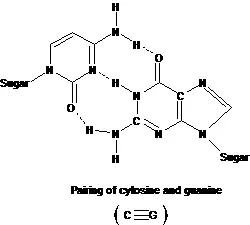
Watson and crick in 1953 proposed that DNA polymers form a duplex structure consisting of two strands of polynucleotide chain coiled around each other in the form of a double helix. Bases of one strand of DNA are paired with bases on the other strand by means of hydrogen bonding. According to Chargaff rule – Thymine and adenine can be joined by 2 hydrogen bonds (T = A) while cytosine and guanine can be joined by three hydrogen bonds

Structure of RNA is similar to DNA except that it is a single strand structure