Introduction to the Chemistry of Life

Figure 2.1 Foods such as bread, fruit, and cheese are rich sources of biological macromolecules.
The elements carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and phosphorus are the key building blocks of the chemicals found in living things. They form the carbohydrates, nucleic acids, proteins, and lipids (all of which will be defined later in this chapter) that are the fundamental molecular components of all organisms. In this chapter, we will discuss these important building blocks and learn how the unique properties of the atoms of different elements affect their interactions with other atoms to form the molecules of life. These interactions determine what atoms combine and the ultimate shape of the molecules and macromolecules, that shape will determine their function.
Food provides an organism with nutrients—the matter it needs to survive. Many of these critical nutrients come in the form of biological macromolecules, or large molecules necessary for life. These macromolecules are built from different combinations of smaller organic molecules. What specific types of biological macromolecules do living things require? How are these molecules formed? What functions do they serve? In this chapter, we will explore these questions.
The Building Blocks of Molecules
At its most fundamental level, life is made up of matter. Matter occupies space and has mass. All matter is composed of elements, substances that cannot be broken down or transformed chemically into other substances. Each element is made of atoms, each with a constant number of protons and unique properties. A total of 118 elements have been defined; however, only 92 occur naturally, and fewer than 30 are found in living cells. The remaining 26 elements are unstable and, therefore, do not exist for very long or are theoretical and have yet to be detected.
Each element is designated by its chemical symbol (such as H, N, O, C, and Na), and possesses unique properties. These unique properties allow elements to combine and to bond with each other in specific ways.
Atoms
An atom is the smallest component of an element that retains all of the chemical properties of that element. For example, one hydrogen atom has all of the properties of the element hydrogen, such as it exists as a gas at room temperature, and it bonds with oxygen to create a water molecule. Hydrogen atoms cannot be broken down into anything smaller while still retaining the properties of hydrogen. If a hydrogen atom were broken down into subatomic particles, it would no longer have the properties of hydrogen.
At the most basic level, all organisms are made of a combination of elements. They contain atoms that combine together to form molecules. In multicellular organisms, such as animals, molecules can interact to form cells that combine to form tissues, which make up organs. These combinations continue until entire multicellular organisms are formed.
All atoms contain protons, electrons, and neutrons. The only exception is hydrogen (H), which is made of one proton and one electron. A proton is a positively charged particle that resides in the nucleus (the core of the atom) of an atom and has a mass of 1 and a charge of +1. An electron is a negatively charged particle that travels in the space around the nucleus. In other words, it resides outside of the nucleus. It has a negligible mass and has a charge of –1.
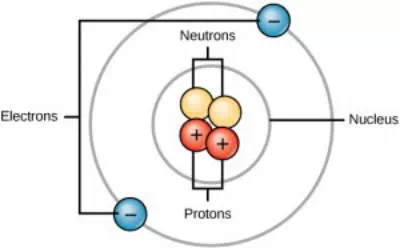
Figure 2.2 Atoms are made up of protons and neutrons located within the nucleus, and electrons surrounding the nucleus.
Neutrons, like protons, reside in the nucleus of an atom. They have a mass of 1 and no charge. The positive (protons) and negative (electrons) charges balance each other in a neutral atom, which has a net zero charge.
Because protons and neutrons each have a mass of 1, the mass of an atom is equal to the number of protons and neutrons of that atom. The number of electrons does not factor into the overall mass, because their mass is so small.
As stated earlier, each element has its own unique properties. Each contains a different number of protons and neutrons, giving it its own atomic number and mass number. The atomic number of an element is equal to the number of protons that element contains. The mass number, or atomic mass, is the number of protons plus the number of neutrons of that element. Therefore, it is possible to determine the number of neutrons by subtracting the atomic number from the mass number.
These numbers provide information about the elements and how they will react when combined. Different elements have different melting and boiling points, and are in different states (liquid, solid, or gas) at room temperature. They also combine in different ways. Some form specific types of bonds, whereas others do not. How they combine is based on the number of electrons present. Because of these characteristics, the elements are arranged into the periodic table of elements, a chart of the elements that includes the atomic number and relative atomic mass of each element. The periodic table also provides key information about the properties of elements —often indicated by color-coding. The arrangement of the table also shows how the electrons in each element are organized and provides important details about how atoms will react with each other to form molecules.
Isotopes are different forms of the same element that have the same number of protons, but a different number of neutrons. Some elements, such as carbon, potassium, and uranium, have naturally occurring isotopes. Carbon-12, the most common isotope of carbon, contains six protons and six neutrons. Therefore, it has a mass number of 12 (six protons and six neutrons) and an atomic number of 6 (which makes it carbon). Carbon-14 contains six protons and eight neutrons. Therefore, it has a mass number of 14 (six protons and eight neutrons) and an atomic number of 6, meaning it is still the element carbon. These two alternate forms of carbon are isotopes. Some isotopes are unstable and will lose protons, other subatomic particles, or energy to form more stable elements. These are called radioactive isotopes or radioisotopes.
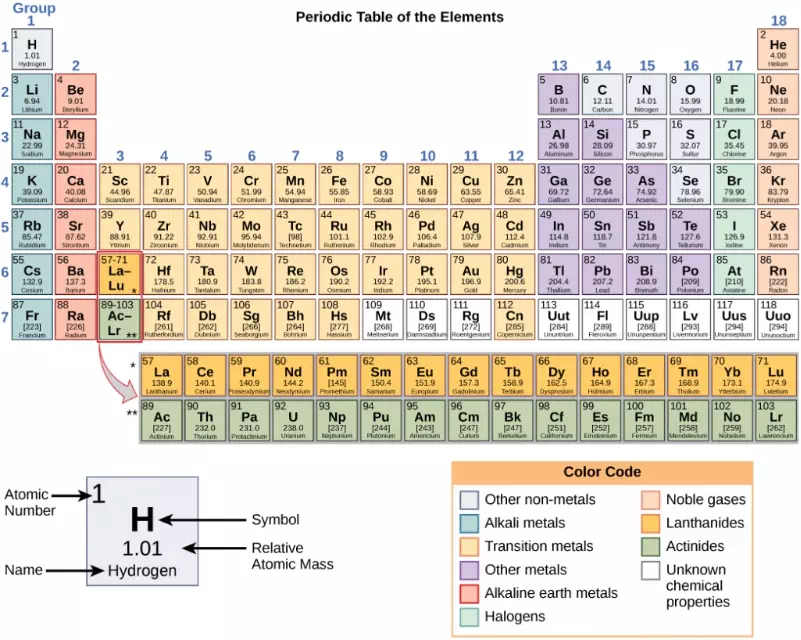
Figure 2.3 Arranged in columns and rows based on the characteristics of the elements, the periodic table provides key information about the elements and how they might interact with each other to form molecules. Most periodic tables provide a key or legend to the information they contain.