Photosynthesis
The shared evolutionary history of all photosynthetic organisms is conspicuous, as the basic process has changed little over eras of time. Even between the giant tropical leaves in the rainforest and tiny cyanobacteria, the process and components of photosynthesis that use water as an electron donor remain largely the same. Photosystems function to absorb light and use electron transport chains to convert energy. The Calvin cycle reactions assemble carbohydrate molecules with this energy.
However, as with all biochemical pathways, a variety of conditions leads to varied adaptations that affect the basic pattern. Photosynthesis in dry-climate plants (Figure 5.16) has evolved with adaptations that conserve water. In the harsh dry heat, every drop of water and precious energy must be used to survive. Two adaptations have evolved in such plants. In one form, a more efficient use of CO2 allows plants to photosynthesize even when CO2 is in short supply, as when the stomata are closed on hot days. The other adaptation performs preliminary reactions of the Calvin cycle at night, because opening the stomata at this time conserves water due to cooler temperatures. In addition, this adaptation has allowed plants to carry out low levels of photosynthesis without opening stomata at all, an extreme mechanism to face extremely dry periods.

Figure 5.16 Living in the harsh conditions of the desert has led plants like this cactus to evolve variations in reactions outside the Calvin cycle. These variations increase efficiency and help conserve water and energy. (credit: Piotr Wojtkowski)
Photosynthesis in Prokaryotes
The two parts of photosynthesis—the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle—have been described, as they take place in chloroplasts. However, prokaryotes, such as cyanobacteria, lack membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic photosynthetic autotrophic organisms have infoldings of the plasma membrane for chlorophyll attachment and photosynthesis (Figure 5.17). It is here that organisms like cyanobacteria can carry out photosynthesis.
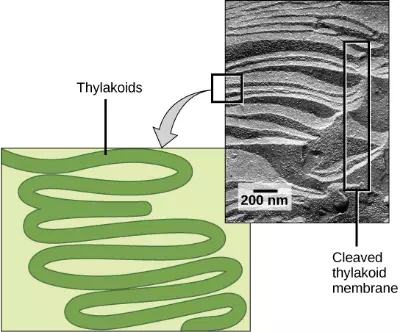
Figure 5.17 A photosynthetic prokaryote has infolded regions of the plasma membrane that function like thylakoids. Although these are not contained in an organelle, such as a chloroplast, all of the necessary components are present to carry out photosynthesis. (credit: scale-bar data from Matt Russell)
The Energy Cycle
Living things access energy by breaking down carbohydrate molecules. However, if plants make carbohydrate molecules, why would they need to break them down? Carbohydrates are storage molecules for energy in all living things. Although energy can be stored in molecules like ATP, carbohydrates are much more stable and efficient reservoirs for chemical energy. Photosynthetic organisms also carry out the reactions of respiration to harvest the energy that they have stored in carbohydrates, for example, plants have mitochondria in addition to chloroplasts.
You may have noticed that the overall reaction for photosynthesis:
6CO2+6H2O→C612O6+6O26CO2+6H2O→C6H12O6+6O
is the reverse of the overall reaction for cellular respiration:
6O2+C6H12O6→6CO2+6H2O6O2+C6H12O6→6CO2+6H2O
Photosynthesis produces oxygen as a byproduct, and respiration produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct.
In nature, there is no such thing as waste. Every single atom of matter is conserved, recycling indefinitely. Substances change form or move from one type of molecule to another, but never disappear (Figure 5.18).
CO2 is no more a form of waste produced by respiration than oxygen is a waste product of photosynthesis. Both are byproducts of reactions that move on to other reactions. Photosynthesis absorbs energy to build carbohydrates in chloroplasts, and aerobic cellular respiration releases energy by using oxygen to break down carbohydrates. Both organelles use electron transport chains to generate the energy necessary to drive other reactions. Photosynthesis and cellular respiration function in a biological cycle, allowing organisms to access life-sustaining energy that originates millions of miles away in a star.
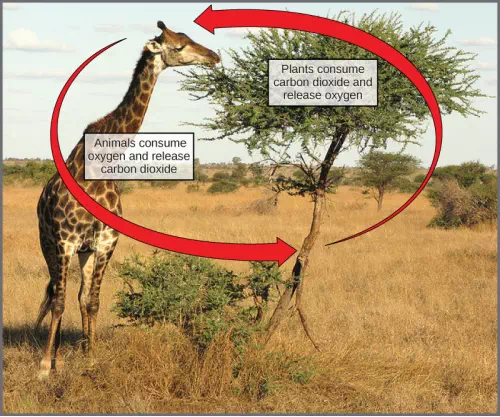
Figure 5.18 In the carbon cycle, the reactions of photosynthesis and cellular respiration share reciprocal reactants and products. (credit: modification of work by Stuart Bassil)
Summary
Using the energy carriers formed in the first stage of photosynthesis, the Calvin cycle reactions fix CO2 from the environment to build carbohydrate molecules. An enzyme, RuBisCO, catalyzes the fixation reaction, by combining CO2 with RuBP. The resulting six-carbon compound is broken down into two three-carbon compounds, and the energy in ATP and NADPH is used to convert these molecules into G3P. One of the three-carbon molecules of G3P leaves the cycle to become a part of a carbohydrate molecule. The remaining G3P molecules stay in the cycle to be formed back into RuBP, which is ready to react with more CO2. Photosynthesis forms a balanced energy cycle with the process of cellular respiration. Plants are capable of both photosynthesis and cellular respiration, since they contain both chloroplasts and mitochondria.