Animalia Kingdom
Introduction
· The organisms, which are eukaryotic, multicellular, and heterotrophic, are categorized as Animalia kingdom.

· The organisms of Animalia kingdom have no cell-wall.
· Most of animals of Animalia kingdom are mobile.
Classification of Animalia Kingdom
· Based on the extent and type of the body design differentiation, Animalia kingdom classified as −
o Porifera
o Coelenterata
o Platyhelminthes
o Nematoda
o Annelida
o Arthropoda
o Mollusca
o Echinodermata
o Protochordata
o Vertebrata
§ Pisces
§ Amphibia
§ Reptilia
§ Aves
§ Mammalia
· Let’s discuss each of them in brief −
Porifera
· The literal meaning of ‘porifera’ is the organisms with holes.
· The organisms of porifera are non-motile and attached to some solid support.
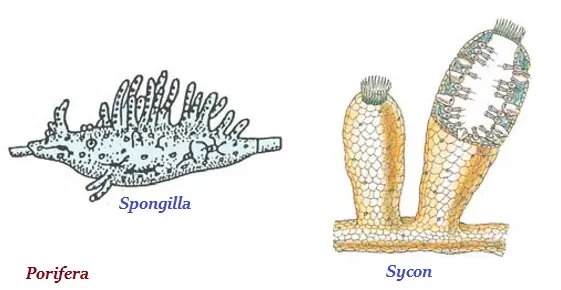
· The examples of this group are Sycon, Spongilla, Euplectelia, etc.
Coelenterata
· Organisms of coelenterata group live in water.
· The organisms of this group have cavity in their bodies.
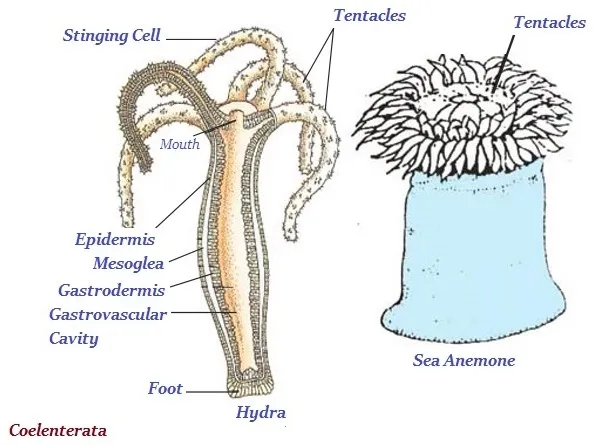
· Hydra and sea anemone are the common example of coelenterate.
Platyhelminthes
· The organisms of this group do not have true internal body cavity or coelom; so, they neither have well-developed organs.
· The bodies of organisms of this group are flattened from top to bottom; therefore, they are also known as flatworms.
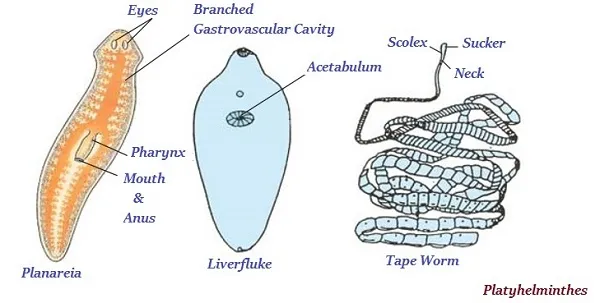
· Planareia, liverfluke, tape worm, etc., are the typical examples of this group.
Nematoda
· The organisms of nematode have cylindrical body.
· The organisms have tissue, but as such no well-developed body (i.e. no real organ).
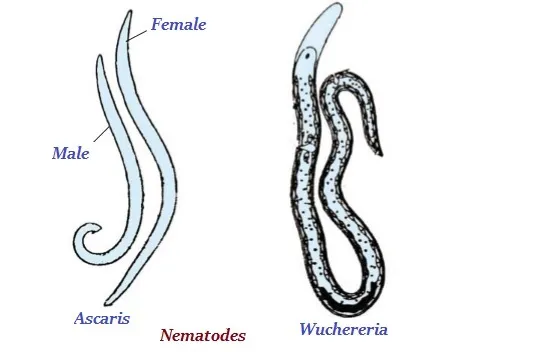
· The filarial worms (causing elephantiasis disease), roundworm in the intestines, etc., are the common examples of nematodes.
Annelida
· The organisms of annelida group live almost everywhere including fresh water, marine water as well as on land.
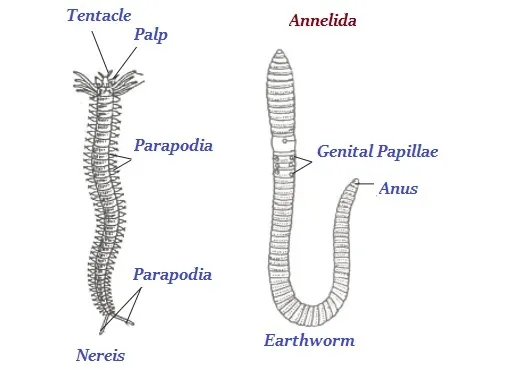
· Earthworms, nereis, and leeches are the familiar examples of annelida.
Arthropoda
· Arthropoda, probably, is the largest group of animals.
· The animals of this group don’t have well defined blood vessels rather there is an open circulatory system.
· The literal meaning of arthropod is jointed legs; so, they have jointed legs.
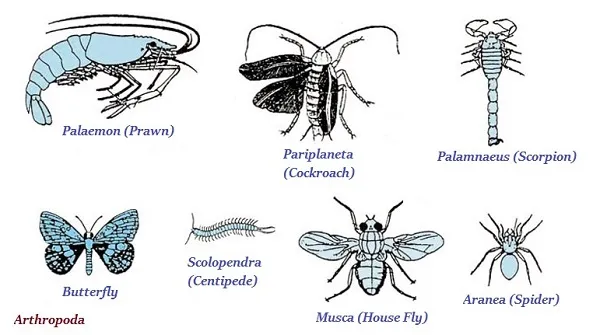
· Prawns, butterflies, houseflies, spiders, scorpions, etc. are the typical examples of arthropod.
Mollusca
· The organisms of mollusca are invertebrate.
· Most of the organisms of Mollusca group live in water.
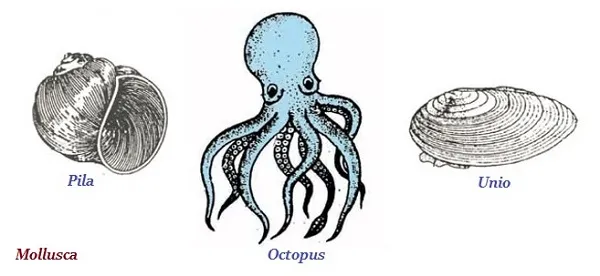
· Snails and mussels are the typical example of Mollusca.
Echinodermata
· The organisms of Echinodermata have spiny skinned.
· Echinodermata are free-living marine organisms.
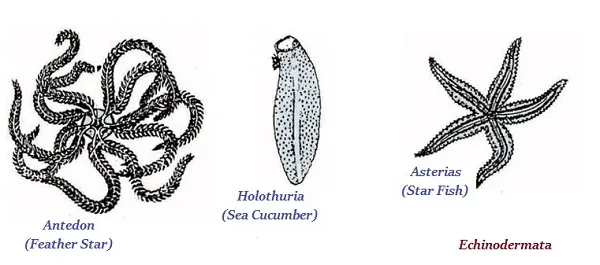
· The examples of echinodermata are starfish, sea urchins, feather star, etc.
Protochordata
· The organisms of protochordata are normally marine. E.g. Balanoglossus, Herdemania, and Amphioxus
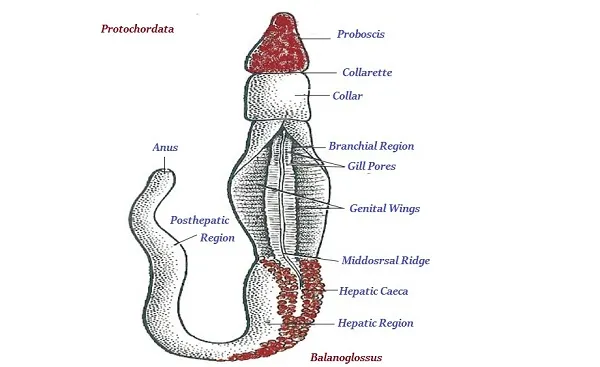
· The organisms of protochordata show a typical feature of body design, called as notochord; however, it does present there throughout the life.