DNA Double-Helical Structure
DNA has a double-helical structure. It is composed of two strands, or polymers, of nucleotides. The strands are formed with bonds between phosphate and sugar groups of adjacent nucleotides. The strands are bonded to each other at their bases with hydrogen bonds, and the strands coil about each other along their length, hence the “double helix” description, which means a double spiral.
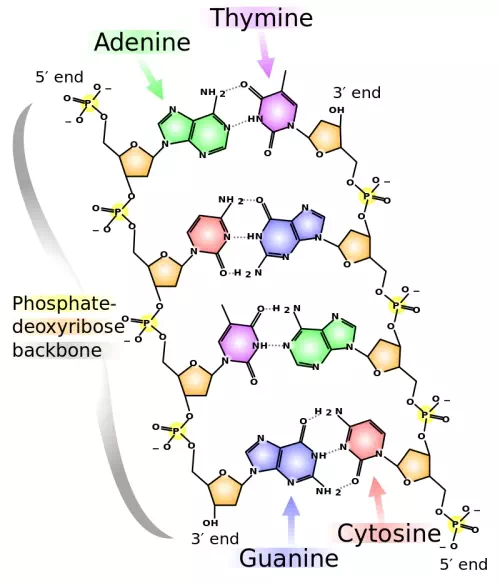
Figure 2.22 Chemical structure of DNA, with colored label identifying the four bases as well as the phosphate and deoxyribose components of the backbone. (Chemical Structure of DNA by Madeleine Price Ball is CC0).
The alternating sugar and phosphate groups lie on the outside of each strand, forming the backbone of the DNA. The nitrogenous bases are stacked in the interior, like the steps of a staircase, and these bases pair; the pairs are bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. The bases pair in such a way that the distance between the backbones of the two strands is the same all along the molecule. The rule is that nucleotide A pairs with nucleotide T, and G with C, see section 9.1 for more details.
Summary
Living things are carbon-based because carbon plays such a prominent role in the chemistry of living things. The four covalent bonding positions of the carbon atom can give rise to a wide diversity of compounds with many functions, accounting for the importance of carbon in living things. Carbohydrates are a group of macromolecules that are a vital energy source for the cell, provide structural support to many organisms, and can be found on the surface of the cell as receptors or for cell recognition. Carbohydrates are classified as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, depending on the number of monomers in the molecule.
Lipids are a class of macromolecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic in nature. Major types include fats and oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids. Fats and oils are a stored form of energy and can include triglycerides. Fats and oils are usually made up of fatty acids and glycerol.
Proteins are a class of macromolecules that can perform a diverse range of functions for the cell. They help in metabolism by providing structural support and by acting as enzymes, carriers or as hormones. The building blocks of proteins are amino acids. Proteins are organized at four levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Protein shape and function are intricately linked; any change in shape caused by changes in temperature, pH, or chemical exposure may lead to protein denaturation and a loss of function.
Nucleic acids are molecules made up of repeating units of nucleotides that direct cellular activities such as cell division and protein synthesis. Each nucleotide is made up of a pentose sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. There are two types of nucleic acids: DNA and RNA.