What are Plastids?
Plastids are double-membrane organelles which are found in the cells of plants and algae. Plastids are responsible for manufacturing and storing of food. These often contain pigments that are used in photosynthesis and different types of pigments that can change the colour of the cell.

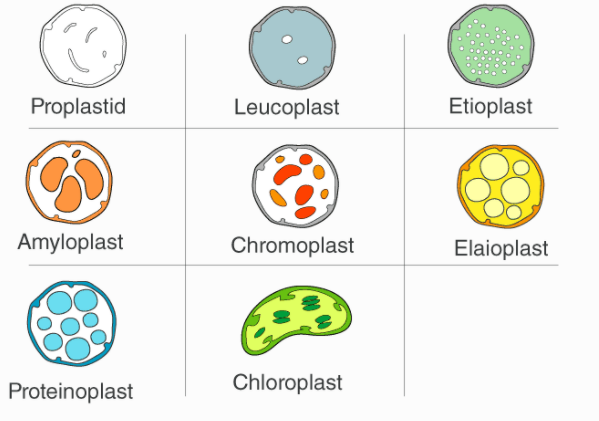
There are different types of plastids with their specialized functions. Among them, a few are mainly classified based on the presence or absence of the Biological pigments and their stages of development.
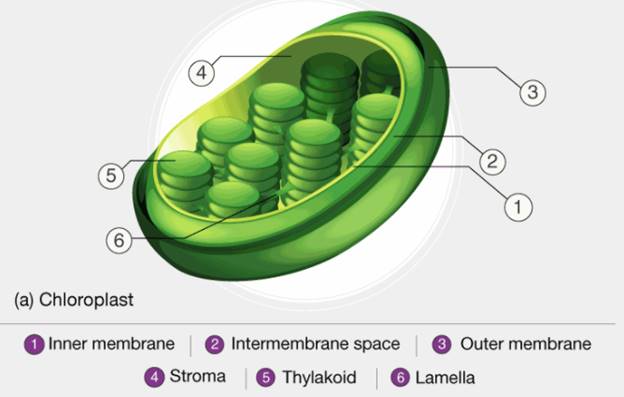
Chloroplasts are biconvex shaped, semi-porous, double membraned, cell organelle found within the mesophyll of the plant cell. They are the sites for synthesizing food by the process of photosynthesis.
Chromoplasts is the name given to an area for all the pigments to be kept and synthesized in the plant. These can be usually found in flowering plants, ageing leaves and fruits. Chloroplasts convert into chromoplasts. Chromoplasts have carotenoid pigments that allow different colours that you see in leaves and fruits. The main reason for its different colour is for attracting pollinators.
These are basically chloroplasts that go with the ageing process. Geronoplasts refer to the chloroplasts of the leaves that help to convert into different other organelles when the leaf is no longer using photosynthesis usually in an autumn month.
These are the non-pigmented organelles which are colourless. Leucoplasts are usually found in most of the non-photosynthetic parts of the plant like roots. They act as a storage sheds for starches, lipids, and proteins depending on the need of the plants. They are mostly used for converting amino acids and fatty acids.
Leucoplasts are of three types:
There are many plants which are inherited from the plastids from just a single parent. Angiosperms inherit plastids from the female gamete while there are many gymnosperms that inherit plastids from the male pollen. Algae inherit plastids from one parent only. The inheritance of the plastids-DNA seems to be 100% uniparental. In hybridisation, the inheritance of plastid seems to be more erratic.