What is Endoplasmic Reticulum?
Endoplasmic reticulum transpires in two forms: a type with ribosome-studded surface and another with a smooth surface. The latter is called the smooth endoplasmic reticulum, and the former is called the rough endoplasmic reticulum. These membranes form continuous folds, eventually joining the outer layer of the nuclear membrane. Except for sperm cells and red blood cells, the endoplasmic reticulum is observed in every other type of eukaryotic cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum Diagram
The below diagram shows the variants of endoplasmic reticulum:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes embedded within its structure, giving a “rough” appearance. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum does not have these ribosomes, hence appear “smooth.”
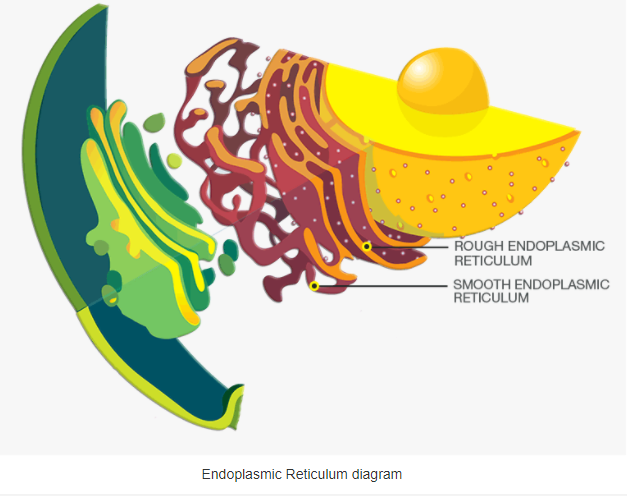
Structure of Endoplasmic Reticulum
The structure of endoplasmic reticulum is shaped like a sac. Since ER is of two types, each has its own distinguishing features:
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure
- The rough endoplasmic reticulum is named so because of its appearance.
- It is a series of connected flattened sacs having several ribosomes on its outer surface, hence the name.
- It synthesizes and secretes proteins in the liver, hormones and other substances in the glands.
- Rough ER is prominent in cells where protein synthesis happens (such as hepatocytes)
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Structure
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum, on the other hand, does not have ribosomes.
- The smooth endoplasmic reticulum has a tubular form.
- It participates in the production of phospholipids, the chief lipids in cell membranes and are essential in the process of metabolism.
- Smooth ER transports the products of the rough ER to other cellular organelles, especially the Golgi apparatus.
Endoplasmic Reticulum Function
As stated above, the endoplasmic reticulum is categorised into two types, and both these types of ER perform specific functions:
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Function:
- Smooth ER is responsible for the synthesis of essential lipids such as phospholipids and cholesterol.
- Smooth ER is also responsible for the production and secretion of steroid hormones.
- It is also responsible for the metabolism of carbohydrates.
- The smooth ER store and release calcium ions. These are quite important for the nervous system and muscular system.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Function:
- The majority of the functions of rough ER is associated with protein synthesis.
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum also plays a vital role in protein folding.
- Also ensures quality control (regarding correct protein folding).
- The second most important function after protein synthesis and protein folding is protein sorting.

