Excretory System
The human excretory system functions to remove waste from the body through the skin as sweat, the lungs in the form of exhaled carbon dioxide, and through the urinary system in the form of urine. All three of these systems participate in osmoregulation and waste removal. Here we focus on the urinary system, which is comprised of the paired kidneys, the ureter, urinary bladder and urethra (Figure 11.3). The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped structures that are located just below the liver in the body cavity. Each of the kidneys contains more than a million tiny units called nephrons that filter blood containing the metabolic wastes from cells. All the blood in the human body is filtered about 60 times a day by the kidneys. The nephrons remove wastes, concentrate them, and form urine that is collected in the bladder.
Internally, the kidney has three regions—an outer cortex, a medulla in the middle, and the renal pelvis, which is the expanded end of the ureter. The renal cortex contains the nephrons—the functional unit of the kidney. The renal pelvis collects the urine and leads to the ureter on the outside of the kidney. The ureters are urine-bearing tubes that exit the kidney and empty into the urinary bladder.
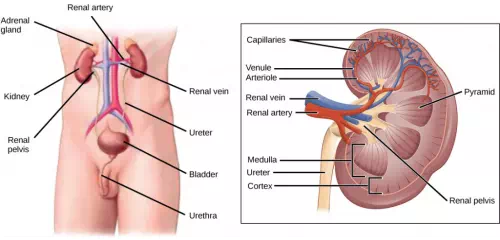
Figure 11.3 The human excretory system is made up of the kidneys, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. The kidneys filter blood and form urine, which is stored in the bladder until it is eliminated through the urethra. On the right, the internal structure of the kidney is shown. (credit: modification of work by NCI, NIH)
Blood enters each kidney from the aorta, the main artery supplying the body below the heart, through a renal artery. It is distributed in smaller vessels until it reaches each nephron in capillaries. Within the nephron the blood comes in intimate contact with the waste-collecting tubules in a structure called the glomerulus. Water and many solutes present in the blood, including ions of sodium, calcium, magnesium, and others; as well as wastes and valuable substances such as amino acids, glucose and vitamins, leave the blood and enter the tubule system of the nephron. As materials pass through the tubule much of the water, required ions, and useful compounds are reabsorbed back into the capillaries that surround the tubules leaving the wastes behind. Some of this reabsorption requires active transport and consumes ATP. Some wastes, including ions and some drugs remaining in the blood, diffuse out of the capillaries into the interstitial fluid and are taken up by the tubule cells. These wastes are then actively secreted into the tubules. The blood then collects in larger and larger vessels and leaves the kidney in the renal vein. The renal veinjoins the inferior vena cava, the main vein that returns blood to the heart from the lower body. The amounts of water and ions reabsorbed into the circulatory system are carefully regulated and this is an important way the body regulates its water content and ion levels. The waste is collected in larger tubules and then leaves the kidney in the ureter, which leads to the bladder where urine, the combination of waste materials and water, is stored.
The bladder contains sensory nerves, stretch receptors that signal when it needs to be emptied. These signals create the urge to urinate, which can be voluntarily suppressed up to a limit. The conscious decision to urinate sets in play signals that open the sphincters, rings of smooth muscle that close off the opening, to the urethra that allows urine to flow out of the bladder and the body.
Dialysis Technician
Dialysis is a medical process of removing wastes and excess water from the blood by diffusion and ultrafiltration. When kidney function fails, dialysis must be done to artificially rid the body of wastes and fluids. This is a vital process to keep patients alive. In some cases, the patients undergo artificial dialysis until they are eligible for a kidney transplant. In others who are not candidates for kidney transplants, dialysis is a lifelong necessity.
Dialysis technicians typically work in hospitals and clinics. While some roles in this field include equipment development and maintenance, most dialysis technicians work in direct patient care. Their on-the-job duties, which typically occur under the direct supervision of a registered nurse, focus on providing dialysis treatments. This can include reviewing patient history and current condition, assessing and responding to patient needs before and during treatment, and monitoring the dialysis process. Treatment may include taking and reporting a patient’s vital signs, preparing solutions and equipment to ensure accurate and sterile procedures.
Homeostasis is a dynamic equilibrium that is maintained in body tissues and organs. It is dynamic because it is constantly adjusting to the changes that the systems encounter. It is an equilibrium because body functions are kept within a normal range, with some fluctuations around a set point. The kidneys are the main osmoregulatory organs in mammalian systems; they function to filter blood and maintain the dissolved ion concentrations of body fluids. They are made up internally of three distinct regions—the cortex, medulla, and pelvis. The blood vessels that transport blood into and out of the kidneys arise from and merge with the aorta and inferior vena cava, respectively. The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, which actively filters blood and generates urine. The urine leaves the kidney through the ureter and is stored in the urinary bladder. Urine is voided from the body through the urethra.