Plantae Kingdom
Introduction
· Plantae kingdom includes all sorts of plants belonging to multicellular eukaryotes.

· These plants are autotrophs and they use chlorophyll for the photosynthesis.
Classification of Plantae Kingdom
· Based on distinct body structure, components, etc. plantae kingdom is further classified as −
o Thallophyta
o Bryophyta
o Pteridophyta
o Gymnosperms
o Angiosperms
· Let’s discuss each of them in brief −
Thallophyta
· The plants of thallophyta do not have well-differentiated body design.
· The plants in thallophyta are known as algae and they are predominantly aquatic.

· Some of the significant examples of thallophyta are Spirogyra, Ulothrix, Cladophora, Chara, etc.
Bryophyta
· The plants of amphibian group are categorized as bryophyta.
· Though not distinctly developed, but the plant body can be differentiated to form stem and leaf-like structures.
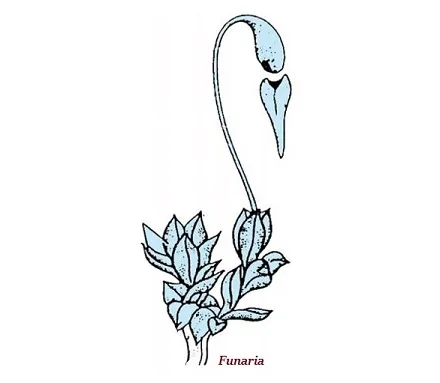
· The examples of bryophyta are moss (Funaria) and Marchantia.
Pteridophyta
· Plants of pteridophyta have defined roots, stem, and leaves.
· Pteridophyta plants have specialized tissue that transports water and other materials from one part to another part of the plant.
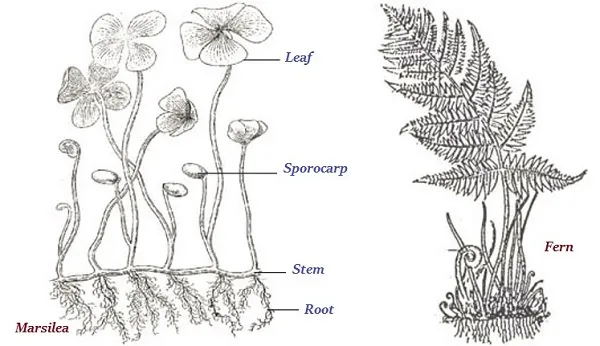
· Examples of pteridophyta are Marsilea, ferns, and horse-tails.
· The commonality among the thallophytes, the bryophytes, and the pteridophytes are – all of them have naked embryos, which are known as spores.
· The reproductive organs of plants of these groups are known as ‘cryptogamae,’ which means ‘hidden reproductive organs’.
Gymnosperm
· The plants of gymnosperm bear naked seeds.
· These plants are normally perennial, evergreen, and woody.

· Examples of gymnosperm are pines (such as deodar, cycas, etc.
Angiosperms
· The plants of angiosperm bear covered seeds.
· Plants of angiospherms are also known as flowing plants.

· Plant embryos in seeds have a typical structures known as cotyledons, which is also called as ‘seed leaves.’