Vertebrata
Introduction
The organisms of this kingdom have a true vertebral column and the internal skeleton structure.
Classification of Vertebrata
∑ Vertebrates are further classified as −
o Pisces
o Amphibia
o Reptilia
o Aves
o Mammalia
∑ Letís discuss each of them in brief −
Pisces
∑ The organisms of this group are typically different types of fishes.
∑ Fishes can live only in water.
∑ The skin fish is covered with scales/plates.
∑ Fish use oxygen dissolved in water by using gills
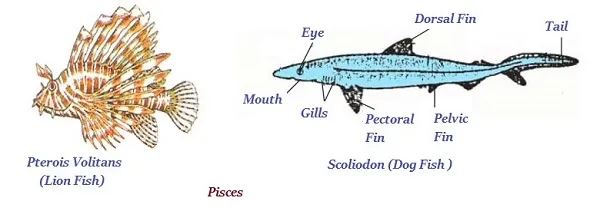
∑ The tail of fish helps in their movements.
∑ Fishes are cold-blooded organisms and their hearts have only two chambers.
∑ Fishes lay eggs.
Amphibia
∑ The organisms of amphibia have mucus glands in the skin, and they have three-chambered heart.
∑ Amphibian can live in water as well as on land.
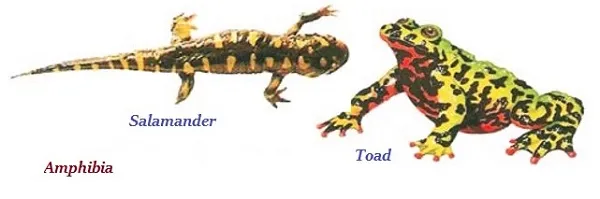
∑ The organisms of amphibian respire through either gills or lungs.
∑ The organisms of amphibia lay eggs.
Reptilia
∑ The organisms of this group are cold bolded.
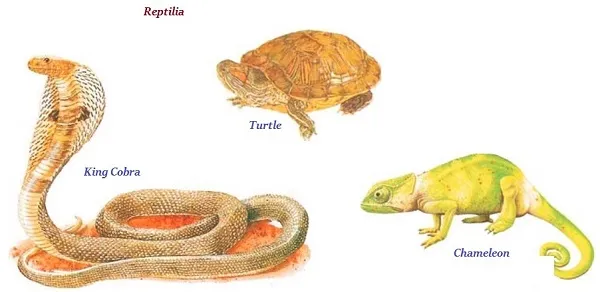
∑ The organisms of reptilia lay eggs with tough coverings.
Aves
∑ The organisms of Aves group are warm-blooded.
∑ The organisms of Aves group lay eggs except a few, such as bat.
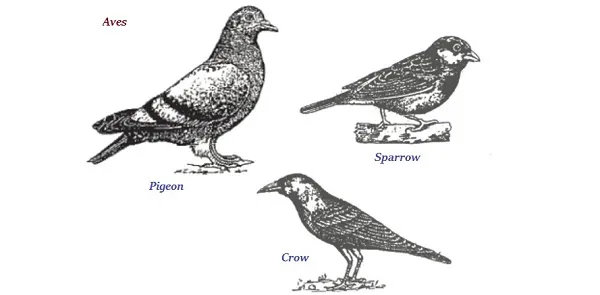
∑ Most of the Aves have feathers.
Mammalia
∑ The organisms of Mammalia group are warm-blooded and they have four-chambered hearts.
∑ Mammalia are typically characterized for their mammary glands.
∑ Mammary glands produce milk to nourish the young one.
∑ Most of the mammals produce live baby; however, a few of mammals, such as, the platypus and the echidna lay eggs.
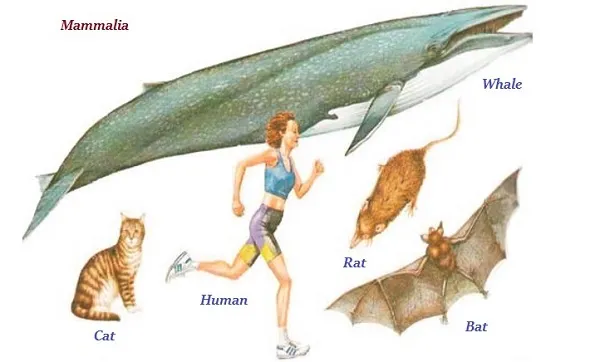
∑ Mammalsí skin has hairs along with sweat and oil glands.