Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The human circulatory system has a complex network of blood vessels that reach all parts of the body. This extensive network supplies the cells, tissues, and organs with oxygen and nutrients, and removes carbon dioxide and waste compounds.
The medium for transport of gases and other molecules is the blood, which continually circulates through the system. Pressure differences within the system cause the movement of the blood and are created by the pumping of the heart.
Gas exchange between tissues and the blood is an essential function of the circulatory system. In humans, other mammals, and birds, blood absorbs oxygen and releases carbon dioxide in the lungs. Thus the circulatory and respiratory system, whose function is to obtain oxygen and discharge carbon dioxide, work in tandem.
The Respiratory System (Basic level)
Take a breath in and hold it. Wait several seconds and then let it out. Humans, when they are not exerting themselves, breathe approximately 15 times per minute on average. This equates to about 900 breaths an hour or 21,600 breaths per day. With every inhalation, air fills the lungs, and with every exhalation, it rushes back out. That air is doing more than just inflating and deflating the lungs in the chest cavity. The air contains oxygen that crosses the lung tissue, enters the bloodstream, and travels to organs and tissues. There, oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide, which is a cellular waste material. Carbon dioxide exits the cells, enters the bloodstream, travels back to the lungs, and is expired out of the body during exhalation.
Breathing is both a voluntary and an involuntary event. How often a breath is taken and how much air is inhaled or exhaled is regulated by the respiratory center in the brain in response to signals it receives about the carbon dioxide content of the blood. However, it is possible to override this automatic regulation for activities such as speaking, singing and swimming under water.
During inhalation the diaphragm descends creating a negative pressure around the lungs and they begin to inflate, drawing in air from outside the body. The air enters the body through the nasal cavity located just inside the nose (Figure 11.9). As the air passes through the nasal cavity, the air is warmed to body temperature and humidified by moisture from mucous membranes. These processes help equilibrate the air to the body conditions, reducing any damage that cold, dry air can cause. Particulate matter that is floating in the air is removed in the nasal passages by hairs, mucus, and cilia. Air is also chemically sampled by the sense of smell.
From the nasal cavity, air passes through the pharynx (throat) and the larynx (voice box) as it makes its way to the trachea (Figure 11.9). The main function of the trachea is to funnel the inhaled air to the lungs and the exhaled air back out of the body. The human trachea is a cylinder, about 25 to 30 cm (9.8–11.8 in) long, which sits in front of the esophagus and extends from the pharynx into the chest cavity to the lungs. It is made of incomplete rings of cartilage and smooth muscle. The cartilage provides strength and support to the trachea to keep the passage open. The trachea is lined with cells that have cilia and secrete mucus. The mucus catches particles that have been inhaled, and the cilia move the particles toward the pharynx.
The end of the trachea divides into two bronchi that enter the right and left lung. Air enters the lungs through the primary bronchi. The primary bronchus divides, creating smaller and smaller diameter bronchi until the passages are under 1 mm (.03 in) in diameter when they are called bronchioles as they split and spread through the lung. Like the trachea, the bronchus and bronchioles are made of cartilage and smooth muscle. Bronchi are innervated by nerves of both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems that control muscle contraction (parasympathetic) or relaxation (sympathetic) in the bronchi and bronchioles, depending on the nervous system’s cues. The final bronchioles are the respiratory bronchioles. Alveolar ducts are attached to the end of each respiratory bronchiole. At the end of each duct are alveolar sacs, each containing 20 to 30 alveoli. Gas exchange occurs only in the alveoli. The alveoli are thin-walled and look like tiny bubbles within the sacs. The alveoli are in direct contact with capillaries of the circulatory system. Such intimate contact ensures that oxygen will diffuse from the alveoli into the blood. In addition, carbon dioxide will diffuse from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled. The anatomical arrangement of capillaries and alveoli emphasizes the structural and functional relationship of the respiratory and circulatory systems. Estimates for the surface area of alveoli in the lungs vary around 100 m2. This large area is about the area of half a tennis court. This large surface area, combined with the thin-walled nature of the alveolar cells, allows gases to easily diffuse across the cells.
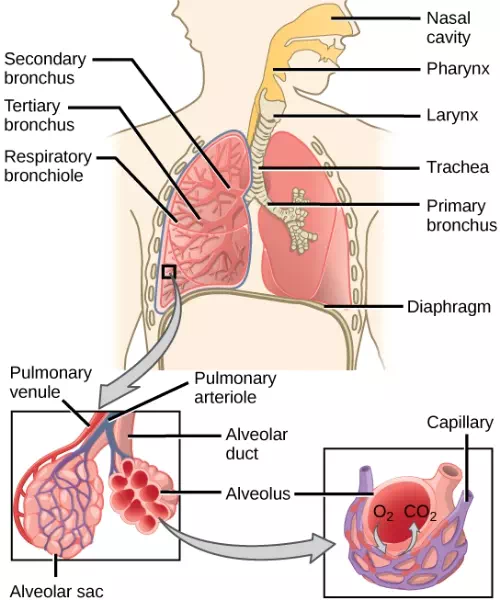
Figure 11.9 Air enters the respiratory system through the nasal cavity, and then passes through the pharynx and the trachea into the lungs. (credit: modification of work by NCI)
Systems of Gas Exchange
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
· Describe the passage of air from the outside environment to the lungs
· Explain how the lungs are protected from particulate matter
The primary function of the respiratory system is to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body’s tissues and remove carbon dioxide, a cell waste product. The main structures of the human respiratory system are the nasal cavity, the trachea, and lungs.
All aerobic organisms require oxygen to carry out their metabolic functions. Along the evolutionary tree, different organisms have devised different means of obtaining oxygen from the surrounding atmosphere. The environment in which the animal lives greatly determines how an animal respires. The complexity of the respiratory system is correlated with the size of the organism. As animal size increases, diffusion distances increase and the ratio of surface area to volume drops. In unicellular organisms, diffusion across the cell membrane is sufficient for supplying oxygen to the cell (Figure 11.10). Diffusion is a slow, passive transport process. In order for diffusion to be a feasible means of providing oxygen to the cell, the rate of oxygen uptake must match the rate of diffusion across the membrane. In other words, if the cell were very large or thick, diffusion would not be able to provide oxygen quickly enough to the inside of the cell. Therefore, dependence on diffusion as a means of obtaining oxygen and removing carbon dioxide remains feasible only for small organisms or those with highly-flattened bodies, such as many flatworms (Platyhelminthes). Larger organisms had to evolve specialized respiratory tissues, such as gills, lungs, and respiratory passages accompanied by a complex circulatory systems, to transport oxygen throughout their entire body.

Figure 11.10 The cell of the unicellular algae Ventricaria ventricosa is one of the largest known, reaching one to five centimeters in diameter. Like all single-celled organisms, V. ventricosa exchanges gases across the cell membrane.
Direct Diffusion
For small multicellular organisms, diffusion across the outer membrane is sufficient to meet their oxygen needs. Gas exchange by direct diffusion across surface membranes is efficient for organisms less than 1 mm in diameter. In simple organisms, such as cnidarians and flatworms, every cell in the body is close to the external environment. Their cells are kept moist and gases diffuse quickly via direct diffusion. Flatworms are small, literally flat worms, which ‘breathe’ through diffusion across the outer membrane (Figure 11.11). The flat shape of these organisms increases the surface area for diffusion, ensuring that each cell within the body is close to the outer membrane surface and has access to oxygen. If the flatworm had a cylindrical body, then the cells in the center would not be able to get oxygen.

Figure 11.11. This flatworm’s process of respiration works by diffusion across the outer membrane. (credit: Stephen Childs)
Skin and Gills
Earthworms and amphibians use their skin (integument) as a respiratory organ. A dense network of capillaries lies just below the skin and facilitates gas exchange between the external environment and the circulatory system. The respiratory surface must be kept moist in order for the gases to dissolve and diffuse across cell membranes.
Organisms that live in water need to obtain oxygen from the water. Oxygen dissolves in water but at a lower concentration than in the atmosphere. The atmosphere has roughly 21 percent oxygen. In water, the oxygen concentration is much smaller than that. Fish and many other aquatic organisms have evolved gills to take up the dissolved oxygen from water (Figure 11.12). Gills are thin tissue filaments that are highly branched and folded. When water passes over the gills, the dissolved oxygen in water rapidly diffuses across the gills into the bloodstream. The circulatory system can then carry the oxygenated blood to the other parts of the body. In animals that contain coelomic fluid instead of blood, oxygen diffuses across the gill surfaces into the coelomic fluid. Gills are found in mollusks, annelids, and crustaceans.

Figure 11.12
This common carp, like many other aquatic organisms, has gills that allow it to
obtain oxygen from water. (credit: “Guitardude012″/Wikimedia Commons)
The folded surfaces of the gills provide a large surface area to ensure that the fish gets sufficient oxygen. Diffusion is a process in which material travels from regions of high concentration to low concentration until equilibrium is reached. In this case, blood with a low concentration of oxygen molecules circulates through the gills. The concentration of oxygen molecules in water is higher than the concentration of oxygen molecules in gills. As a result, oxygen molecules diffuse from water (high concentration) to blood (low concentration), as shown in Figure 11.13. Similarly, carbon dioxide molecules in the blood diffuse from the blood (high concentration) to water (low concentration).
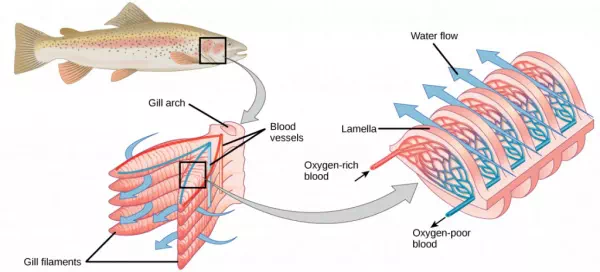
Figure 11.13. As water flows over the gills, oxygen is transferred to blood via the veins. (credit “fish”: modification of work by Duane Raver, NOAA)
Tracheal Systems
Insect respiration is independent of its circulatory system; therefore, the blood does not play a direct role in oxygen transport. Insects have a highly specialized type of respiratory system called the tracheal system, which consists of a network of small tubes that carries oxygen to the entire body. The tracheal system is the most direct and efficient respiratory system in active animals. The tubes in the tracheal system are made of a polymeric material called chitin.
Insect bodies have openings, called spiracles, along the thorax and abdomen. These openings connect to the tubular network, allowing oxygen to pass into the body (Figure 11.14) and regulating the diffusion of CO2 and water vapor. Air enters and leaves the tracheal system through the spiracles. Some insects can ventilate the tracheal system with body movements.
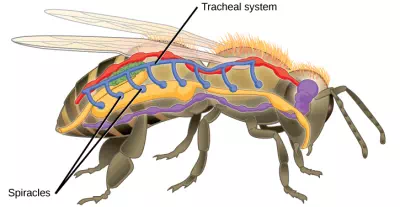
Figure 11.14. Insects perform respiration via a tracheal system.
Mammalian Systems
In mammals, pulmonary ventilation occurs via inhalation (breathing). During inhalation, air enters the body through thenasal cavity located just inside the nose (Figure 11.15). As air passes through the nasal cavity, the air is warmed to body temperature and humidified. The respiratory tract is coated with mucus to seal the tissues from direct contact with air. Mucus is high in water. As air crosses these surfaces of the mucous membranes, it picks up water. These processes help equilibrate the air to the body conditions, reducing any damage that cold, dry air can cause. Particulate matter that is floating in the air is removed in the nasal passages via mucus and cilia. The processes of warming, humidifying, and removing particles are important protective mechanisms that prevent damage to the trachea and lungs. Thus, inhalation serves several purposes in addition to bringing oxygen into the respiratory system.
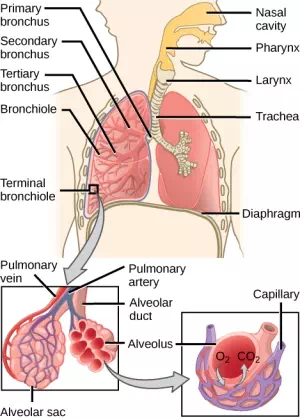
Figure 11.15. Air enters the respiratory system through the nasal cavity and pharynx, and then passes through the trachea and into the bronchi, which bring air into the lungs. (credit: modification of work by NCI)
Which of the following statements about the mammalian respiratory system is false?
1. When we breathe in, air travels from the pharynx to the trachea.
2. The bronchioles branch into bronchi.
3. Alveolar ducts connect to alveolar sacs.
4. Gas exchange between the lung and blood takes place in the alveolus.
From the nasal cavity, air passes through the pharynx (throat) and the larynx (voice box), as it makes its way to thetrachea (Figure 11.16). The main function of the trachea is to funnel the inhaled air to the lungs and the exhaled air back out of the body. The human trachea is a cylinder about 10 to 12 cm long and 2 cm in diameter that sits in front of the esophagus and extends from the larynx into the chest cavity where it divides into the two primary bronchi at the midthorax. It is made of incomplete rings of hyaline cartilage and smooth muscle (Figure 11.17). The trachea is lined with mucus-producing goblet cells and ciliated epithelia. The cilia propel foreign particles trapped in the mucus toward the pharynx. The cartilage provides strength and support to the trachea to keep the passage open. The smooth muscle can contract, decreasing the trachea’s diameter, which causes expired air to rush upwards from the lungs at a great force. The forced exhalation helps expel mucus when we cough. Smooth muscle can contract or relax, depending on stimuli from the external environment or the body’s nervous system.
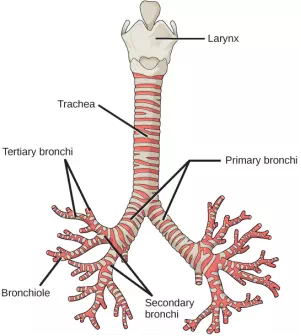
Figure 11.16.
The trachea and bronchi are made of incomplete rings of cartilage. (credit:
modification of work by Gray’s Anatomy)
Lungs: Bronchi and Alveoli
The end of the trachea bifurcates (divides) to the right and left lungs. The lungs are not identical. The right lung is larger and contains three lobes, whereas the smaller left lung contains two lobes (Figure 11.17). The muscular diaphragm, which facilitates breathing, is inferior (below) to the lungs and marks the end of the thoracic cavity.
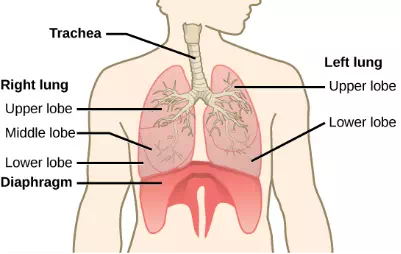
Figure 11.17. The trachea bifurcates into the right and left bronchi in the lungs. The right lung is made of three lobes and is larger. To accommodate the heart, the left lung is smaller and has only two lobes.
In the lungs, air is diverted into smaller and smaller passages, or bronchi. Air enters the lungs through the twoprimary (main) bronchi (singular: bronchus). Each bronchus divides into secondary bronchi, then into tertiary bronchi, which in turn divide, creating smaller and smaller diameter bronchioles as they split and spread through the lung. Like the trachea, the bronchi are made of cartilage and smooth muscle. At the bronchioles, the cartilage is replaced with elastic fibers. Bronchi are innervated by nerves of both the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems that control muscle contraction (parasympathetic) or relaxation (sympathetic) in the bronchi and bronchioles, depending on the nervous system’s cues. In humans, bronchioles with a diameter smaller than 0.5 mm are the respiratory bronchioles. They lack cartilage and therefore rely on inhaled air to support their shape. As the passageways decrease in diameter, the relative amount of smooth muscle increases.
The terminal bronchioles subdivide into microscopic branches called respiratory bronchioles. The respiratory bronchioles subdivide into several alveolar ducts. Numerous alveoli and alveolar sacs surround the alveolar ducts. The alveolar sacs resemble bunches of grapes tethered to the end of the bronchioles (Figure 11.18). In the acinar region, thealveolar ducts are attached to the end of each bronchiole. At the end of each duct are approximately 100 alveolar sacs, each containing 20 to 30 alveoli that are 200 to 300 microns in diameter. Gas exchange occurs only in alveoli. Alveoli are made of thin-walled parenchymal cells, typically one-cell thick, that look like tiny bubbles within the sacs. Alveoli are in direct contact with capillaries (one-cell thick) of the circulatory system. Such intimate contact ensures that oxygen will diffuse from alveoli into the blood and be distributed to the cells of the body. In addition, the carbon dioxide that was produced by cells as a waste product will diffuse from the blood into alveoli to be exhaled. The anatomical arrangement of capillaries and alveoli emphasizes the structural and functional relationship of the respiratory and circulatory systems. Because there are so many alveoli (~300 million per lung) within each alveolar sac and so many sacs at the end of each alveolar duct, the lungs have a sponge-like consistency. This organization produces a very large surface area that is available for gas exchange. The surface area of alveoli in the lungs is approximately 75 m2. This large surface area, combined with the thin-walled nature of the alveolar parenchymal cells, allows gases to easily diffuse across the cells.
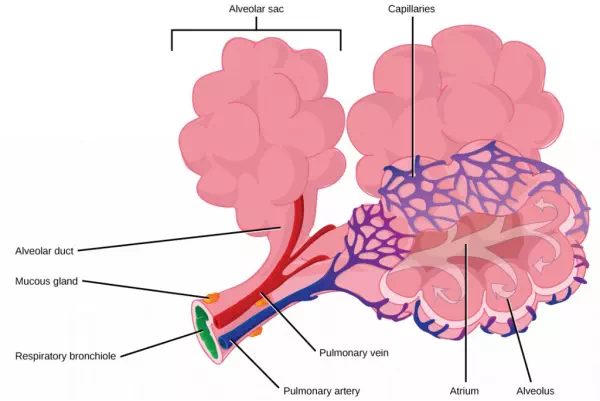
Figure 11.18.
Terminal bronchioles are connected by respiratory bronchioles to alveolar ducts
and alveolar sacs. Each alveolar sac contains 20 to 30 spherical alveoli and
has the appearance of a bunch of grapes. Air flows into the atrium of the
alveolar sac, then circulates into alveoli where gas exchange occurs with the
capillaries. Mucous glands secrete mucous into the airways, keeping them moist
and flexible. (credit: modification of work by Mariana Ruiz Villareal)
Protective Mechanisms
The air that organisms breathe contains particulate matter such as dust, dirt, viral particles, and bacteria that can damage the lungs or trigger allergic immune responses. The respiratory system contains several protective mechanisms to avoid problems or tissue damage. In the nasal cavity, hairs and mucus trap small particles, viruses, bacteria, dust, and dirt to prevent their entry.
If particulates do make it beyond the nose, or enter through the mouth, the bronchi and bronchioles of the lungs also contain several protective devices. The lungs produce mucus—a sticky substance made of mucin, a complex glycoprotein, as well as salts and water—that traps particulates. The bronchi and bronchioles contain cilia, small hair-like projections that line the walls of the bronchi and bronchioles (Figure 11.19). These cilia beat in unison and move mucus and particles out of the bronchi and bronchioles back up to the throat where it is swallowed and eliminated via the esophagus.
In humans, for example, tar and other substances in cigarette smoke destroy or paralyze the cilia, making the removal of particles more difficult. In addition, smoking causes the lungs to produce more mucus, which the damaged cilia are not able to move. This causes a persistent cough, as the lungs try to rid themselves of particulate matter, and makes smokers more susceptible to respiratory ailments.
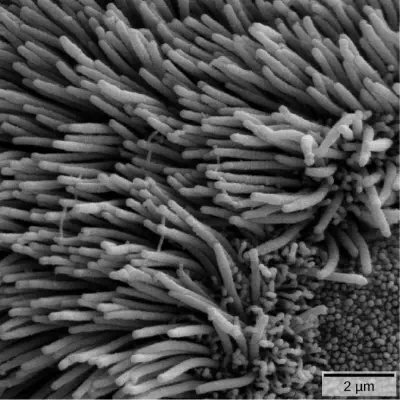
Figure 11.19.
The bronchi and bronchioles contain cilia that help move mucus and other
particles out of the lungs. (credit: Louisa Howard, modification of work by Dartmouth
Electron Microscope Facility)
Animal respiratory systems are designed to facilitate gas exchange. In mammals, air is warmed and humidified in the nasal cavity. Air then travels down the pharynx, through the trachea, and into the lungs. In the lungs, air passes through the branching bronchi, reaching the respiratory bronchioles, which house the first site of gas exchange. The respiratory bronchioles open into the alveolar ducts, alveolar sacs, and alveoli. Because there are so many alveoli and alveolar sacs in the lung, the surface area for gas exchange is very large. Several protective mechanisms are in place to prevent damage or infection. These include the hair and mucus in the nasal cavity that trap dust, dirt, and other particulate matter before they can enter the system. In the lungs, particles are trapped in a mucus layer and transported via cilia up to the esophageal opening at the top of the trachea to be swallowed.
Which of the following statements about the human respiratory system is false?
A) When we breathe in, air travels from the pharynx to the trachea.
B) The bronchioles branch into bronchi.
C) Alveolar ducts connect to alveolar sacs.
D) Gas exchange between the lungs and blood takes place in the alveolus.