Immunological Memory
The adaptive immune system has a memory component that allows for a rapid and large response upon reinvasion of the same pathogen. During the adaptive immune response to a pathogen that has not been encountered before, known as the primary immune response, plasma cells secreting antibodies and differentiated T cells increase, then plateau over time. As B and T cells mature into effector cells, a subset of the naïve populations differentiates into B and T memory cells with the same antigen specificities (Figure 12.17). A memory cell is an antigen-specific B or T lymphocyte that does not differentiate into an effector cell during the primary immune response, but that can immediately become an effector cell on reexposure to the same pathogen. As the infection is cleared and pathogenic stimuli subside, the effectors are no longer needed and they undergo apoptosis. In contrast, the memory cells persist in the circulation.
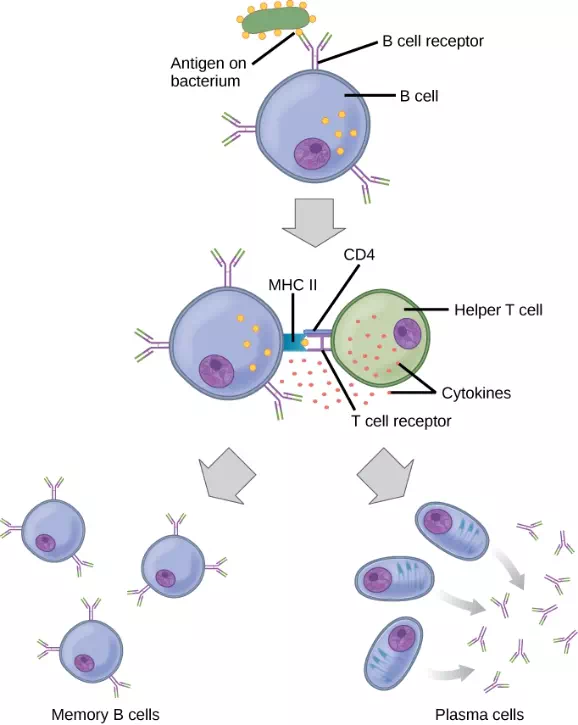
Figure 12.17 After initially binding an antigen to the B cell receptor, a B cell internalizes the antigen and presents it on MHC class II. A helper T cell recognizes the MHC class II- antigen complex and activates the B cell. As a result, memory B cells and plasma cells are made.
The Rh antigen is found on Rh-positive red blood cells. An Rh-negative female can usually carry an Rh-positive fetus to term without difficulty. However, if she has a second Rh-positive fetus, her body may launch an immune attack that causes hemolytic disease of the newborn. Why do you think hemolytic disease is only a problem during the second or subsequent pregnancies?
<!– If the blood of the mother and fetus mixes, memory cells that recognize the Rh antigen of the fetus can form in the mother late in the first pregnancy. During subsequent pregnancies, these memory cells launch an immune attack on the fetal blood cells of an Rh-positive fetus. Injection of anti-Rh antibody during the first pregnancy prevents the immune response from occurring.–>
If the pathogen is never encountered again during the individual’s lifetime, B and T memory cells will circulate for a few years or even several decades and will gradually die off, having never functioned as effector cells. However, if the host is re-exposed to the same pathogen type, circulating memory cells will immediately differentiate into plasma cells and TC cells without input from APCs or TH cells. This is known as the secondary immune response. One reason why the adaptive immune response is delayed is because it takes time for naïve B and T cells with the appropriate antigen specificities to be identified, activated, and proliferate. On reinfection, this step is skipped, and the result is a more rapid production of immune defenses. Memory B cells that differentiate into plasma cells output tens to hundreds-fold greater antibody amounts than were secreted during the primary response (Figure 12.18). This rapid and dramatic antibody response may stop the infection before it can even become established, and the individual may not realize they had been exposed.
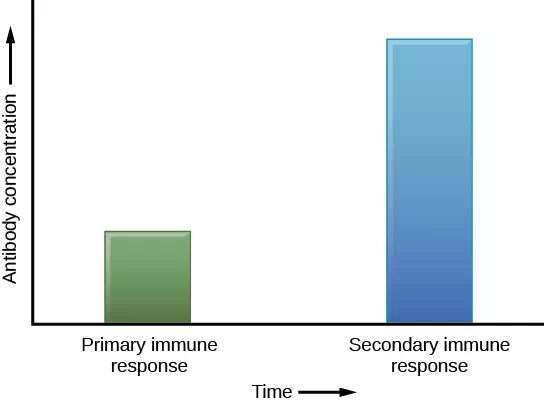
Figure 12.18 In the primary response to infection, antibodies are secreted first from plasma cells. Upon re-exposure to the same pathogen, memory cells differentiate into antibody-secreting plasma cells that output a greater amount of antibody for a longer period of time.
Vaccination is based on the knowledge that exposure to noninfectious antigens, derived from known pathogens, generates a mild primary immune response. The immune response to vaccination may not be perceived by the host as illness but still confers immune memory. When exposed to the corresponding pathogen to which an individual was vaccinated, the reaction is similar to a secondary exposure. Because each reinfection generates more memory cells and increased resistance to the pathogen, some vaccine courses involve one or more booster vaccinations to mimic repeat exposures.